
1
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use
CARVYKTI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for
CARVYKTI.
CARVYKTI
®
(ciltacabtagene autoleucel) suspension for intravenous
infusion
Initial U.S. Approval: 2022
WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME, NEUROLOGIC
TOXICITIES, HLH/MAS, PROLONGED and RECURRENT
CYTOPENIA, and SECONDARY HEMATOLOGICAL
MALIGNANCIES
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
• Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), including fatal or life-threatening
reactions, occurred in patients following treatment with CARVYKTI.
Do not administer CARVYKTI to patients with active infection or
inflammatory disorders. Treat severe or life-threatening CRS with
tocilizumab or tocilizumab and corticosteroids. (2.2, 2.3, 5.2)
• Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS),
which may be fatal or life-threatening, occurred following treatment
with CARVYKTI, including before CRS onset, concurrently with
CRS, after CRS resolution, or in the absence of CRS. Monitor for
neurologic events after treatment with CARVYKTI. Provide
supportive care and/or corticosteroids as needed. (2.2, 2.3, 5.3)
• Parkinsonism and Guillain-Barré syndrome and their associated
complications resulting in fatal or life-threatening reactions have
occurred following treatment with CARVYKTI. (5.3)
• Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation
Syndrome (HLH/MAS), including fatal and life-threatening reactions,
occurred in patients following treatment with CARVYKTI.
HLH/MAS can occur with CRS or neurologic toxicities. (5.4)
• Prolonged and/or recurrent cytopenias with bleeding and infection
and requirement for stem cell transplantation for hematopoietic
recovery occurred following treatment with CARVYKTI. (5.6)
• Secondary hematological malignancies, including myelodysplastic
syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia, have occurred following
treatment with CARVYKTI. T-cell malignancies have occurred
following treatment of hematologic malignancies with BCMA- and
CD19-directed genetically modified autologous T-cell
immunotherapies, including CARVYKTI. (5.10)
• CARVYKTI is available only through a restricted program under a
Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the
CARVYKTI REMS. (5.5)
--------------------------RECENT MAJOR CHANGES----------------------------
Boxed Warnings 12/2023
Boxed Warnings 04/2024
Indications and Usage (1) 04/2024
Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, 5.9) 12/2023
Warnings and Precautions (5) 04/2024
-----------------------------INDICATIONS AND USAGE--------------------------
CARVYKTI (ciltacabtagene autoleucel) is a B-cell maturation antigen
(BCMA)-directed genetically modified autologous T cell immunotherapy
indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory
multiple myeloma who have received at least 1 prior line of therapy, including
a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent, and are refractory to
lenalidomide. (1)
------------------------DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION----------------------
For autologous use only. For intravenous use only.
• Administer a lymphodepleting regimen of cyclophosphamide and
fludarabine before infusion of CARVYKTI. (2.2)
• Do NOT use a leukodepleting filter. (2.2)
• Verify the patient’s identity prior to infusion. (2.2)
• Premedicate with acetaminophen and an H1-antihistamine. (2.2)
• Avoid prophylactic use of systemic corticosteroids. (2.2)
• Confirm availability of tocilizumab prior to infusion. (2.2, 5.1)
• Dosing of CARVYKTI is based on the number of chimeric antigen
receptor (CAR)-positive viable T cells. (2.1)
• Recommended dose range is 0.5-1.0×10
6
CAR-positive viable T cells per
kg of body weight, with a maximum dose of 1×10
8
CAR-positive viable
T cells per single-dose infusion. (2.1)
• Administer CARVYKTI at a REMS-certified healthcare facility. (2.2)
----------------------DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS---------------------
• CARVYKTI is a cell suspension for intravenous infusion. (3)
• A single dose of CARVYKTI contains a cell suspension of 0.5-1.0×10
6
CAR-positive viable T cells per kg body weight in one infusion bag. (3)
----------------------------CONTRAINDICATIONS---------------------------------
None (4)
-------------------------WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS----------------------
• Prolonged and Recurrent Cytopenias: Patients may exhibit ≥Grade 3
cytopenias following CARVYKTI infusion. One or more recurrences of
Grade 3 or higher cytopenias may occur after partial or complete recovery
of cytopenias. Monitor blood counts prior to and after CARVYKTI
infusion. Prolonged neutropenia has been associated with increased risk of
infection. (5.6)
• Infections: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection; treat
appropriately. (5.7)
• Hypogammaglobulinemia: Monitor and consider immunoglobulin
replacement therapy. (5.8)
• Hypersensitivity Reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions have occurred.
Monitor for hypersensitivity reactions during infusion. (5.9)
• Secondary Malignancies: Secondary hematological malignancies,
including myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia, have
occurred. T-cell malignancies have occurred following treatment of
hematologic malignancies with BCMA- and CD19-directed genetically
modified autologous T-cell immunotherapies, including CARVYKTI. In
the event that a secondary malignancy occurs after treatment with
CARVYKTI, contact Janssen Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736. (5.10)
• Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines: Advise patients to refrain
from driving and engaging in hazardous occupations or activities, such as
operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery, for at least 8 weeks
after receiving CARVYKTI and in the event of any new onset of
neurologic toxicities. (5.11)
------------------------------ADVERSE REACTIONS-------------------------------
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions (incidence greater than
20%) are pyrexia, cytokine release syndrome, hypogammaglobulinemia,
hypotension, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, infections-pathogen unspecified,
cough, chills, diarrhea, nausea, encephalopathy, decreased appetite, upper
respiratory tract infection, headache, tachycardia, dizziness, dyspnea, edema,
viral infections, coagulopathy, constipation, and vomiting. The most common
Grade 3 or 4 laboratory adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to
50%) include lymphopenia, neutropenia, white blood cell decreased,
thrombocytopenia, and anemia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen
Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736 (1-800-JANSSEN) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-
1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication
Guide.
Revised: 04/2024
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME,
NEUROLOGIC TOXICITIES, HLH/MAS, PROLONGED
and RECURRENT CYTOPENIA, and SECONDARY
HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES
1
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dose
2.2 Administration
2.3 Management of Severe Adverse Reactions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS

2
5.1
Increased Early Mortality
5.2 Cytokine Release Syndrome
5.3 Neurologic Toxicities
5.4 Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
(HLH)/Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS)
5.5 CARVYKTI REMS
5.6 Prolonged and Recurrent Cytopenias
5.7 Infections
5.8 Hypogammaglobulinemia
5.9 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.10 Secondary Malignancies
5.11 Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Immunogenicity
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not
listed.

3
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME, NEUROLOGIC TOXICITIES,
HLH/MAS, PROLONGED and RECURRENT CYTOPENIA, and SECONDARY
HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES
Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS), including fatal or life-threatening reactions, occurred in
patients following treatment with CARVYKTI. Do not administer CARVYKTI to patients
with active infection or inflammatory disorders. Treat severe or life-threatening CRS with
tocilizumab or tocilizumab and corticosteroids [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3),
Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS), which may be fatal or
life-threatening, occurred following treatment with CARVYKTI, including before CRS
onset, concurrently with CRS, after CRS resolution, or in the absence of CRS. Monitor for
neurologic events after treatment with CARVYKTI. Provide supportive care and/or
corticosteroids as needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3), Warnings and Precautions
(5.3)].
Parkinsonism and Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and their associated complications
resulting in fatal or life-threatening reactions have occurred following treatment with
CARVYKTI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis/Macrophage Activation Syndrome (HLH/MAS),
including fatal and life-threatening reactions, occurred in patients following treatment with
CARVYKTI. HLH/MAS can occur with CRS or neurologic toxicities [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.4)].
Prolonged and/or recurrent cytopenias with bleeding and infection and requirement for stem
cell transplantation for hematopoietic recovery occurred following treatment with
CARVYKTI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Secondary hematological malignancies, including myelodysplastic syndrome and acute
myeloid leukemia, have occurred in patients following treatment with CARVYKTI. T-cell
malignancies have occurred following treatment of hematologic malignancies with BCMA-
and CD19-directed genetically modified autologous T-cell immunotherapies, including
CARVYKTI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
CARVYKTI is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and
Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the CARVYKTI REMS Program [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.5)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CARVYKTI (ciltacabtagene autoleucel) is a B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-directed
genetically modified autologous T cell immunotherapy indicated for the treatment of adult patients
with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, who have received at least 1 prior line of therapy,
including a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent, and are refractory to
lenalidomide.

4
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For autologous use only. For intravenous use only.
2.1 Dose
CARVYKTI is provided as a single dose for infusion containing a suspension of chimeric antigen
receptor (CAR)-positive viable T cells in one infusion bag.
The recommended dose range is 0.5-1.0×10
6
CAR-positive viable T cells per kg of body weight,
with a maximum dose of 1×10
8
CAR-positive viable T cells per single infusion.
2.2 Administration
CARVYKTI is for autologous use only. The patient’s identity must match the patient identifiers
on the CARVYKTI cassette and infusion bag. Do not infuse CARVYKTI if the information on
the patient-specific labels does not match the intended patient.
Preparing the Patient for CARVYKTI Infusion
Confirm availability of CARVYKTI prior to starting the lymphodepleting chemotherapy regimen.
Pretreatment
Administer the lymphodepleting chemotherapy regimen: cyclophosphamide 300 mg/m
2
intravenously (IV) and fludarabine 30 mg/m
2
IV daily for 3 days.
See the prescribing information of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine for information on dose
adjustment in renal impairment.
Lymphodepleting regimen must be delayed if a patient has serious adverse reactions from
preceding bridging therapies (including clinically significant active infection, cardiac toxicity, and
pulmonary toxicity) or active graft versus host disease in patient with prior allogeneic stem cell
transplant. Consider repeating lymphodepleting regimen if CARVYKTI dosing is delayed by more
than 14 days and patient has recovered from toxicity of the first lymphodepleting regimen.
Administer CARVYKTI infusion 2 to 4 days after the completion of the lymphodepleting
chemotherapy regimen.
CARVYKTI infusion should be delayed if a patient has any of the following conditions:
• Clinically significant active infection or inflammatory disorders.
• Grade ≥3 non-hematologic toxicities of cyclophosphamide and fludarabine conditioning,
except for Grade 3 nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation. CARVYKTI infusion
should be delayed until resolution of these events to Grade ≤1.

5
Premedication
Administer the following pre-infusion medications to all patients 30 - 60 minutes prior to
CARVYKTI infusion:
• Antipyretics (oral or intravenous acetaminophen 650 to 1000 mg).
• Antihistamine (oral or intravenous diphenhydramine 25 to 50 mg or equivalent).
Avoid prophylactic use of systemic corticosteroids because their use may interfere with the activity
of CARVYKTI.
Receipt of CARVYKTI
• All sites approved for infusion will support required storage conditions for vapor phase of
liquid nitrogen.
• CARVYKTI is shipped directly to the cell laboratory or clinical pharmacy associated with
the infusion center in the vapor phase of a liquid nitrogen shipper.
• Confirm the patient’s identity with the patient identifiers on the shipper.
• If the patient is not expected to be ready for same-day administration, before the shipper
expires, transfer CARVYKTI to onsite vapor phase of liquid nitrogen storage.
Preparation of CARVYKTI for Infusion
Do not thaw the product until it is ready to be used. Coordinate the timing of CARVYKTI thaw
and infusion. Confirm the infusion time in advance and adjust the start time for thaw so that
CARVYKTI is available for infusion when the patient is ready. Once thawed, the CARVYKTI
infusion must be completed within 2.5 hours at room/ambient temperature (20°C to 25°C).
Prior to thawing the product, confirm that tocilizumab and emergency equipment are available
prior to the infusion and during the recovery period.
1. Confirm patient identity: Prior to CARVYKTI preparation, match the patient’s identity
with the patient identifiers on the CARVYKTI cassette. Do not remove the CARVYKTI
infusion bag from the cassette if the information on the patient-specific label does not
match the intended patient. Contact Janssen Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736 if there are
any discrepancies between the labels and the patient identifiers.
2. Once patient identification is confirmed, remove the CARVYKTI product bag from the
cassette and check that the patient information on the cassette label matches the patient
information on the bag label.
3. Inspect the product bag for any breaches of container integrity, such as breaks or cracks
before and after thawing. Do not administer if the bag is compromised, and contact Janssen
Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736.
4. Place the infusion bag inside a sealable plastic bag (preferably sterile) prior to thawing.

6
5. Thaw CARVYKTI at 37°C±2°C using either a water bath or dry thaw method until there
is no visible ice in the infusion bag. Total time from start of thaw until completion of
thawing should be no more than 15 minutes.
6. Remove the infusion bag from the sealable plastic bag and wipe dry. Gently mix the
contents of the bag to disperse clumps of cellular material. If visible cell clumps remain,
continue to gently mix the contents of the bag. Small clumps of cellular material should
disperse with gentle manual mixing. Do not pre-filter into a different container, wash, spin
down, or resuspend CARVYKTI in new media prior to infusion.
7. Do not re-freeze or refrigerate thawed product.
Administration
• For autologous infusion only.
• Do NOT use a leukocyte-depleting filter.
• Ensure that a minimum of two doses of tocilizumab and emergency equipment are
available prior to infusion and during the recovery period.
• Central venous access may be utilized for the infusion of CARVYKTI and is encouraged
in patients with poor peripheral access.
1. Confirm the patient’s identity with the patient identifiers on the infusion bag. Do not infuse
CARVYKTI if the information on the patient-specific label does not match the intended
patient.
2. Prime the tubing of the infusion set with normal saline prior to infusion.
3. Once thawed, administer the entire contents of the CARVYKTI bag by intravenous
infusion within 2.5 hours using infusion sets fitted with an in-line filter.
4. Gently mix the contents of the bag during CARVYKTI infusion to disperse cell clumps.
5. After the entire content of the product bag is infused, flush the administration line, inclusive
of the in-line filter, with normal saline with a volume equal or greater to the total hold up
volume of the primary administration set used inclusive of the drip tube, to ensure that all
product is delivered.
CARVYKTI contains human blood cells that are genetically modified with replication-
incompetent, self-inactivating, lentiviral vector. Follow universal precautions and local biosafety
guidelines for handling and disposal of CARVYKTI to avoid potential transmission of infectious
diseases.
Monitoring After Infusion
Administer CARVYKTI at a REMS-certified healthcare facility.

7
Monitor patients at least daily for 10 days following CARVYKTI infusion at a certified healthcare
facility for signs and symptoms of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic toxicities.
Monitor periodically for 4 weeks for signs and symptoms of delayed neurologic toxicity.
Instruct patients to remain within proximity of a certified healthcare facility for at least 4 weeks
following infusion.
Instruct patients to refrain from driving or hazardous activities for at least 8 weeks following
infusion.
2.3 Management of Severe Adverse Reactions
Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
Identify CRS based on clinical presentation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Evaluate for
and treat other causes of fever, hypoxia and hypotension. Consider laboratory testing to monitor
for disseminated intravascular coagulation, hematology parameters, as well as pulmonary, cardiac,
renal, and hepatic function. If CRS is suspected, manage according to the recommendations in
Table 1.
Patients who experience CRS should be closely monitored for cardiac and other organ function
until resolution of symptoms. Consider anti-seizure prophylaxis with levetiracetam in patients who
experience CRS.
Patients who experience Grade 2 or higher CRS (e.g., hypotension not responsive to fluids, or
hypoxia requiring supplemental oxygenation) should be monitored with continuous telemetry and
pulse oximetry.
For severe or life-threatening CRS, consider intensive care unit level monitoring and supportive
therapy.
For CRS refractory to first line interventions such as tocilizumab or tocilizumab and
corticosteroids, consider alternate treatment options (i.e., higher corticosteroid dose, alternative
anti-cytokine agents, e.g., anti-IL1 and/or anti-TNFα, anti-T cell therapies). Refractory CRS is
characterized by fevers, end-organ toxicity (e.g., hypoxia, hypotension) not improving within
12 hours of first line interventions or development of HLH/MAS.
If concurrent neurologic toxicity is suspected during CRS, administer:
• Corticosteroids according to the more aggressive intervention based on the CRS and
neurologic toxicity grades in Tables 1 and 2
• Tocilizumab according to the CRS grade in Table 1
• Anti-seizure medication according to the neurologic toxicity in Table 2

8
Table 1: CRS grading and management guidance
CRS Grade
a
Tocilizumab
b
/ Corticosteroids
f
Grade 1
Temperature ≥38°C
c
In patients with:
• Early onset of fever (if onset less than 72 hours after infusion)
Tocilizumab 8 mg/kg intravenously (IV) over 1 hour (not to exceed
800 mg) may be considered.
Corticosteroids: N/A
Grade 2
Symptoms require and respond to
moderate intervention.
Temperature ≥38°C
c
with:
Hypotension not requiring vasopressors,
and/or,
Hypoxia requiring oxygen via cannula
e
or blow-by,
or,
Grade 2 organ toxicity.
g
Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV over 1 hour (not to exceed
800 mg).
Repeat tocilizumab every 8 hours as needed if not responsive to
intravenous fluids up to 1 liter or increasing supplemental oxygen.
Consider dexamethasone 10 mg IV every 12-24 hours.
If no improvement within 24 hours or rapid progression, repeat
tocilizumab and escalate dose and frequency of dexamethasone
(20 mg IV every 6 to 12 hours).
If no improvement within 24 hours or continued rapid progression,
switch to methylprednisolone 2 mg/kg IV every 12 hours.
After 2 doses of tocilizumab, consider alternative anti-cytokine
agents.
d
Do not exceed 3 doses of tocilizumab in 24 hours, or 4 doses in total.
Grade 3
Symptoms require and respond to
aggressive intervention.
Temperature ≥38°C
c
with:
Hypotension requiring one vasopressor
with or without vasopressin,
and/or,
Hypoxia requiring oxygen via high-flow
nasal cannula
e
, facemask, non-rebreather
mask, or Venturi mask,
or,
Grade 3 organ toxicity or Grade 4
transaminitis.
Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV over 1 hour (not to exceed
800 mg).
Repeat tocilizumab every 8 hours as needed if not responsive to
intravenous fluids up to 1 liter or increasing supplemental oxygen.
Consider dexamethasone 10 mg IV every 12 hours.
If no improvement within 24 hours or rapid progression, repeat
tocilizumab and escalate dose and frequency of dexamethasone
(20 mg IV every 6 to 12 hours).
If no improvement within 24 hours or continued rapid progression,
switch to methylprednisolone 2 mg/kg IV every 12 hours.
After 2 doses of tocilizumab, consider alternative anti-cytokine
agents.
d
Do not exceed 3 doses of tocilizumab in 24 hours, or 4 doses in total.

9
CRS Grade
a
Tocilizumab
b
/ Corticosteroids
f
Grade 4
Life-threatening symptoms.
Requirements for ventilator support,
continuous veno-venous hemodialysis
(CVVHD).
Temperature ≥38°C
c
with:
Hypotension requiring multiple
vasopressors (excluding vasopressin),
and/or,
Hypoxia requiring positive pressure
(e.g., CPAP, BiPAP, intubation, and
mechanical ventilation),
or,
Grade 4 organ toxicity (excluding
transaminitis).
Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV over 1 hour (not to exceed
800 mg).
Repeat tocilizumab every 8 hours as needed if not responsive to
intravenous fluids up to 1 liter or increasing supplemental oxygen.
Administer dexamethasone 20 mg IV every 6 hours.
After 2 doses of tocilizumab, consider alternative anti-cytokine
agents
d
.
Do not exceed 3 doses of tocilizumab in 24 hours, or 4 doses in total.
If no improvement within 24 hours, consider methylprednisolone (1-
2 g IV, repeat every 24 hours if needed; taper as clinically indicated)
or other immunosuppressants (e.g. other anti-T cell therapies).
a
Based on ASTCT 2019 grading system (Lee et.al, 2019), modified to include organ toxicity.
b
Refer to tocilizumab prescribing information for details.
c
Attributed to CRS. Fever may not always be present concurrently with hypotension or hypoxia, as it may be masked by interventions such as
antipyretics or anti-cytokine therapy (e.g., tocilizumab or steroids). Absence of fever does not impact CRS management decision. In this case,
CRS management is driven by hypotension and/or hypoxia and by the more severe symptom not attributable to any other cause.
d
Monoclonal antibodies targeting cytokines may be considered based on institutional practice for unresponsive CRS.
e
Low-flow nasal cannula is ≤6 L/min; high-flow nasal cannula is >6 L/min.
f
Continue corticosteroids use until the event is Grade 1 or less; taper steroids if total corticosteroid exposure is greater than 3 days.
g
Organ toxicity grading based on National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 5.0.
Neurologic Toxicities
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neurologic toxicities (ICANS and other neurologic
toxicities) (Table 2). Rule out other causes of neurologic signs or symptoms. Provide intensive
care and supportive therapy for severe or life-threatening neurologic toxicities. Please see section
5.3 for non ICANS neurologic toxicities. If ICANS is suspected, manage according to the
recommendations in Table 2.
If concurrent CRS is suspected during the neurologic toxicity event, administer:
• Corticosteroids according to the more aggressive intervention based on the CRS and
neurologic toxicity grades in Tables 1 and 2
• Tocilizumab according to CRS grade in Table 1
• Anti-seizure medication according to neurologic toxicity in Table 2

10
Table 2: Guideline for management of ICANS
ICANS Grade
a
Corticosteroids
Grade 1
ICE score 7-9
b
or depressed level of consciousness: awakens
spontaneously.
Consider dexamethasone
c
10 mg IV every 12 to 24 hours for
2 to 3 days.
Consider non-sedating, anti-
seizure medicines (e.g.,
levetiracetam) for seizure prophylaxis.
Grade 2
ICE score-3-6
b
or depressed level of consciousness: awakens to
voice
Administer dexamethasone
c
10 mg IV every 12 hours for 2-
3 days, or longer for persistent symptoms.
Consider steroid taper if total corticosteroid exposure is
greater than 3 days.
If no improvement after 24 hours or worsening of
neurologic toxicity, increase the dose and/or frequency of
dexamethasone up to a maximum of 20 mg IV every
6 hours.
Consider non-sedating, anti-
seizure medicines (e.g.,
levetiracetam) for seizure prophylaxis.
Grade 3
ICE score-0-2
b
(If ICE score is 0, but the patient is arousable (e.g.,
awake with global aphasia) and able to perform
assessment)
or depressed level of consciousness: awakens only
to tactile stimulus,
or seizures, either:
• any clinical seizure, focal or generalized, that
resolves rapidly, or
• non-convulsive seizures on EEG that resolve
with intervention,
or raised intracranial pressure (ICP): focal/local
edema on neuroimaging
d
.
Administer dexamethasone
c
10 mg-20 mg IV every 6 hours.
If no improvement after 24 hours or worsening of
neurologic toxicity, escalate dexamethasone
c
dose to at least
20 mg IV every 6 hours,
OR escalate to high-dose methylprednisolone (1-2 g/day,
repeat every 24 hours if needed; taper as clinically
indicated)
Consider non-sedating, anti-
seizure medicines (e.g.,
levetiracetam) for seizure prophylaxis.
If cerebral edema is suspected, consider hyperventilation and
hyperosmolar therapy. Give high-dose methylprednisolone
(1-2 g, repeat every 24 hours if needed; taper as clinically
indicated).

11
ICANS Grade
a
Corticosteroids
Grade 4
ICE score-0
b
(Patient is unarousable and unable to
perform ICE assessment)
or depressed level of consciousness either:
• patient is unarousable or requires vigorous or
repetitive tactile stimuli to arouse, or
• stupor or coma,
or seizures, either:
• life-threatening prolonged seizure (>5 min), or
• repetitive clinical or electrical seizures without
return to baseline in between,
or motor findings
e
:
• deep focal motor weakness such as hemiparesis
or paraparesis,
or raised ICP/cerebral edema, with
signs/symptoms such as:
• diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging, or
• decerebrate or decorticate posturing, or
• cranial nerve VI palsy, or
• papilledema, or
• Cushing’s triad
Administer dexamethasone
c
20 mg IV every 6 hours.
If no improvement after 24 hours or worsening of
neurologic toxicity, escalate to high-dose
methylprednisolone (1-2 g/day, repeated every 24 hours if
needed; taper as clinically indicated).
Consider non-sedating, anti-
seizure medicines (e.g.,
levetiracetam) for seizure prophylaxis.
If raised ICP/cerebral edema is suspected, consider
hyperventilation and hyperosmolar therapy. Give high-dose
methylprednisolone (1-2 g/day, repeat every 24
hours if
needed; taper as clinically indicated), and consider neurology
and/or neurosurgery consultation.
Note: ICANS grade and management is determined by the most severe event (ICE score, level of consciousness, seizure, motor findings, raised
ICP/cerebral edema), not attributable to any other cause.
a
ASTCT 2019 criteria for grading Neurologic Toxicity (Lee et.al, 2019).
b
If patient is arousable and able to perform Immune Effector Cell-Associated Encephalopathy (ICE) Assessment, assess: Orientation (oriented
to year, month, city, hospital = 4 points); Naming (name 3 objects, e.g., point to clock, pen, button = 3 points); Following Commands (e.g.,
“show me 2 fingers” or “close your eyes and stick out your tongue” = 1 point); Writing (ability to write a standard sentence = 1 point); and
Attention (count backwards from 100 by ten = 1 point). If patient is unarousable and unable to perform ICE Assessment (Grade 4 ICANS) =
0 points.
c
All references to dexamethasone administration are dexamethasone or equivalent.
d
Intracranial hemorrhage with or without associated edema is not considered a neurotoxicity feature and is excluded from ICANS grading. It
may be graded according to NCI CTCAE v5.0.
e
Tremors and myoclonus associated with immune effector cell therapies may be graded according to NCI CTCAE v5.0, but they do not
influence ICANS grading.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CARVYKTI is a cell suspension for intravenous infusion.
A single dose of CARVYKTI contains a cell suspension of 0.5-1.0×10
6
CAR-positive viable
T cells per kg body weight in one infusion bag up to a maximum of 1×10
8
CAR-positive viable
T cells [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.

12
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Early Mortality
In CARTITUDE-4, a randomized (1:1), controlled trial, there was a numerically higher
percentage of early deaths in patients randomized to the CARVYKTI treatment arm compared to
the control arm. Among patients with deaths occurring within the first 10 months from
randomization, a greater proportion (29/208; 14%) occurred in the CARVYKTI arm compared to
(25/211; 12%) in the control arm [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Of the 29 deaths that occurred in
the CARVYKTI arm within the first 10 months of randomization, 10 deaths occurred prior to
CARVYKTI infusion, and 19 deaths occurred after CARVYKTI infusion. Of the 10 deaths that
occurred prior to CARVYKTI infusion, all occurred due to disease progression, and none
occurred due to adverse events. Of the 19 deaths that occurred after CARVYKTI infusion, 3
occurred due to disease progression, and 16 occurred due to adverse events. The most common
adverse events were due to infection (n=12).
5.2 Cytokine Release Syndrome
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), including fatal or life-threatening reactions, occurred following
treatment with CARVYKTI. Among patients receiving CARVYKTI for relapsed or refractory
multiple myeloma in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies (N=285), CRS occurred in
84% (238/285), including ≥ Grade 3 CRS (ASTCT 2019) in 4% (11/285) of patients. The median
time to onset of CRS, any grade, was 7 days (range: 1 to 23 days). Cytokine release syndrome
resolved in 82% with a median duration of 4 days (range: 1 to 97 days). The most common
manifestations of CRS in all patients combined (≥ 10%) included fever (84%), hypotension (29%)
and aspartate aminotransferase increased (11%). Serious events that may be associated with CRS
include pyrexia, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, respiratory failure, disseminated
intravascular coagulation, capillary leak syndrome, and supraventricular and ventricular
tachycardia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1].
Cytokine release syndrome occurred in 78% of patients in CARTITUDE-4 (3% Grade 3 to 4) and
in 95% of patients in CARTITUDE-1 (4% Grade 3 to 4).
Identify CRS based on clinical presentation. Evaluate for and treat other causes of fever, hypoxia,
and hypotension. CRS has been reported to be associated with findings of HLH/MAS, and the
physiology of the syndromes may overlap. HLH/MAS is a potentially life-threatening condition.
In patients with progressive symptoms of CRS or refractory CRS despite treatment, evaluate for
evidence of HLH/MAS. Please see Section 5.4; Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
(HLH)/Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS).
Ensure that a minimum of two doses of tocilizumab are available prior to infusion of CARVYKTI.
Of the 285 patients who received CARVYKTI in clinical trials, 53% (150/285) patients received
tocilizumab; 35% (100/285) received a single dose, while 18% (50/285) received more than 1 dose
of tocilizumab. Overall, 14% (39/285) of patients received at least one dose of corticosteroids for
treatment of CRS.

13
Monitor patients at least daily for 10 days following CARVYKTI infusion at a REMS-certified
healthcare facility for signs and symptoms of CRS. Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of CRS
for at least 4 weeks after infusion. At the first sign of CRS, immediately institute treatment with
supportive care, tocilizumab, or tocilizumab and corticosteroids, as indicated in Table 1 [see
Dosing and Administration (2.3)].
Counsel patients to seek immediate medical attention should signs or symptoms of CRS occur at
any time [see Patient Counseling information (17)].
5.3 Neurologic Toxicities
Neurologic toxicities, which may be severe, life-threatening or fatal, occurred following treatment
with CARVYKTI. Neurologic toxicities included ICANS, neurologic toxicity with signs and
symptoms of parkinsonism, GBS, immune mediated myelitis, peripheral neuropathies and cranial
nerve palsies. Counsel patients on the signs and symptoms of these neurologic toxicities, and on
the delayed nature of onset of some of these toxicities. Instruct patients to seek immediate medical
attention for further assessment and management if signs or symptoms of any of these neurologic
toxicities occur at any time [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies for
relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma, one or more neurologic toxicities occurred in 24%
(69/285), including ≥ Grade 3 cases in 7% (19/285) of patients. The median time to onset was 10
days (range: 1 to 101) with 63/69 (91%) of cases developing by 30 days. Neurologic toxicities
resolved in 72% (50/69) of patients with a median duration to resolution of 23 days (range: 1 to
544). Of patients developing neurotoxicity, 96% (66/69) also developed CRS. Subtypes of
neurologic toxicities included ICANS in 13%, peripheral neuropathy in 7%, cranial nerve palsy in
7%, parkinsonism in 3%, and immune mediated myelitis in 0.4% of the patients [see Adverse
Reactions (6.1)].
Immune Effector Cell-associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS)
Patients receiving CARVYKTI may experience fatal or life-threatening ICANS following
treatment with CARVYKTI, including before CRS onset, concurrently with CRS, after CRS
resolution, or in the absence of CRS.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
ICANS occurred in 13% (36/285), including Grade ≥ 3 in 2% (6/285) of the patients. The median
time to onset of ICANS was 8 days (range: 1 to 28 days). ICANS resolved in 30 of 36 (83%) of
patients with a median time to resolution of 3 days (range: 1 to 143 days). The median duration
of ICANS was 6 days (range: 1 to 1229 days) in all patients including those with ongoing
neurologic events at the time of death or data cut off. Of patients with ICANS 97% (35/36) had
CRS. The onset of ICANS occurred during CRS in 69% of patients, before and after the onset of
CRS in 14% of patients respectively.
Immune Effector Cell-associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome occurred in 7% of patients in
CARTITUDE-4 (0.5% Grade 3) and in 23% of patients in CARTITUDE-1 (3% Grade 3).

14
The most frequent ≥2% manifestations of ICANS included encephalopathy (12%), aphasia (4%),
headache (3%), motor dysfunction (3%), ataxia (2%) and sleep disorder (2%) [see Adverse
Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor patients at least daily for 10 days following CARVYKTI infusion at the REMS-certified
healthcare facility for signs and symptoms of ICANS. Rule out other causes of ICANS symptoms.
Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of ICANS for at least 4 weeks after infusion and treat
promptly. Neurologic toxicity should be managed with supportive care and/or corticosteroids as
needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Parkinsonism
Neurologic toxicity with parkinsonism has been reported in clinical trials of CARVYKTI.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
parkinsonism occurred in 3% (8/285), including Grade ≥ 3 in 2% (5/285) of the patients. The
median time to onset of parkinsonism was 56 days (range: 14 to 914 days). Parkinsonism resolved
in 1 of 8 (13%) of patients with a median time to resolution of 523 days. The median duration of
parkinsonism was 243.5 days (range: 62 to 720 days) in all patients including those with ongoing
neurologic events at the time of death or data cut off. The onset of parkinsonism occurred after
CRS for all patients and after ICANS for 6 patients.
Parkinsonism occurred in 1% of patients in CARTITUDE-4 (no Grade 3 to 4) and in 6% of patients
in CARTITUDE-1 (4% Grade 3 to 4).
The manifestations of parkinsonism included movement disorders, cognitive impairment, and
personality changes [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of parkinsonism that may be delayed in onset and
managed with supportive care measures. There is limited efficacy information with medications
used for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease for the improvement or resolution of parkinsonism
symptoms following CARVYKTI treatment.
Guillain-Barré Syndrome
A fatal outcome following GBS occurred following treatment with CARVYKTI despite treatment
with intravenous immunoglobulins. Symptoms reported include those consistent with Miller-
Fisher variant of GBS, encephalopathy, motor weakness, speech disturbances, and
polyradiculoneuritis.
Monitor for GBS. Evaluate patients presenting with peripheral neuropathy for GBS. Consider
treatment of GBS with supportive care measures and in conjunction with immunoglobulins and
plasma exchange, depending on severity of GBS.
Immune Mediated Myelitis
Grade 3 myelitis occurred 25 days following treatment with CARVYKTI in CARTITUDE-4 in a
patient who received CARVYKTI as subsequent therapy. Symptoms reported included
hypoesthesia of the lower extremities and the lower abdomen with impaired sphincter control.

15
Symptoms improved with the use of corticosteroids and intravenous immune globulin. Myelitis
was ongoing at the time of death from other cause [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy occurred following treatment with CARVYKTI.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
peripheral neuropathy occurred in 7% (21/285), including Grade ≥ 3 in 1% (3/285) of the patients.
The median time to onset of peripheral neuropathy was 57 days (range: 1 to 914 days). Peripheral
neuropathy resolved in 11 of 21 (52%) of patients with a median time to resolution of 58 days
(range: 1 to 215 days). The median duration of peripheral neuropathy was 149.5 days (range: 1 to
692 days) in all patients including those with ongoing neurologic events at the time of death or
data cut off [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Peripheral neuropathies occurred in 7% of patients in CARTITUDE-4 (0.5% Grade 3 to 4) and in
7% of patients in CARTITUDE-1 (2% Grade 3 to 4).
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathies.
Patients who experience peripheral neuropathy may also experience cranial nerve palsies or GBS.
Cranial Nerve Palsies
Cranial nerve palsies occurred following treatment with CARVYKTI.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
cranial nerve palsies occurred in 7% (19/285), including Grade ≥ 3 in 1% (1/285) of the patients.
The median time to onset of cranial nerve palsies was 21 days (range: 17 to 101 days). Cranial
nerve palsies resolved in 17 of 19 (89%) of patients with a median time to resolution of 66 days
(range: 1 to 209 days). The median duration of cranial nerve palsies was 70 days (range: 1 to 262
days) in all patients including those with ongoing neurologic events at the time of death or data
cut off [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Cranial nerve palsies occurred in 9% of patients in CARTITUDE-4 (1% Grade 3 to 4) and in 3%
of patients in CARTITUDE-1 (1% Grade 3 to 4).
The most frequent cranial nerve affected was the 7
th
cranial nerve. Additionally, cranial nerves III,
V, and VI have been reported to be affected.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of cranial nerve palsies. Consider management with
systemic corticosteroids, depending on the severity and progression of signs and symptoms.
5.4 Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)/Macrophage Activation Syndrome
(MAS)
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
HLH/MAS occurred in 1% (3/285) of patients. All events of HLH/MAS had onset within 99 days

16
of receiving CARVYKTI, with a median onset of 10 days (range: 8 to 99 days) and all occurred
in the setting of ongoing or worsening CRS. The manifestations of HLH/MAS included
hyperferritinemia, hypotension, hypoxia with diffuse alveolar damage, coagulopathy and
hemorrhage, cytopenia and multi-organ dysfunction, including renal dysfunction and respiratory
failure.
Patients who develop HLH/MAS have an increased risk of severe bleeding. Monitor hematologic
parameters in patients with HLH/MAS and transfuse per institutional guidelines. Fatal cases of
HLH/MAS occurred following treatment with CARVYKTI [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
HLH is a life-threatening condition with a high mortality rate if not recognized and treated early.
Treatment of HLH/MAS should be administered per institutional standards.
5.5 CARVYKTI REMS
Because of the risk of CRS and neurologic toxicities, CARVYKTI is available only through a
restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the
CARVYKTI REMS [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. The required
components of the CARVYKTI REMS are:
• Healthcare facilities that dispense and administer CARVYKTI must be enrolled and
comply with the REMS requirements.
• Certified healthcare facilities must have on-site, immediate access to tocilizumab.
• Ensure that a minimum of 2 doses of tocilizumab are available for each patient for infusion
within 2 hours after CARVYKTI infusion, if needed for treatment of CRS.
Further information is available at www.carvyktirems.com or 1-844-672-0067.
5.6 Prolonged and Recurrent Cytopenias
Patients may exhibit prolonged and recurrent cytopenias following lymphodepleting
chemotherapy and CARVYKTI infusion.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies, Grade
3 or higher cytopenias not resolved by day 30 following CARVYKTI infusion occurred in 62%
(176/285) of the patients and included thrombocytopenia 33% (94/285), neutropenia 27%
(76/285), lymphopenia 24% (67/285) and anemia 2% (6/285). After Day 60 following
CARVYKTI infusion 22%, 20%, 5%, and 6% of patients had a recurrence of Grade 3 or 4
lymphopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia respectively, after initial recovery of
their Grade 3 or 4 cytopenia. Seventy-seven percent (219/285) of patients had one, two or three or
more recurrences of Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias after initial recovery of Grade 3 or 4 cytopenia. Sixteen
and 25 patients had Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, respectively, at the time of death
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor blood counts prior to and after CARVYKTI infusion. Manage cytopenias with growth
factors and blood product transfusion support according to local institutional guidelines.

17
5.7 Infections
CARVYKTI should not be administered to patients with active infection or inflammatory
disorders. Severe, life-threatening, or fatal infections, occurred in patients after CARVYKTI
infusion.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
infections occurred in 57% (163/285), including ≥ Grade 3 in 24% (69/285) of patients. Grade 3
or 4 infections with an unspecified pathogen occurred in 12%, viral infections in 6%, bacterial
infections in 5%, and fungal infections in 1% of patients. Overall, 5% (13/285) of patients had
Grade 5 infections, 2.5% of which were due to COVID-19. Patients treated with CARVYKTI had
an increased rate of fatal COVID-19 infections compared to the standard therapy arm [see Adverse
Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection before and after CARVYKTI infusion and
treat patients appropriately. Administer prophylactic, pre-emptive and/or therapeutic
antimicrobials according to the standard institutional guidelines. Febrile neutropenia was observed
in 5% of patients after CARVYKTI infusion and may be concurrent with CRS. In the event of
febrile neutropenia, evaluate for infection and manage with broad-spectrum antibiotics, fluids and
other supportive care, as medically indicated.
Counsel patients on the importance of prevention measures. Follow institutional guidelines for the
vaccination and management of immunocompromised patients with COVID-19.
Viral Reactivation
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure
and death, can occur in patients with hypogammaglobulinemia.
Perform screening for Cytomegalovirus (CMV), HBV, hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or any other infectious agents if clinically indicated in accordance
with clinical guidelines before collection of cells for manufacturing.
Consider antiviral therapy to prevent viral reactivation per local institutional guidelines/clinical
practice.
5.8 Hypogammaglobulinemia
Hypogammaglobulinemia can occur in patients receiving treatment with CARVYKTI.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
hypogammaglobulinemia adverse event was reported in 36% (102/285) of patients; laboratory IgG
levels fell below 500 mg/dl after infusion in 93% (265/285) of patients. Hypogammaglobulinemia
either as an adverse reaction or laboratory IgG level below 500 mg/dl, after infusion occurred in
94% (267/285) of patients treated. Fifty six percent (161/285) of patients received intravenous
immunoglobulin (IVIG) post CARVYKTI for either an adverse reaction or prophylaxis [see
Adverse Reactions (6.1)].

18
Monitor immunoglobulin levels after treatment with CARVYKTI and administer IVIG for IgG
<400 mg/dL. Manage per local institutional guidelines, including infection precautions and
antibiotic or antiviral prophylaxis.
Use of Live Vaccines
The safety of immunization with live viral vaccines during or following CARVYKTI treatment
has not been studied. Vaccination with live virus vaccines is not recommended for at least 6 weeks
prior to the start of lymphodepleting chemotherapy, during CARVYKTI treatment, and until
immune recovery following treatment with CARVYKTI.
5.9 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions occurred following treatment with CARVYKTI.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
hypersensitivity reactions occurred in 5% (13/285), all of which were ≤ Grade 2. Manifestations
of hypersensitivity reactions included flushing, chest discomfort, tachycardia, wheezing, tremor,
burning sensation, non-cardiac chest pain, and pyrexia.
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, may be due to the dimethyl sulfoxide
(DMSO) in CARVYKTI. Patients should be carefully monitored for 2 hours after infusion for
signs and symptoms of severe reaction. Treat promptly and manage patients appropriately
according to the severity of the hypersensitivity reaction.
5.10 Secondary Malignancies
Patients treated with CARVYKTI may develop secondary malignancies.
Among patients receiving CARVYKTI in the CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 studies,
myeloid neoplasms occurred in 5% (13/285) of patients (9 cases of myelodysplastic syndrome, 3
cases of acute myeloid leukemia, and 1 case of myelodysplastic syndrome followed by acute
myeloid leukemia). The median time to onset of myeloid neoplasms was 447 days (range: 56 to
870 days) after treatment with CARVYKTI. Ten of these 13 patients died following the
development of myeloid neoplasms; 2 of the 13 cases of myeloid neoplasm occurred after initiation
of subsequent antimyeloma therapy. Cases of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid
leukemia have also been reported in the post marketing setting.
T-cell malignancies have occurred following treatment of hematologic malignancies with BCMA-
and CD19-directed genetically modified autologous T-cell immunotherapies, including
CARVYKTI. Mature T-cell malignancies, including CAR-positive tumors, may present as soon
as weeks following infusions, and may include fatal outcomes [see Boxed Warning, Adverse
Reactions (6.1, 6.3), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Monitor life-long for secondary malignancies. In the event that a secondary malignancy occurs,
contact Janssen Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736 for reporting and to obtain instructions on
collection of patient samples.

19
5.11 Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
Due to the potential for neurologic events, including altered mental status, seizures, neurocognitive
decline or neuropathy, patients receiving CARVYKTI are at risk for altered or decreased
consciousness or coordination in the 8 weeks following CARVYKTI infusion. Advise patients to
refrain from driving and engaging in hazardous occupations or activities, such as operating heavy
or potentially dangerous machinery during this initial period, and in the event of new onset of any
neurologic toxicities.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are also described elsewhere in the labeling:
• Increased Early Mortality [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Clinical Studies (14)].
• Cytokine Release Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
• Neurologic Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
• Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)/Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS)
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
• Prolonged and Recurrent Cytopenias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
• Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
• Hypogammaglobulinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
• Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
• Secondary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates
observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of
another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data described in the WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS section reflect exposure to
CARVYKTI in 285 patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: one randomized, open
label with 188 patients in CARTITUDE-4 and one single-arm, open label study with 97 patients
in CARTITUDE-1.
CARTITUDE-4
The safety of CARVYKTI was evaluated in CARTITUDE-4, a randomized, open label multicenter
study, in which patients with relapsed and lenalidomide refractory multiple myeloma received
CARVYKTI meeting the product specifications (N=188) or standard therapy (N=211) [see
Clinical Studies (14)]. Patients with known active or prior history of central nervous system
involvement, patients who exhibit clinical signs of meningeal involvement of multiple myeloma

20
and patients with a history of Parkinson’s disease or other neurodegenerative disorder, were
excluded from the trial. Patients received CARVYKTI at a median dose of 0.71×10
6
CAR-positive
viable T-cells/kg (range: 0.41 to 1.08×10
6
cells/kg). The median age of the 188 participants was
62 years (range: 27 to 78 years); 40% were 65 years or older, and 57% were male; 76% were
White, were 9% Hispanic or Latino, 8% were Asian, and 3% were Black.
The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status at baseline was 0 in 56%,
1 in 44%. For the details about the study population, see Clinical Studies (14).
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions (≥20%) included pyrexia, CRS,
hypogammaglobulinemia, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract
infection, viral infections, headache, hypotension, and nausea.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 34% of patients. The most common nonlaboratory serious
adverse reactions (≥5%) were pneumonia (9%), viral infection (6%), CRS (6%), and cranial nerve
palsies (5%).
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 10% of patients treated with
CARVYKTI.
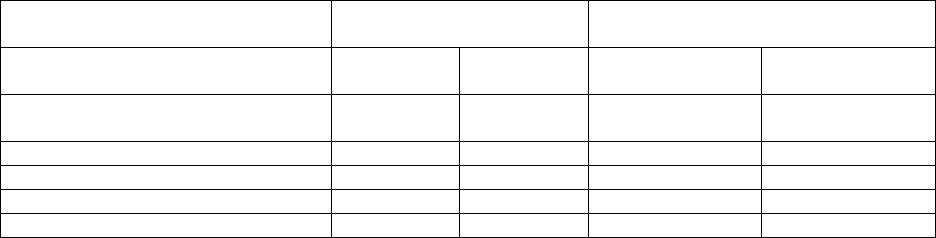
Table 3: Adverse reactions observed in at least 10% of patients treated with CARVYKTI (N=188)
and standard therapy (N=208) in CARTITUDE-4
CARVYKTI
N=188
Standard Therapy
N=208
System Organ Class (SOC)
Preferred term
Any Grade
(%)
Grade 3 or
higher (%)
Any Grade
(%)
Grade 3 or
higher (%)
Gastrointestinal disorders
-
-
-
-
Diarrhea
a
27
3
27
2
Nausea
20
0
18
1
Constipation
10
0
21
1
General disorders and
administrative site conditions
-
-
-
-
Pyrexia
79
5
16
1
Fatigue
b
28
3
50
3
Edema
c
11
1
20
1
Pain
d
10
1
14
<1
Immune system disorders
-
-
-
-
Hypogammaglobulinemia
e
94
9
72
<1
Cytokine release syndrome
78
3
<1
0
Infections and infestations
-
-
-
-
Upper respiratory tract infection
f
25
1
40
5
Viral infection
g
23
4
31
6
Bacterial infection
h
15
6
17
4
Pneumonia
i
14
9
18
11
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
-
-
-
-
Decreased appetite
10
0
5
0
Musculoskeletal and connective
tissue disorders
-
-
-
-
Musculoskeletal pain
j
34
2
47
4
Nervous system disorders
-
-
-
-
Headache
k
23
0
13
0
Encephalopathy
l
11
2
4
1
21
CARVYKTI
N=188
Standard Therapy
N=208
System Organ Class (SOC)
Preferred term
Any Grade
(%)
Grade 3 or
higher (%)
Any Grade
(%)
Grade 3 or
higher (%)
Respiratory, thoracic and
mediastinal disorders
-
-
-
-
Cough
m
15
0
18
0
Hypoxia
12
3
1
1
Vascular disorders
-
-
-
-
Hypotension
n
23
4
3
0
Adverse reactions are reported using MedDRA version 25.0
a
Diarrhea includes Colitis, and Diarrhea.
b
Fatigue includes Asthenia, Fatigue, and Malaise.
c
Edema includes Face edema, Generalized edema, Localized edema, Edema peripheral, Periorbital edema, Peripheral swelling, Pulmonary
edema, and Scrotal edema.
d
Pain includes Anorectal discomfort, Catheter site pain, Flank pain, Inflammatory pain, Pain, Pain in jaw, Pain of skin, Pelvic pain,
Rhinalgia, and Sacral pain.
e
Hypogammaglobulinemia includes subjects with adverse event of hypogammaglobulinemia and/or laboratory IgG levels that fell below 500
mg/dL following CARVYKTI infusion or standard therapy.
f
Upper respiratory tract infection includes Bronchitis, Nasal congestion, Nasopharyngitis, Pharyngitis, Respiratory tract infection, Rhinitis,
Rhinorrhea, Rhinovirus infection, Sinusitis, Upper respiratory tract infection, and Viral pharyngitis.
g
Viral infection includes Adenovirus infection, Asymptomatic COVID-19, COVID-19, Cytomegalovirus infection, Cytomegalovirus
infection reactivation, Cytomegalovirus viremia, Hepatitis B reactivation, Herpes simplex reactivation, Herpes virus infection, Herpes
zoster, Human herpesvirus 6 infection, Influenza, Lymphadenitis viral, Metapneumovirus infection, Parainfluenza virus infection,
Parvovirus B19 infection, Parvovirus infection, Respiratory syncytial virus infection, Respiratory tract infection viral, and Rotavirus
infection.
h
Bacterial infection includes Bordetella infection, Bronchitis bacterial, Campylobacter infection, Catheter site infection, Cellulitis,
Chalazion, Citrobacter infection, Clostridium difficile colitis, Device related infection, Gingivitis, Perichondritis, Pyelonephritis acute,
Salmonellosis, Skin infection, Staphylococcal infection, Superinfection bacterial, Vascular access site infection, and Vascular device
infection.
i
Pneumonia includes COVID-19 pneumonia, Lower respiratory tract infection, Metapneumovirus pneumonia, Pneumonia, Pneumonia
moraxella, Pneumonia pseudomonal, and Pneumonia streptococcal.
j
Musculoskeletal pain includes Arthralgia, Back pain, Bone pain, Bursitis, Musculoskeletal chest pain, Musculoskeletal pain, Myalgia,
Myositis, Neck pain, Non-cardiac chest pain, Osteoarthritis, Pain in extremity, Plantar fasciitis, Rotator cuff syndrome, Spinal pain, and
Tendonitis.
k
Headache includes Headache and Tension headache.
l
Encephalopathy includes Amnesia, Bradyphrenia, Confusional state, Depressed level of consciousness, Disturbance in attention, Immune
effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome, Lethargy, and Psychomotor retardation.
m
Cough includes Cough, Productive cough, and Upper-airway cough syndrome.
n
Hypotension includes Hypotension, and Orthostatic hypotension.
Other clinically important adverse reactions that occurred in less than 10% of patients treated with
CARVYKTI include the following:
• Blood and lymphatic system disorders: coagulopathy
a
(5%), febrile neutropenia (2%),
lymphocytosis (2%),
• Cardiac disorders: tachycardia
b
(5%), cardiac arrhythmias
c
(3%)
• Gastrointestinal disorders: abdominal pain
d
(6%), vomiting (5%)
• General disorders and administration site conditions: chills (6%)
• Immune system disorders: HLH (1%)
• Infections and Infestations: gastroenteritis
e
(7%), sepsis
f
(9%), urinary tract
infection
g
(5%), fungal infection
h
(3%)
• Investigations: c-reactive protein increased (6%)
22
• Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: hypophosphatemia (10%), hyperferritinemia (7%)
• Neoplasms benign, malignant, and unspecified (incl cysts and polyps): hematologic
malignancy
i
(3%)
• Nervous system disorders: dizziness
j
(9%), cranial nerve palsies
k
(9%), motor
dysfunction
l
(9%), peripheral neuropathy
m
(7%), sleep disorder
n
(6%), tremor (4%),
aphasia
o
(3%), ataxia
p
(3%),
• Psychiatric disorders: delirium
q
(2%) personality changes
r
(2%)
• Renal and urinary disorders: renal failure
s
(5%)
• Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: dyspnea
t
(10%)
• Skin and subcutaneous tissues: rash
u
(7%)
• Vascular Disorders: hemorrhage
v
(9%), hypertension (7%), thrombosis
w
(3%), capillary
leak syndrome (1%)
a
Coagulopathy includes Blood fibrinogen decreased, Coagulation test abnormal, Coagulopathy, Disseminated
intravascular coagulation, and Hypofibrinogenemia.
b
Tachycardia includes Sinus tachycardia, and Tachycardia.
c
Cardiac arrhythmias includes Atrial fibrillation, and Atrioventricular block second degree.
d
Abdominal pain includes Abdominal discomfort, Abdominal pain, Abdominal pain lower, Abdominal pain
upper, and Dyspepsia.
e
Gastroenteritis includes Enterocolitis viral, Enterovirus infection, Gastroenteritis, Gastroenteritis rotavirus,
Gastroenteritis salmonella, Gastrointestinal infection, and Large intestine infection.
f
Sepsis includes Bacteremia, Candida sepsis, Device related bacteremia, Enterococcal bacteremia, Hemophilus
sepsis, Neutropenic sepsis, Pseudomonal sepsis, Sepsis, Septic shock, Staphylococcal bacteremia, Systemic
candida, and Urosepsis.
g
Urinary tract infection includes Cystitis, Escherichia urinary tract infection, and Urinary tract infection.
h
Fungal infection includes Candida infection, Oral candidiasis, Tongue fungal infection, and Vulvovaginal
candidiasis.
i
Hematologic malignancy includes Myelodysplastic syndrome, Acute myeloid leukemia, and T-cell lymphoma.
Incidence based on cutoff date of 01 November 2022 (median follow-up time of 15.9 months).
j
Dizziness includes Dizziness, Dizziness postural, Presyncope, Syncope, and Vertigo.
k
Cranial nerve palsies includes Facial paralysis, Facial paresis, IIIrd nerve paralysis, and Trigeminal palsy.
l
Motor dysfunction includes Bradykinesia, Coordination abnormal, Dysgraphia, Extrapyramidal disorder,
Micrographia, Muscle spasms, Muscular weakness, and Parkinsonism.
m
Neuropathy peripheral includes Peripheral motor neuropathy, Peripheral sensory neuropathy, and
Polyneuropathy.
n
Sleep disorder includes Insomnia, Sleep disorder, and Somnolence.
o
Aphasia includes Aphasia, and Dysarthria.
p
Ataxia includes Ataxia, Balance disorder, Dysmetria, and Gait disturbance.
q
Delirium includes Agitation, Disorientation, and Hallucination.
r
Personality changes includes Personality change, and Reduced facial expression.
s
Renal failure includes Acute kidney injury, Blood creatinine increased, Chronic kidney disease, Renal failure,
and Renal impairment.
t
Dyspnea includes Dyspnea, Dyspnea exertional, Respiratory failure, Tachypnea, and Wheezing.
u
Rash includes Dermatitis psoriasiform, Drug eruption, Erythema, Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta,
Rash, Rash erythematous, Rash maculo-papular, Rash papular, and Urticaria.
v
Hemorrhage includes Catheter site hemorrhage, Conjunctival hemorrhage, Contusion, Epistaxis, Hematemesis,
Hematoma, and Hematuria.
w
Thrombosis includes Deep vein thrombosis, Pulmonary embolism, and Venous thrombosis limb.

23
Laboratory Abnormalities
Table 4 presents the most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities based on laboratory data,
occurring in at least 10% of patients.
Table 4: Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities in at least 10% of patients treated with CARVYKTI
(N=188) and standard therapy (N=208) in CARTITUDE-4
CARVYKTI
(N=188)
Standard Therapy
(N=208)
Laboratory Abnormality
Grade 3 or 4 (%)
Grade 3 or 4 (%)
Lymphocyte count decreased
99
62
Neutrophil count decreased
95
88
White blood cell decreased
94
69
Platelet count decreased
47
20
Hemoglobin decreased
34
17
Laboratory abnormalities graded using NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 5.0. Laboratory abnormalities are sorted
by decreasing frequency in the Grade column.
Other clinically important Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (based on laboratory data) that
occurred in less than 10% of patients treated with CARVYKTI include fibrinogen decreased,
gamma glutamyl transferase increased, hypokalemia, alanine aminotransferase increased,
aspartate aminotransferase increased, alkaline phosphatase increased, hypoalbuminemia,
hyponatremia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, and blood bilirubin
increased.
CARTITUDE-1
The safety data described in this section reflect the exposure of 97 adult patients with
relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma in the CARTITUDE-1 study (USA cohort) to CARVYKTI
and includes 17 patients (18%) with manufacturing failures either because they received
CARVYKTI that did not meet product release specifications or there were insufficient data to
confirm product release specifications for CARVYKTI. Patients received CARVYKTI across a
dose range of 0.51 to 0.95×10
6
CAR-positive viable T cells/kg body weight [see Clinical Studies
(14)]. Patients with a history of CNS disease (such as seizure or cerebrovascular ischemia) or
requiring ongoing treatment with chronic immunosuppression were excluded. The median
duration of follow-up was 18 months. The median age of the study population was 61 years (range:
43 to 78 years); 36% were 65 years or older, and 59% were men. The Eastern Cooperative
Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status at baseline was 0 in 40%, 1 in 56%, and 2 in 4% of
patients. Three of the patients treated with CARVYKTI had a creatinine clearance of <45 mL/min
at baseline. For the details about the study population, see Clinical Studies (14).
The most common (greater or equal to 10%) Grade 3 or higher nonlaboratory adverse reactions
were infections-pathogen unspecified (19%), pneumonia (13%), hematologic malignancy (10%)
and hypotension (10%).
The most common nonlaboratory adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 20%)
included pyrexia, CRS, hypogammaglobulinemia, hypotension, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue,
infections of unspecified pathogen, cough, chills, diarrhea, nausea, encephalopathy, decreased
appetite, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, tachycardia, dizziness, dyspnea, edema, viral
infections, coagulopathy, constipation, and vomiting.

24
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 55% of patients. The most common non-laboratory (greater
than or equal to 5%) serious adverse reactions included CRS (21%), sepsis (7%), encephalopathy
(10%), and pneumonia (8%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 9% of patients.
Table 5 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred in at least 10% of patients treated with
CARVYKTI.
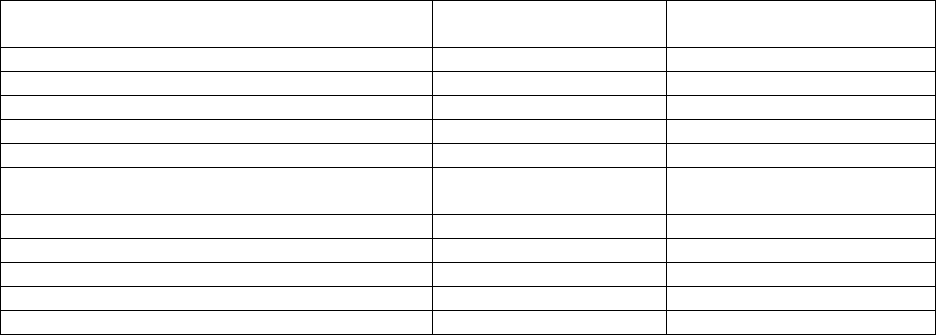
Table 5: Adverse reactions observed in at least 10% of patients treated with CARVYKTI in
CARTITUDE-1 (N=97)
System Organ Class (SOC)
Preferred term
Any Grade (%)
Grade 3 or higher (%)
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
-
-
Coagulopathy
a
22
2
Febrile Neutropenia
10
9
Cardiac disorders
-
-
Tachycardia
b
27
1
Gastrointestinal disorders
-
-
Diarrhea
c
33
1
Nausea
31
1
Constipation
22
0
Vomiting
20
0
General disorders and administrative site
conditions
-
-
Pyrexia
96
5
Fatigue
d
47
7
Chills
33
0
Edema
e
23
0
Immune system disorders
-
-
Cytokine release syndrome
f
95
5
Hypogammaglobulinemia
g
93
2
Infections and infestations
h
-
-
Infections-pathogen unspecified
i
41
19
Upper respiratory tract infection
j
28
3
Viral infections
k
23
7
Pneumonia
l
14
13
Sepsis
m
10
7
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
-
-
Decreased appetite
29
1
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
-
-
Musculoskeletal pain
n
48
2
Nervous system disorders
-
-
Encephalopathy
o
30
6
Headache
27
0
Dizziness
p
23
1
Motor dysfunction
q
16
3
Psychiatric disorders
-
-
Insomnia
13
0
25
System Organ Class (SOC)
Preferred term
Any Grade (%)
Grade 3 or higher (%)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
-
-
Cough
r
39
0
Dyspnea
s
23
3
Nasal congestion
15
0
Hypoxia
12
4
Neoplasms benign, malignant, and unspecified
(incl cysts and polyps)
Hematologic malignancy
t
10
10
Vascular disorders
-
-
Hypotension
u
51
10
Hypertension
19
6
Hemorrhage
v
16
4
Adverse reactions are reported using MedDRA version 23.0
a
Coagulopathy includes Activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged, Coagulopathy, Disseminated intravascular coagulation,
Hypofibrinogenemia, International normalized ratio increased, and Prothrombin time prolonged. Also includes terms reported under
investigation SOC.
b
Tachycardia includes Sinus tachycardia, and Tachycardia.
c
Diarrhea includes Colitis, and Diarrhea.
d
Fatigue includes Asthenia, Fatigue, and Malaise.
e
Edema includes Face edema, Generalized edema, Localized edema, Edema peripheral, Periorbital edema, Peripheral swelling, Pulmonary
edema, and Scrotal edema.
f
Cytokine release syndrome includes CRS, and Systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
g
Hypogammaglobulinemia includes subjects with adverse event of hypogammaglobulinemia (12%) and/or laboratory IgG levels that fell below
500 mg/dL following CARVYKTI infusion (92%).
h
Infections and infestations System Organ Class Adverse Events are grouped by pathogen type and selected clinical syndromes.
i
Infections - pathogen unspecified includes Abscess limb, Atypical pneumonia, Bacteremia, Bronchitis, Conjunctivitis, Enterocolitis
infectious, Folliculitis, Gastroenteritis, Lung abscess, Lung opacity, Osteomyelitis, Otitis media, Parotitis, Perirectal abscess, Pneumonia,
Rash pustular, Rhinitis, Sepsis, Septic shock, Sinusitis, Skin infection, Soft tissue infection, Upper respiratory tract infection, and Urinary
tract infection.
j
Upper respiratory tract infection includes Human rhinovirus test positive, Rhinitis, Rhinovirus infection, Sinusitis, Upper respiratory tract
infection, and Viral upper respiratory tract infection. Also includes terms reported under investigation SOC. Upper respiratory tract infections
may also be included under pathogen categories.
k
Viral infection includes Adenovirus test positive, Coronavirus infection, Cytomegalovirus syndrome, Cytomegalovirus viremia, Enterovirus
infection, Gastroenteritis viral, Herpes zoster, Herpes zoster disseminated, Influenza, Influenza like illness, Oral herpes, Parainfluenza virus
infection, Rhinovirus infection, Urinary tract infection viral, and Viral upper respiratory tract infection.
l
Pneumonia includes Atypical pneumonia, Lung abscess, Lung opacity, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, Pneumonia, and Pneumonia
aspiration.
m
Sepsis includes Bacteremia, Bacterial sepsis, Pseudomonal bacteremia, Sepsis, Septic shock, and Staphylococcal bacteremia.
n
Musculoskeletal pain includes Arthralgia, Back pain, Bone pain, Joint stiffness, Muscle strain, Musculoskeletal chest pain, Musculoskeletal
discomfort, Musculoskeletal pain, Musculoskeletal stiffness, Myalgia, Neck pain, Non-cardiac chest pain, and Pain in extremity.
o
Encephalopathy includes Amnesia, Bradyphrenia, Confusional state, Depressed level of consciousness, Disturbance in attention,
Encephalopathy, Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome, Lethargy, Memory impairment, Mental impairment, Mental status
changes, Noninfective encephalitis, and Somnolence.
p
Dizziness includes Dizziness, Presyncope, and Syncope.
q
Motor dysfunction includes Motor dysfunction, Muscle spasms, Muscle tightness, Muscular weakness, and Myoclonus.
r
Cough includes Cough, Productive cough, and Upper-airway cough syndrome.
s
Dyspnea includes Acute respiratory failure, Dyspnea, Dyspnea exertional, Respiratory failure, and Tachypnea.
t
Hematologic malignancy includes Myelodysplastic syndrome and Acute myeloid leukemia.
u
Hypotension includes Hypotension, and Orthostatic hypotension.
v
Hemorrhage includes Conjunctival hemorrhage, Contusion, Ecchymosis, Epistaxis, Eye contusion, Hematochezia, Hemoptysis, Infusion site
hematoma, Oral contusion, Petechiae, Post procedural hemorrhage, Pulmonary hemorrhage, Retinal hemorrhage, and Subdural hematoma.

26
Other clinically important adverse reactions that occurred in less than 10% of patients treated with
CARVYKTI include the following:
• Cardiac disorders: cardiac arrhythmias
a
(8%), chest pain
b
(7%)
• Eye disorders: diplopia (1%)
• Gastrointestinal disorders: dysphagia (1%)
• Immune system disorders: HLH (1%), hypersensitivity reaction (5%)
• Infections and Infestations: bacterial infections
c
(9%), urinary tract infection
d
(4.1%)
• Injury, Poisoning and Procedural complications: fall (3.1%)
• Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: tumor lysis syndrome (1%)
• Musculoskeletal and Connective tissue disorders: posture abnormal (1%)
• Nervous system disorders: aphasia
e
(8%), ataxia
f
(8%), peripheral neuropathy
g
(7%),
tremor (6%), parkinsonism (4.1%), micrographia (4.1%), dysgraphia (3.1%), reduced
facial expression (3.1%), cranial nerve palsies (3.1%), bradykinesia (2.1%), paresis
h
(1%),
cogwheel rigidity (1%), cerebrovascular accident (1%), seizure (1%), slow speech (1%),
nystagmus (1%)
• Psychiatric disorders: delirium
i
(5%) depression
j
(4.1%), psychomotor retardation (1%)
• Renal and urinary disorders: renal failure
k
(7%)
• Skin and subcutaneous tissues: rash
l
(8%)
• Vascular Disorders: thrombosis
m
(5%)
a
Cardiac arrhythmias includes atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular
extrasystoles, ventricular tachycardia.
b
Chest pain includes Angina pectoris, Chest discomfort, and Chest pain.
c
Bacterial infection includes Abscess limb, Cholecystitis, Cholecystitis acute, Clostridium difficile colitis,
Clostridium difficile infection, Enterocolitis bacterial, Osteomyelitis, Perirectal abscess, Soft tissue infection,
Staphylococcal infection.
d
Urinary tract infection includes Urinary tract infection, and Urinary tract infection viral.
e
Aphasia includes Aphasia, Dysarthria, and Speech disorder.
f
Ataxia includes Ataxia, Balance disorder, and Gait disturbance.
g
Peripheral neuropathy includes Peripheral neuropathy, Peripheral motor neuropathy and Peripheral sensory
neuropathy
.
h
Paresis includes Facial paralysis, and Peroneal nerve palsy.
i
Delirium includes Agitation, Hallucination, Irritability, Personality change, and Restlessness.
j
Depression includes Depression, and Flat affect.
k
Renal failure includes Acute kidney injury, Blood creatinine increased, Chronic kidney disease, and Renal
impairment.
l
Rash includes Erythema, Rash, Rash maculo-papular, and Rash pustular.
m
Thrombosis includes Deep vein thrombosis, and Device related thrombosis.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Table 6 presents the most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities based on laboratory data,
occurring in at least 10% of patients.

27
Table 6: Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities in at least 10% of patients treated with CARVYKTI
in CARTITUDE-1 (N=97)
Laboratory Abnormality
Grade 3 or 4 (%)
Lymphopenia
99
Neutropenia
98
White blood cell decreased
98
Anemia
72
Thrombocytopenia
63
Aspartate aminotransferase increased
21
Laboratory abnormalities graded using NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 5.0. Laboratory abnormalities are sorted
by decreasing frequency in the Grade column.
Other clinically important Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (based on laboratory data) that
occurred in less than 10% of patients treated with CARVYKTI include the following: fibrinogen
decreased, hypoalbuminemia, alanine aminotransferase increased, hyponatremia, hypocalcemia,
gamma glutamyl transferase increased, alkaline phosphatase increased, hypokalemia, blood
bilirubin increased.
6.2 Immunogenicity
The immunogenicity of CARVYKTI has been evaluated using a validated assay for the detection
of binding antibodies against the extracellular portion of the anti-BCMA CAR pre-dose, and at
multiple timepoints post-infusion. In CARTITUDE-1, 19 of 97 (19.6%) patients were positive for
anti-product antibodies. In CARTITUDE-4, 39 of 186 patients (21%) were positive for anti-CAR
antibodies.
There was no clear evidence that the observed anti-product antibodies impact CARVYKTI kinetics
of initial expansion and persistence, efficacy, or safety.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
Because adverse events to marketed products are reported voluntarily from a population of
uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal
relationship to product exposure.
The following adverse event has been identified during postmarketing use of CARVYKTI.
Neoplasms: T cell malignancies
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
HIV and the lentivirus used to make CARVYKTI have limited, short spans of identical genetic
material (RNA). Therefore, some commercial HIV nucleic acid tests (NATs) may yield
false-positive results in patients who have received CARVYKTI.

28
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on the use of CARVYKTI in pregnant women. No reproductive and
developmental toxicity studies in animals have been conducted with CARVYKTI to assess
whether it can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. It is not known whether
CARVYKTI has the potential to be transferred to the fetus and cause fetal toxicity. Based on the
mechanism of action, if the transduced cells cross the placenta, they may cause fetal toxicity,
including B-cell lymphocytopenia and hypogammaglobulinemia. Therefore, CARVYKTI is not
recommended for women who are pregnant, or for women of childbearing potential not using
contraception. Pregnant women should be advised that there may be risks to the fetus. Pregnancy
after CARVYKTI therapy should be discussed with the treating physician.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and
miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of CARVYKTI in human milk, the effect on the
breastfed infant, and the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of
breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CARVYKTI and any
potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from CARVYKTI or from the underlying maternal
condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy status for females of child-bearing age should be verified prior to starting treatment
with CARVYKTI.
Contraception
There are insufficient data to provide a recommendation concerning duration of contraception
following treatment with CARVYKTI.
In clinical trials, female patients of childbearing potential were advised to practice a highly
effective method of contraception and male patients with partners of childbearing potential or
whose partners were pregnant were instructed to use a barrier method of contraception, until one
year after the patient has received CARVYKTI infusion.
See the prescribing information for lymphodepleting chemotherapy for information on the need
for contraception in patients who receive the lymphodepleting chemotherapy.

29
Infertility
There are no data on the effect of CARVYKTI on fertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of CARVYKTI in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 97 patients in CARTITUDE-1 that received CARVYKTI, 28% were 65 to 75 years of age,
and 8% were 75 years of age or older. CARTITUDE-1 did not include sufficient numbers of
patients aged 65 and older to determine whether the effectiveness differs compared with that of
younger patients. In 62 patients less than 65 years of age, all grade and Grade 3 and higher
neurologic toxicities occurred in 19% (12/62) and 6% (4/62), respectively. Of the 35 patients ≥65
years of age, all grade and Grade 3 and higher neurologic toxicities occurred in 37% (13/35) and
20% (7/35), respectively.
Of the 188 patients in CARTITUDE-4 that received CARVYKTI, 38% were 65 to 75 years of age,
and 2% were 75 years of age or older. In 112 patients less than 65 years of age, all grade and Grade
3 and higher neurologic toxicities occurred in 16% (18/112) and 3% (3/112) respectively. Of the
76 patients ≥65 years of age, all grade and Grade 3 and higher neurologic toxicities occurred in
34% (26/76) and 7% (5/76) respectively.
11 DESCRIPTION
CARVYKTI
®
(ciltacabtagene autoleucel) is a BCMA-directed genetically modified autologous T
cell immunotherapy. CARVYKTI is prepared from the patient’s peripheral blood mononuclear
cells, which are obtained via a standard leukapheresis procedure. The mononuclear cells are
enriched for T cells and genetically modified ex vivo by transduction with a replication-
incompetent lentiviral vector to express a CAR comprising an anti-BCMA targeting domain,
which consists of two single-domain antibodies linked to a 4-1BB costimulatory domain and a
CD3-zeta signaling domain.
The transduced anti-BCMA CAR T cells are expanded in cell culture, washed, formulated into a
suspension and cryopreserved. The product must pass a sterility test before release for shipping as
a frozen suspension in a patient-specific infusion bag. The product is thawed and then infused back
into the patient, where the anti-BCMA CAR T cells can recognize and eliminate
BCMA-expressing target cells. [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), How Supplied/Storage and
Handling (16)].
In addition to T cells, CARVYKTI may contain Natural Killer (NK) cells. The formulation
contains 5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
CARVYKTI is a BCMA-directed, genetically modified autologous T cell immunotherapy, which
involves reprogramming a patient’s own T cells with a transgene encoding a CAR that identifies

30
and eliminates cells that express BCMA. The CARVYKTI CAR protein features two BCMA-
targeting single-domain antibodies designed to confer high avidity against human BCMA, a 4-
1BB co-stimulatory domain and a CD3-zeta (CD3ζ) signaling cytoplasmic domain. Upon binding
to BCMA-expressing cells, the CAR promotes T cell activation, expansion, and elimination of
target cells.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
After a single infusion of CARVYKTI, expansion of CAR-positive T cells coincided with
decreases of serum soluble BCMA, serum M-protein, and/or free light chains. Across all patients,
levels of IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ and IL-2 receptor alpha increased post-infusion and peaked at Days 7–
14. The serum levels of all cytokines generally returned to baseline levels within 2–3 months post-
infusion.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of CARVYKTI was assessed in 285 adult patients with relapsed or
refractory multiple myeloma in CARTITUDE-1 and CARTITUDE-4 receiving a single infusion
at the median dose of 0.71×10
6
CAR-positive viable T cells/kg (range: 0.41×10
6
to
1.08×10
6
cells/kg).
Following a single infusion, CARVYKTI exhibited an initial expansion phase followed by a rapid
decline, and then a slower decline. However, high inter-individual variability was observed.
Table 7: Pharmacokinetic parameters of CARVYKTI in patients with multiple myeloma
Parameter
Summary Statistics
CARTITUDE-1
N=97
CARTITUDE-4
N=188
C
max
(copies/µg genomic DNA)
Median (range), n
47806 (7189 - 115234), 97
34891 (935 - 104861), 185
t
max
(day)
Median (range), n
12.7 (8.7 - 329.8), 97
12.8 (7.8 - 222.8), 185
AUC
0-28d
(copies*day/µg genomic
DNA)
Median (range), n
371569 (58691 - 2024126),
97
293490 (9215 - 1738455),
184
t
1/2
(day)
Median (range), n
15.3 (3.0 - 95.4), 42
11.7 (4.1 - 179.6), 49
After the cell expansion, the persistence phase of CARVYKTI was observed for all patients. At
the time of analysis in CARTITUDE-1 (n=65) and CARTITUDE-4 (n=87) studies, the median
time for CAR transgene levels in peripheral blood to return to the pre-dose baseline level was
approximately 100 days (range: 28 to 365 days) and 109 days (range: 29 to 366 days) post-infusion
respectively.
Detectable CARVYKTI exposures in bone marrow indicate a distribution of CARVYKTI from
systemic circulation to bone marrow. Similar to blood transgene levels, bone marrow transgene
levels declined over time and exhibited high inter-individual variability.
Patients with higher CAR-T cell expansion tended to have higher rates of CRS. Some patients
required tocilizumab, corticosteroids, and anakinra for the management of CRS. CARVYKTI
continues to expand and persist following administration of tocilizumab, corticosteroids, and
anakinra. In CARTITUDE-1, CARVYKTI median C
max
and AUC
0-28d
in patients treated with
tocilizumab (n=68) for CRS were 168% and 209% of those in patients (n=29) who did not receive
tocilizumab for CRS, respectively. The median C
max
and AUC
0-28d
of CARVYKTI in patients who
received corticosteroids (n=21) for CRS were 186% and 307% of those in patients who did not

31
receive corticosteroids (n=76) for CRS, respectively. In addition, the median C
max
and AUC
0-28d
of CARVYKTI in patients who received anakinra (n=18) for CRS were 139% and 232% of those
in patients who did not receive anakinra (n=79) for CRS, respectively. In CARTITUDE-4, the
results related to tocilizumab and corticosteroid were consistent with CARTITUDE-1.
Specific Populations
The pharmacokinetics of CARVYKTI (C
max
and AUC
0-28d
) were not impacted by age (27 to
78 years), gender, body weight, race, mild hepatic dysfunction [(total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of
normal (ULN) and aspartate aminotransferase > ULN) or (ULN < total bilirubin ≤1.5 times
ULN)], mild renal dysfunction (60 mL/min ≤ creatinine clearance [CRCL] <90 mL/min) or
moderate renal dysfunction (30 mL/min ≤ creatinine clearance <60 mL/min). Formal renal and
hepatic impairment studies of CARVYKTI were not conducted.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No genotoxicity or carcinogenicity studies have been performed with CARVYKTI as they were
not indicated. In vitro studies with CARVYKTI manufactured from healthy donors and patients
with multiple myeloma showed no evidence of cytokine independent growth and no preferential
integration near genes associated with oncogenic transformation.
No studies have been conducted to evaluate the effects of CARVYKTI on fertility.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
CARTITUDE-4
Efficacy of CARVYKTI was evaluated in CARTITUDE-4 (NCT04181827) a randomized, open
label, multicenter controlled study in adult patients with relapsed and lenalidomide-refractory
multiple myeloma, who previously received at least 1 prior line of therapy including a proteasome
inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent. A total of 419 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive
either a sequence of apheresis, bridging therapy, lymphodepletion and CARVYKTI (n=208) or
standard therapy which included daratumumab, pomalidomide and dexamethasone (DPd) or
bortezomib, pomalidomide and dexamethasone (PVd) selected by physician prior to
randomization based on patient’s prior antimyeloma therapy (n=211). Randomization was
stratified by physician’s choice of treatment (DPd vs. PVd), ISS (I vs. II vs. III) and number of
prior lines of therapy (1 vs. 2 or 3).
Patients with known active or prior history of central nervous system involvement, patients who
exhibit clinical signs of meningeal involvement of multiple myeloma and patients with a history
of Parkinson’s disease or other neurodegenerative disorder, were excluded from the trial.
In the overall study population (N=419), the median age was 61 years (range: 27 to 80 years), 57%
were male, 75% were White, 3% were Black or African American, 9% were Asian, and 7% were
Hispanic or Latino. Most patients (94%) were International Staging System (ISS) Stage I or II.
High-risk cytogenetics [presence of t(4:14), (14:16), and 17p13 del] were present in 34% of
patients. Nineteen percent of patients had presence of soft tissue plasmacytoma.

32
Patients had received a median of 2 (range: 1 to 3) prior lines of therapy and 85% of patients had
received prior autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). Ninety-nine percent of patients were
refractory to their last line of prior therapy. Forty-seven percent were refractory to a proteasome
inhibitor (PI) and 100% were refractory to an immunomodulatory agent.
All 208 patients randomized to the CARVYKTI arm underwent apheresis, twelve (6%) were not
treated with CARVYKTI due to progressive disease (n=10) or death (n=2), and twenty (10%)
progressed prior to infusion with CARVYKTI but were able to receive CARVYKTI as subsequent
therapy. Eight (4%) patients received CAR-T positive T cells that did not meet product release
specification for CARVYKTI (non-conforming product).
Patients randomized to CARVYKTI were to receive lymphodepleting chemotherapy consisting of
fludarabine 30 mg/m
2
/day and cyclophosphamide 300 mg/m
2
/day concurrently for 3 days followed
by CARVYKTI infusion 5 to 7 days after start of lymphodepleting chemotherapy. At least one
cycle of DPd or PVd bridging therapy was received for disease control between leukapheresis and
the start of the lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
CARVYKTI was administered as a single IV infusion 5 to 7 days after the start of a
lymphodepleting chemotherapy at a median dose of 0.71×10
6
CAR-positive viable T-cells/kg
(range: 0.39 to 1.07×10
6
cells/kg).
In the 176 patients that received CARVYKTI as study treatment, the median time from the day
after receipt of apheresis material at manufacturing facility to release of product for infusion was
44 days (range: 25 to 127 days) and the median time from first apheresis to CARVYKTI infusion
was 79 days (range: 45 days to 246 days).
The primary efficacy measure was progression-free survival (PFS) analyzed based on the Intent-
To-Treat Analysis Set (see Table 8 and Figure 1). After a median follow-up of 15.9 months,
median PFS was 12 months (95% CI: 9.8, 14) for standard therapy arm and NE (95% CI: 22.8,
NE) for CARVYKTI arm (Hazard ratio: 0.41 [95% CI: 0.30, 0.56]). The estimated PFS rate at 12
months was 75.9% (95% CI: 69.4%, 81.1%) in the CARVYKTI arm and 49.5% (95% CI: 42.3%,
56.3%) in the standard therapy arm.
Table 8: Efficacy results for CARTITUDE-4 (Intent-To-Treat Analysis Set)
CARVYKTI
(N=208)
Standard Therapy
(N=211)
Progression-Free Survival
a
-
-
Number of events, n (%)
65 (31.3)
119 (56.4)
Median, months [95% CI]
b
NE [22.8, NE]
12 [9.8, 14.0]
Hazard ratio [95% CI]
c
0.41 [0.30, 0.56]
-
p-value
d
<0.0001
-
Complete Response or Better Rate
a
, % [95% CI]
74.0 [67.5, 79.9]
22.3 [16.8, 28.5]
p-value
e
<0.0001
-
Stringent Complete Response
a
(sCR), n (%)
137 (65.9)
38 (18.0)
Complete Response
a
(CR), n (%)
17 (8.2)
9 (4.3)
Overall Response Rate, ORR (sCR + CR + VGPR +
PR)
a
, % [95% CI]
84.6 [79.0, 89.2]
67.8 [61.0, 74.0]
p-value
e
<0.0001
-

33
Very Good Partial Response
a
(VGPR), n (%)
16 (7.7)
49 (23.2)
Partial Response
a
(PR), n (%)
6 (2.9)
47 (22.3)
NE=not estimable; CI=confidence interval
Notes: Based on a median duration of follow up of 15.9 months
a
Per the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) consensus, as assessed by IRC
b
Kaplan-Meier estimate
c
Based on a stratified Cox proportional hazards model. A hazard ratio <1 indicates an advantage for CARVYKTI Arm. For all stratified
analyses, stratification was based on investigator’s choice (PVd or DPd), ISS staging (I, II, III) and number of prior lines (1 vs. 2 or 3) as
randomized.
d
Stratified log-rank test
e
Stratified Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel Chi-Squared test
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier Curve of PFS in CARTITUDE-4 (Intent-To-Treat Analysis Set)
Note: Intent-to-treat analysis set consists of subjects who were randomized in the study.
Data cutoff date: November 1, 2022
In the CARVYKTI arm, the estimated median duration of response (DOR) has not been reached
in patients who achieved PR or better or in patients who achieved CR or better. In the standard
therapy arm, the estimated median DOR was 16.6 months (95% CI: 12.9, NE).
A higher proportion of patients in the CARVYKTI arm compared to the standard therapy arm died
within the first 10 months of randomization as shown in Figure 2.

34
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier Curve of Overall Survival in CARTITUDE-4 (Intent-to-Treat Analysis Set)
Note: Intent-to-treat analysis set consists of subjects who were randomized to the study.
Data cutoff date: November 1, 2022.
34% of the planned OS events have occurred.
CARTITUDE-1
The efficacy of CARVYKTI was evaluated in CARTITUDE-1 (NCT03548207), an open-label,
single-arm, multicenter trial in adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma, who
previously received at least 3 prior lines of therapy including a proteasome inhibitor, an
immunomodulatory agent, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Patients with known active or prior history of significant central nervous system (CNS) disease,
including CNS multiple myeloma, plasma cell leukemia, allogeneic stem cell transplant within
6 months before apheresis or ongoing treatment with immunosuppressants, creatinine clearance
<40 mL/min, absolute lymphocyte concentration <300/µL, absolute neutrophil count
<750 cells/mm
3
, platelet count <50,000/mm
3
, hepatic transaminases >3 times the upper limit of
normal, cardiac ejection fraction <45%, or with active serious infection were excluded from the
trial.
Of the 113 patients who underwent leukapheresis, 16 patients did not receive CARVYKTI due to
progressive disease (n=2), death (n=9), or withdrawal from study (n=5). There were 97 patients in

35
the efficacy evaluable population who received CARVYKTI, including 17 patients (18%) with
manufacturing failures either because they received CARVYKTI that did not meet product release
specifications for CARVYKTI or received CARVYKTI for which there were insufficient data to
confirm product release specifications for CARVYKTI.
Of the 97 efficacy-evaluable patients, the median age was 61 years (range: 43 to 78 years), 59%
were male, 71% were white, and 18% were black. Most patients (86%) were ISS Stage I or II. Of
the 91 patients for whom baseline cytogenetic data were available, high-risk cytogenetics
(presence of t(4:14), t(14:16), or 17p13 del) were present in 24% of patients. Thirteen percent of
the patients had extramedullary disease.
The median number of prior lines of therapy was 6 (range: 3 to 18), with 82% of patients receiving
4 or more prior lines of therapy, 90% of patients had received prior autologous stem cell
transplantation (ASCT) and 8% of patients received an allogeneic transplant. Ninety-nine percent
of patients were refractory to their last line of prior therapy, and 88% were refractory to a
proteasome inhibitor (PI), immunomodulatory agent, and anti-CD38 antibody.
Most patients (75%) treated with CARVYKTI received bridging therapy for control of their
multiple myeloma during the manufacturing process. The median time from leukapheresis to
product availability was 32 days (range: 27 to 66 days).
The most commonly used agents as bridging therapies (≥20% of patients) included
dexamethasone: 62 patients (64%), bortezomib: 26 patients (27%), cyclophosphamide: 22 patients
(23%), and pomalidomide: 21 patients (22%).
Efficacy was established on the basis of overall response rate, complete response rate and duration
of response as assessed by the Independent Review Committee (IRC) using International Myeloma
Working Group (IMWG) criteria (see Table 9 and 10). The median time to first response was 1
month (range: 0.9 to 10.7 months).
Table 9: Summary of efficacy results for CARTITUDE-1 based on IRC using IMWG criteria
CARVYKTI treated
(N=97)
Overall Response Rate (sCR
a
+ VGPR + PR) n (%)
95 (97.9)
95% CI (%)
(92.7, 99.7)
Stringent complete response (sCR)
a
n (%)
78 (80.4)
95% CI
b
(%)
(71.1, 87.8)
Very good partial response (VGPR) n (%)
14 (14.4)
95% CI
b
(%)
(8.1, 23.0)
Partial response (PR) n (%)
3 (3.1)
95% CI
b
(%)
(0.6, 8.8)
Notes: Based on a median duration of follow-up of 28 months.
a
All complete responses were stringent CRs.
b
Exact 95% confidence interval.
CI=confidence interval; IRC=Independent Review Committee; IMWG=International Myeloma Working Group; NE=not estimable.

36
Table 10: Duration of Response (DOR)
CARVYKTI treated
(N=97)
Duration of Response (DOR)
a
-
Number of responders
DOR (Months):Median (95% CI)
b
95
NE (23.3, NE)
Number of responders with sCR
c
DOR if best response is sCR
c
(Months):Median
(95% CI)
b
78
NE (28.3, NE)
Number of responders with VGPR or better
DOR if best response is VGPR or better (Months):Median
(95% CI)
b
92
NE (24.4, NE)
Notes: Based on a median duration of follow-up of 28 months.
a
The estimated DOR rate was 60.3% (95% CI: 49.6%, 69.5%) at 24 months and 51.2% (95% CI: 39.0%, 62.1%) at 30 months.
b
Kaplan-Meier estimate.
c
All complete responses were stringent CRs.
CI=confidence interval; NE=not estimable.
The IRC assessed overall response in the 113 patients that underwent leukapheresis was 84% (95%
CI: 76, 90) with stringent CR rate of 69% (95% CI: 60, 77), VGPR rate of 12% (95% CI: 7, 20)
and PR rate of 3% (95% CI: 1, 8).
15 REFERENCES
1 Lee DW, Santomasso BD, Locke FL, et al. ASTCT consensus grading for cytokine release
syndrome and neurologic toxicity associated with immune effector cells. Biol Blood
Marrow Transplant 2019; 25: 625-638.
2 National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI
CTCAE) v 5.0; 2017.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
CARVYKTI
®
is supplied in one infusion bag containing a frozen suspension of genetically
modified autologous T cells in 5% DMSO, either as a:
• 70 mL suspension in an infusion bag and metal cassette (NDC 57894-111-01)
or
• 30 mL suspension in an infusion bag and metal cassette (NDC 57894-111-02)
Each CARVYKTI infusion bag is individually packed in an aluminum cryo-cassette.
Match the identity of the patient with the patient identifiers on the cassette and infusion bag upon
receipt.
Store and transport below -120°C, e.g., in a container for cryogenic storage in the vapor phase of
liquid nitrogen.
Store CARVYKTI in the original packaging containing the cassette protecting the infusion bag.
Thaw CARVYKTI prior to infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2)].

37
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Inform patients of the risk of manufacturing failure [18%, (17/97 in the clinical study)]. In case of
a manufacturing failure, a second manufacturing of CARVYKTI may be attempted. In addition,
while the patient awaits the product, additional anticancer treatment (other than lymphodepletion)
may be necessary and may increase the risk of adverse reactions during the pre-infusion period,
which could delay or prevent the administration of CARVYKTI.
Advise patients that they will be monitored daily for the first 10 days following the infusion at a
REMS-certified healthcare facility, and instruct patients to remain within proximity of a certified
healthcare facility for at least 4 weeks following the infusion.
Prior to infusion, advise patients of the following risks and to seek immediate medical attention in
the event of the following signs or symptoms:
Increased Early Mortality
Inform patients of the risk of early mortality. In a clinical study, treatment in the CARVYKTI arm
was associated with a higher rate of death (14%) compared to the control arm (12%) in the first 10
months from randomization. This higher rate of death was observed before receiving CARVYKTI
and after treatment with CARVYKTI. The reasons for death were progression of multiple
myeloma and adverse events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Clinical Studies (14)].
Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
Signs or symptoms of CRS, including fever, chills, fatigue, headache, tachycardia, hypotension,
hypoxia, dizziness/lightheadedness or organ toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2),
Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Neurologic Toxicities
Signs or symptoms associated with neurologic events, some of which occur days, weeks or months
following the infusion including [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Adverse Reactions (6.1)]:
ICANS: e.g., aphasia, encephalopathy, depressed level of consciousness, seizures, delirium,
dysgraphia
Parkinsonism: e.g., tremor, micrographia, bradykinesia, rigidity, shuffling gait, stooped
posture, masked facies, apathy, flat affect, lethargy, somnolence
Guillain Barré Syndrome: e.g., motor weakness and polyradiculoneuritis
Peripheral neuropathy: e.g., peripheral motor and/or sensory nerve dysfunction
Cranial Nerve Palsies: e.g., facial paralysis, facial numbness
Prolonged and Recurrent Cytopenias
Signs or symptoms associated with bone marrow suppression including neutropenia,
thrombocytopenia, anemia, or febrile neutropenia for several weeks or months. Signs or symptoms

38
associated with bone marrow suppression may recur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Adverse
Reactions (6.1)].
Infections
Signs or symptoms associated with infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Adverse
Reactions (6.1)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Signs or symptoms associated with hypersensitivity reactions including flushing, chest tightness,
tachycardia, and difficulty breathing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Secondary Malignancies
Secondary hematological malignancies, including myelodysplastic syndrome, acute myeloid
leukemia, and T-cell malignancies have occurred [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions
(5.10), Adverse Reactions (6.1,6.3)].
Advise patients of the need to:
• Have periodic monitoring of blood counts before and after CARVYKTI infusion [see
Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
• Contact Janssen Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-526-7736 if they are diagnosed with a secondary
malignancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
• Refrain from driving and engaging in hazardous occupations or activities, such as operating
heavy or potentially dangerous machinery, for at least 8 weeks after treatment and in the
event of any new onset of neurologic toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
• Tell their physician about their treatment with CARVYKTI before receiving a live virus
vaccine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Manufactured/Marketed by:
Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Horsham, PA 19044, USA
U.S. License Number 1864
Marketed by:
Legend Biotech
Somerset, NJ 08873, USA
For patent information: www.janssenpatents.com
© Johnson & Johnson and its affiliates 2022-2024

39
MEDICATION GUIDE
CARVYKTI
®
(car-vick-tee)
(ciltacabtagene autoleucel)
Read this Medication Guide before you start your CARVYKTI treatment. The more you know about
your treatment, the more active you can be in your care. Talk with your healthcare provider if you have
questions about your health condition or treatment. Reading this Medication Guide does not take the
place of talking with your healthcare provider about your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about CARVYKTI?
CARVYKTI may cause side effects that are severe or life-threatening and can lead to death. Call your
healthcare provider or get emergency help right away if you get any of the following:
• fever (100.4°F/38°C or higher)
• chills or shaking chills
• fast or irregular heartbeat
• difficulty breathing
• very low blood pressure
• dizziness/light headedness
• effects on your nervous system, some of which can occur days or weeks after you receive the
infusion, and may initially be subtle such as:
o feeling confused, less alert, or disoriented, having difficulty speaking or slurred speech, having
difficulty reading, writing, and understanding words, memory loss
o loss of coordination affecting movement and balance, slower movements, changes in
handwriting
o personality changes including a reduced ability to express emotions, being less talkative,
disinterest in activities, and reduced facial expression
o tingling, numbness, and pain of hands and feet, difficulty walking, leg and/or arm weakness,
and difficulty breathing
o facial numbness, difficulty moving muscles of face and eyes
It is important that you tell your healthcare providers that you have received CARVYKTI and to show
them your CARVYKTI Patient Wallet Card. Your healthcare providers may give you other medicines to
treat your side effects.
What is CARVYKTI?
• CARVYKTI is a treatment used for adult patients who have cancer of the bone marrow called
multiple myeloma. It is used when at least one other treatment has not worked or has stopped
working.
•
CARVYKTI is a medicine made from your own white blood cells, which have been changed
(genetically modified) to recognize and attack your multiple myeloma cells.
Before you receive CARVYKTI tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions,
including if you have:
• Current or past neurologic problems (such as seizures, stroke, new or worsening memory loss)
• Lung or breathing problems
• Heart problems
• Liver problems
• Kidney problems
• A recent or active infection
• Low blood counts
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-
counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.

40
How will I receive CARVYKTI?
• CARVYKTI is made from your own white blood cells, so your blood will be collected by a process
called ‘leukapheresis’ (loo-kah-fur-ee-sis). The procedure can take 3 to 6 hours and may need to be
repeated.
• Your white blood cells are sent to a manufacturing center to make CARVYKTI. It takes about 4-5
weeks from the time your cells are received at the manufacturing site and are available to be
shipped back to your healthcare provider, but the time may vary.
• While CARVYKTI is being made you may get other medicines to treat the multiple myeloma. This
is so that your multiple myeloma does not get worse.
Before you get CARVYKTI, your healthcare provider will give you chemotherapy for 3 days to prepare
your body.
30 to 60 minutes before you are given CARVYKTI, you may be given other medicines. These may
include:
• medicines for an allergic reaction (antihistamines)
• medicines for fever (such as acetaminophen)
When your CARVYKTI is ready, your healthcare provider will give CARVYKTI to you through a
catheter (tube) placed into your vein (intravenous infusion). Your dose of CARVYKTI will be given in
one infusion bag. The infusion usually takes approximately 30-60 minutes.
After getting CARVYKTI, you will be monitored at the certified healthcare facility where you
received your treatment for at least 10 days after the infusion.
You should plan to stay close to the location where you received your treatment for at least 4 weeks. Your
healthcare provider will check to see that your treatment is working and help you with any side effects
that may occur. You may be hospitalized if you develop serious side effects until your side effects are
under control and it is safe for you to leave the hospital.
Your healthcare provider will want to do blood tests to follow your progress. It is important that you have
your blood tested. If you miss an appointment, call your healthcare provider as soon as possible to
reschedule.
What should I avoid after receiving CARVYKTI?
• Do not drive, or operate heavy machinery, or do other activities that could be dangerous if you are
not mentally alert, for at least 8 weeks after you get CARVYKTI. This is because the treatment can
cause memory and coordination problems, sleepiness, confusion, dizziness, seizures, or other
neurologic side effects as discussed by your healthcare provider.
• You must not be given certain vaccines called live vaccines for some time before and after
CARVYKTI treatment. Talk to your healthcare provider if you need to have any vaccinations.
• Do not donate blood, organs, tissues, or cells for transplantation.

41
What are the possible or reasonably likely side effects of CARVYKTI?
The most common side effects of CARVYKTI include:
• fever (100.4°F/38°C or higher), chills
• dizziness or light-headedness
• headache, muscle or joint pain, feeling very tired
• altered mental state, confusion
• infections
• low levels of antibodies (immunoglobulins) in the blood
• cough, being short of breath
• diarrhea, nausea, decreased appetite, constipation
• fast or irregular heartbeat
• problems with blood clotting
In a study comparing CARVYKTI to standard therapy, there was a higher rate of death in the first 10
months in the CARVYKTI arm (14%) compared to the standard therapy arm (12%). The increased rate
of deaths occurred before receiving CARVYKTI and after treatment with CARVYKTI. The reasons for
death were progression of multiple myeloma and side effects of the treatment.
CARVYKTI can cause a very common side effect called cytokine release syndrome or CRS, which can
be severe or fatal. Symptoms of CRS include fever, difficulty breathing, dizziness or lightheadedness,
nausea, headache, fast heartbeat, low blood pressure, or fatigue. Tell your healthcare provider right away
if you develop fever or any of these other symptoms after receiving CARVYKTI.
CARVYKTI can increase the risk of life-threatening infections including COVID-19 that may lead to
death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop fever, chills, or any signs or symptoms of
an infection.
CARVYKTI can cause various neurologic side effects, some of which may be severe or fatal.
Symptoms include but are not limited to confusion, disorientation, loss of consciousness, seizures,
difficulty speaking, reading or writing, tremor, slower movements, changes in personality, depression,
tingling and numbness of hands and feet, leg and arm weakness, and facial numbness.
CARVYKTI can lower one or more types of your blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, or
platelets [cells that help blood to clot]), which may make you feel weak or tired or increase your risk of
severe infection or bleeding that may lead to death. After treatment, your healthcare provider will test
your blood to check for this. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get a fever, chills, or any
signs or symptoms of an infection, are feeling tired, or have bruising or bleeding.
CARVYKTI may increase your risk of getting cancers including certain types of blood cancers. Your
healthcare provider should monitor you for this.
Having CARVYKTI in your blood may cause some commercial Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
tests to incorrectly give you an HIV-positive result even though you may be HIV-negative.
These are not all the possible side effects of CARVYKTI. Call your healthcare provider if you have any
side effects.
You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of CARVYKTI
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. If you
would like more information about CARVYKTI, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your
healthcare provider for information about CARVYKTI that is written for health professionals. For more
information go to www.CARVYKTI.com or call 1-800-526-7736.

42
What are the ingredients in CARVYKTI?
Active ingredient: ciltacabtagene autoleucel
Inactive ingredients: DMSO
Manufactured/Marketed by: Janssen Biotech, Inc., Horsham, PA 19044, USA. U.S. License Number 1864
Marketed by: Legend Biotech, Somerset, NJ 08873, USA. For patent information: www.janssenpatents.com.
For more information, call 1-800-526-7736 or go to www.CARVYKTI.com.
© Johnson & Johnson and its affiliates 2022-2024
This Medication guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: April 2024
