
(2265)
Haryana Government Gazette
EXTRAORDINARY
Published by Authority
© Govt. of Haryana
No. 122–2022/Ext.] CHANDIGARH, FRIDAY, JULY 8, 2022 (ASADHA 17, 1944 SAKA)
HARYANA GOVERNMENT
INDUSTRIES & COMMERCE DEPARTMENT
Notification
The 8th July, 2022
No. 20/01/2022-4IB-I.— The Governor of Haryana is pleased to notify the ‗Haryana Electric Vehicle
Policy-2022‘ which will be effective from 10th of July, 2022 for a period of 5 years. The Haryana Electric Vehicle
Policy-2022 is placed below at Annexure-‗A‘.
The policy has been concurred by the Finance Department vide their U.O. No. 11/02/2022-3FD-
III/2022/14630 dated 24.06.2022 and approved by the Council of Ministers in its meeting held on 27.06.2022.
VIJAYENDRA KUMAR,
Chandigarh: Principal Secretary to Government of Haryana,
The 8th July, 2022. Industries & Commerce Department.

2266 HARYANA GOVT. GAZ. (EXTRA.), JULY 8, 2022 (ASAR. 17, 1944 SAKA)
HARYANA ELECTRIC VEHICLE POLICY
1. Introduction
The number of vehicles in Haryana has been increasing rapidly over the last decade. However, vehicles driven
on fossil fuels are a major source of environmental pollution and pose serious health hazards and the stocks of fossil-
fuels are fast depleting across the globe. The situation demands that alternative clean, eco-friendly technologies be
explored for running of vehicles.
Haryana Government aims to contribute to improve the environment, reduce carbon footprints and
aggressively motivate the citizens to buy Electric Vehicles through this policy. The Government of India has also
launched ―The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles in India (FAME Scheme I and II)‖ scheme in
2015 which has been extended subsequently in 2019, under National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) with
the aim to promote eco-friendly electric vehicles in the country.
The Haryana Electric Vehicle Policy focuses on following aspects:
Encourage and incentivize Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles, major components of EVs, batteries for
EVs in Haryana and thereby reducing cost of doing business.
Develop charging infrastructure and strengthen e-mobility in the State
Human Capital development
Promote green automotive technology
Promote Research and Development (R&D) on various aspects of electric mobility i.e., manufacturing,
developing prototype vehicles, innovation in the field of battery manufacturing, etc.
This policy places a special emphasis on the creation of end-to-end ecosystem for E-Mobility in the
state and envisages at harnessing Haryana‘s inherent strength in automotive manufacturing sector for supporting
Electric Vehicle manufacturing and adoption within the state.
2. Objectives
i. To promote clean transportation by promotion of use of Electric Vehicles (EVs) in the State.
ii. To make usage of Electric Vehicles affordable and easy, by setting up of a widespread and accessible
charging infrastructure.
iii. To make Haryana a global hub for manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (EVs), major components of
EVs and batteries for EVs.
iv. To generate employment opportunities in the State.
v. To promote Research and Development (R&D) on various aspects of electric mobility.
3. Eligibility
i. This policy shall come into effect on the date of its notification in the Official Gazette of Government
of Haryana.
ii. This policy is applicable to ―new‖ and ―existing‖ units anywhere in B, C, and D blocks and / or in
Govt. approved Industrial Estates / IMTs in Block A.
iii. Existing units desirous of claiming incentives under this policy shall have to comply with the
following:
a. Existing units undertaking expansion / diversification / complete conversion anywhere in B, C,
D category blocks and / or in Govt. approved Industrial Estates / IMTs in Block A
b. Units with an additional investment of at least 50% of FCI (of the already established unit) in
EV sector
c. Units converting completely into EV/EV component/ EV Battery manufacturing
iv. The policy incentives will be available for manufacturers of EV (BEV and FCEV) and Hybrid EV
(PHEV and SHEV); EV components, individual buyers and enterprises setting up charging
infrastructure as defined in clause 4 and detailed in clause 5, 6 and clause 8 of this policy.
v. Large and Mega units shall compulsorily establish a battery disposal/recycling/material recovery
facility at their proposed plant for claiming any incentive under this policy.

HARYANA GOVT. GAZ. (EXTRA.), JULY 8, 2022 (ASAR. 17, 1944 SAKA) 2267
Note
Units availing a particular incentive under this policy will not be eligible to avail similar incentive under
similar head as given in any other Haryana Government policy. However, such units will be eligible for other
incentives not specified in this policy. All incentives specified in this policy (excluding buyer incentives) may
be availed in addition to incentives available under any Government of India scheme/policy. The maximum
limit of the sum of all fiscal incentives shall not exceed 100% of Fixed Capital Investment (FCI) for
manufacturers and owners of Public Charging Station/Swapping Station or 100% of ex-showroom price of the
vehicle for buyers.
4. Definitions
i. Electric Vehicle: Electric Vehicle (EV) refers to automobiles powered by a battery and an electric
motor, including battery electric vehicles (BEV) and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV).
ii. Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV): A vehicle which is powered exclusively by an electric motor; whose
traction energy is supplied exclusively by traction battery installed in the vehicle; and has an ‗Electric
Regenerative Braking System‘.
iii. Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle: Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) use a propulsion system like that of
electric vehicles, where energy stored as hydrogen is converted to electricity by the fuel cell.
iv. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV): A vehicle that for the purpose of mechanical propulsion draws
energy from both of the following on-vehicle sources of energy/power:
A consumable fuel
Rechargeable Energy Storage System (ReESS)
v. Strong Hybrid Electric Vehicle: Strong Hybrid Electric Vehicle (SHEV) is a HEV which has an
engine ‗Stop-Start‘ arrangement, ‗Electric Regenerative Braking System‘ and a ‗Motor Drive‘ (motor
alone is capable to propel/drive the vehicle from a stationary condition)
vi. Plug-in Hybrid Electric vehicle: PHEV is a type of ‗Strong Hybrid Electric Vehicle‘ which has a
provision for ‗Off Vehicle Charging‘ (OVC) of ‗Rechargeable Energy Storage System (ReESS)‘.
vii. Electric Regenerative Braking System: An integrated vehicle braking system which provides for the
conversion of vehicle kinetic energy into electrical energy during braking.
viii. Engine ‘Stop-Start’ arrangement: A system by which the engine is started or stopped in a hybrid
electric vehicle by vehicle control unit at operating conditions depending upon traction power required
for the propulsion of the vehicle.
ix. Off Vehicle Charging (OVC): Rechargeable Energy Storage System (ReESS) in the vehicle has a
provision for external charging.
x. EV Components: Components of EV will include Motor Controller, Electric Engine (motor) for EV,
Regenerative Braking System, Drive System for EV/FCEV/SHEV, Batteries and Cells (Li-ion, hydrogen
or other hi-tech cells) that can be used in EV/FCEV, Battery Management System (BMS), Electric Power
Control Unit (EPCU), Battery Heating System, On-board Charger (OBC), Electric Traction Motors and
controllers, EV Power Train Components, Components related to transmission mechanism, Traction
battery pack, Low Voltage DC-DC Converter(LDC), Power inverter, Vehicle control unit (VCU), EV
Charge Port, Fuel Cell Control Unit, Anode Recirculation Blower for FCEV, Hydrogen gas injector for
Hydrogen Fuel cells, Humidifier/stack Bypass Valve, Stack-isolation and Control Valve for Hydrogen
fuel cells etc.
xi. Charging/Battery equipment: Equipment that is exclusively used to charge the batteries of
BEV/PHEV/SHEV. This equipment can be installed at existing fuel stations or separate charging or
battery swapping stations.
xii. Privately owned public charging station: A dedicated charging station owned by a private entity that
is used for charging personal EV or EV fleet and can be installed at independent homes, group
residential buildings, offices, public places or dedicated parking land which can be self-operated or
CPO-managed (Charged Point Managed for EV fleet charging). The charging stations shall adhere to
the norms laid by Ministry of Power (MoP)
xiii. Electric Mobility Ecosystem: This policy addresses various components and end products of the
electric mobility ecosystem. Such an ecosystem encompasses the ―Electric Vehicles and components
such as Lithium-Ion Batteries (or other advanced batteries with comparable energy/power densities),
Super capacitors, Fuel cell systems, EV Charging equipment, Hydrogen generation, storage and
refueling equipment, Battery swapping equipment, EV Motors & Controllers and other EV powertrain
components, Battery management systems, EV electronics, electric harness etc. integral to the
functioning of an EV.‖

2268 HARYANA GOVT. GAZ. (EXTRA.), JULY 8, 2022 (ASAR. 17, 1944 SAKA)
Other Important definitions
i. Fixed Capital Investment (FCI): Fixed Capital Investment refers to Land, Building and Plant &
Machinery, as specified in the policy / the schemes to be notified under the policy.
ii. Ultra-Mega Project: Project having minimum Fixed Capital Investment of INR 6000 crore in A
Blocks, INR 4,500 crore in B Blocks, INR 3,000 crore in C Blocks and INR 1,500 crore in DBlocks.
iii. MegaProject:Project having minimum Fixed Capital Investment(FCI) of INR 200 crore in Govt.
approved Industrial Estates/IMTsin Block Aandallare as under B Blocks, FCI of over INR 100 crore in
C Blocks and FCI of over INR 75 crore in D Blocks. [Mega and Ultra Mega units setting up in the
State shall also be eligible for a special package of incentives as per HEEP 2020 and future Haryana‘s
Flagship Industrial Policy (if and when released)]
iv. Large Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery greater than INR 50 crore and turnover greater
than INR 250 crore (over and above the of limit of Medium units as defined under the MSMED Act,
2020 or amended by GoI from time to time).
v. Medium Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed INR 50 crore
and turnover does not exceed INR 250 crore as defined under the MSMED Act, 2020 or amended by
GoI from time to time.
vi. Small Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed INR 10 crore and
turnover does not exceed INR 50 crore as defined under the MSMED Act, 2020 or amended by GoI
from time to time.
vii. Micro Enterprise: Investment in Plant and Machinery or Equipment does not exceed INR 1 crore and
turnover does not exceed INR 5 crore as defined under the MSMED Act, 2020 or amended by GoI
from time to time.
5. Incentives for Manufacturers
Manufacturers of Electric (EV, BEV, FCEV) vehicles, charging infrastructure and EV/Hydrogen/Charging
infrastructure component manufacturers shall be eligible for incentives as mentioned below. Manufacturers
producing components intended to be used exclusively for electric vehicle &EV charging infrastructure shall
only be considered for following incentives under this policy:
a. Capital subsidy of Fixed Capital Investment (FCI)
Capital subsidies will be provided to industries manufacturing Electric Vehicles (BEV/FCEV), major
components of EVs, batteries for EVs, manufacturer of charging infrastructure:
S.No.
Industry
Subsidy
No. of beneficiaries
1.
Micro
Industry
25% of FCI or
INR 15 lakh,
whichever is
lower
First 20 units in each segment of electric vehicles
(2 wheelers, 3 wheelers, 4 wheelers, buses/Heavy Vehicle)
battery and charging equipment
2.
Small
Industry
20% of FCI or
INR 40 lakh,
whichever is
lower
First 10 units in each segment of electric vehicles
(2 wheelers, 3 wheelers, 4 wheelers, buses/Heavy Vehicle)
battery and charging equipment
3.
Medium
Industry
20% of FCI or
INR 50 lakh,
whichever is
lower
First 5 units each in each segment of electric vehicles
(2 wheelers, 3wheelers, 4 wheelers, buses/Heavy Vehicle)
battery and charging equipment
4.
Large
Industry
10% of FCI or
INR 10crores,
whichever is
lower
For first 2 units in each segment of electric vehicles
(EV) (2 wheelers, 3 wheelers, 4 wheelers, buses/Heavy
Vehicle), battery and charging equipment
5.
Mega
Industry
20% of FCI or
INR 20crore
whichever is
lower
For first 3 units in the state
*Mega or Ultra mega units setting up in the State will be
also eligible for a special package of incentives as per
HEEP 2020
In order to promote circular economy and responsible disposable of batteries, first 5 units setting up
their manufacturing facility in the state across Medium, Large or Mega category for battery
disposal/recycling/ material recovery shall be eligible for capital subsidy @ 15% of FCI or INR 1.00
crore whichever is lower.

HARYANA GOVT. GAZ. (EXTRA.), JULY 8, 2022 (ASAR. 17, 1944 SAKA) 2269
b. Seed and Conversion Fund
One-time support as a seed funding for existing units converting completely into EV manufacturing
(BEV/FCEV), EV component manufacturing or EV Battery manufacturing @ 25% of the book value
of plant and machinery during the year of application for Micro, Small, Medium, and Large units or IN
2 crore whichever is lower. This will be available for early adopter units under each category as below:
S.No.
Type of unit
Maximum Number of Early adopter units
1
Micro units
First 30 units
2
Small units
First 15 units
3
Medium units
First 15 units
4
Large units
First 15 units
c. Net SGST reimbursement
Net SGST reimbursement for micro, small, medium, large, and mega industries manufacturing Electric
Vehicles, major components of EVs, batteries for EVs shall be as below:
i. Allunitswouldbeallowedreimbursementof50%oftheapplicableNetSGST for a period of 10 years
or up to realization of fixed capital investment whichever is earlier.
ii. In case, where Net SGST deposit under cash ledger is less than 5% of FCI in a year or project
having inverted duty, the Investment subsidy up to 5% of FCI may be given for a period of
8 years in equal installments subject to annual ceiling of INR 5 crore for mega units.
Note: Units availing capital subsidy as in the clause 5.a. shall not be eligible for benefits under
clause 5.c.
d. Reimbursement in Stamp Duty
Reimbursement of 100% stamp duty on purchase /lease of land/shed/buildings to be used for
manufacturing Electric Vehicles, major components of EVs, batteries for EVs and charging
infrastructure after commencement of commercial production. Subsequent transactions on same
property will not be eligible for this reimbursement.
e. Power subsidy and incentives:
i. The Government shall provide special tariff to the units manufacturing electric vehicles, major
components of EVs, batteries for EVs and charging infrastructure as announced by Haryana
Electricity Regulatory Commission every year.
ii. 100% exemption on Electricity Duty for a period of 20 years. For units producing captive
power, the exemption shall be limited to the power consumed for its own operation only, but not
sold to other business entities/private companies/PSUs/DISCOMs/etc. In case of the expansion /
diversification of the existing units, a mechanism shall be made to exempt electricity duty in lieu
of incremental consumption of Power.
iii. Power utilities shall provide uninterrupted 24x7 quality power to all units involved in
manufacturing Electric Vehicles, major components of EVs, batteries for EVs and charging
infrastructure.
f. Water treatment plant incentives
In order to promote water recycling for manufacturing plant, the Haryana Government shall reimburse
50% of the cost of water treatment plant up to INR 50 lakh for first 5 units in each category (Medium,
Large, Mega and Ultra-Mega units).
g. Patent Fee
Financial support by reimbursement of 100% of the actual expenses (including filing fees, consultancy
fees, search fees, maintenance fees and Publishing fees) with a maximum of INR 25 lakh for domestic
and international patent registrations for manufacturing units falling under eligibility of this policy.
h. Employment Generation Subsidy
Employment generation subsidy shall be extended to manufacturing units established only in B, C and
D category blocks, for capacity building of persons belonging to Haryana (skilled/semi-skilled/un-
skilled) [having Haryana Resident Certificate], Subsidy @ INR 48,000/- per employee per annum for
10 years for direct employment on pay roll or contract with valid ESI/PF Number. As per the Haryana
State Employment of Local Candidates Act, 2020 amended from time to time, units shall mandatorily
employ at-least 75% of Haryana Domicile workforce, to be able to receive the employment incentive.

2270 HARYANA GOVT. GAZ. (EXTRA.), JULY 8, 2022 (ASAR. 17, 1944 SAKA)
6. Incentives for Buyers
a. Purchase Incentive
There are individual benefits extended to buyers of EV under Government of India‘s FAME India
scheme Phase II. In the categories covered under FAME Phase II Scheme, individuals would receive
benefits from Government of India. The Haryana Government shall provide benefits to category of
vehicles not covered under FAME-II scheme or any other similar incentive provision announced from
time to time by Government of India within the policy period.
Buyers of Electric Vehicle shall be provided with one-time Purchase Incentive to individuals within
policy period as below:
S.No
.
Vehicle Category
Incentive
1.
Electric Car/Light
EV(BEV/FCEV) ranging from
price of INR15.00 lakh to INR
40.00 lakh
First 1000 units purchased and registered in the state shall
receive purchase incentive of 15% of the ex- showroom
price of vehicle maximum up to INR 6.00 lakh.
2.
Hybrid Electric Car/ Hybrid
Light EV (SHEV/PHEV)
ranging from INR 15.00 lakh to
INR 40.00 lakh
First 200 units purchased and registered in the state shall
receive purchase incentive of 15% of the ex- showroom
price of vehicle maximum up to INR 3.00 lakh.
3.
Electric Car/Light
EV(BEV/FCEV) ranging from
price of INR 40.00 lakh to INR
70.00 lakh
First 1000 units purchased and registered in the state shall
receive purchase incentive of 15% of the ex- showroom
price of vehicle maximum up to INR 10.00 lakh.
4.
Hybrid Electric Car/ Hybrid
Light EV (SHEV/PHEV)
ranging from INR 40.00 lakh to
INR 70.00 lakh
First 200 units purchased and registered in the state shall
receive purchase incentive of 15% of the ex- showroom
price of vehicle maximum up to INR 5.00 lakh.
5.
Hydrogen based vehicle
First 200 units purchased and registered in the state shall
receive purchase incentive of 15% of the ex- showroom
price of vehicle maximum up to INR 10.00 lakh.
6.
Electric Tractors for farmers
First 1000 units purchased and registered in the state shall
receive purchase incentive of 50% of the ex- showroom
price of vehicle up to INR 5.00 lakh.
7.
Hybrid Electric tractor for
farmers
First 100 units purchased and registered in the state shall
receive purchase incentive of 50% of the ex- showroom
price of vehicle up to INR 5.00 lakh.
8.
Electric Bus
First 200 units purchased and registered in the state shall
receive purchase incentive of 10% of the ex- showroom
price of vehicle up to INR 10.00 lakh.
*Incentives of 100 Electric buses shall be reserved for
buses used by government and government owned entities
of Haryana.
Note: Government may revise the Incentive and target number of vehicles from time to time as
required for a response to emerging market and technology landscape.
b. Exemption in Motor Vehicle Tax
Exemption of Motor Vehicle Tax under Haryana Motor Vehicle Tax Act, 2016 for electric vehicles will
be as follows:
S.No.
Vehicle Category
Rate of Tax exemption
1
Electric 2-wheeler
100% exemption on Motor Vehicle Tax for vehicles purchased
and registered in Haryana during policy period for first 30,000
vehicles
2
Electric 3-wheeler
100% exemption on Motor Vehicle Tax for vehicles purchased
and registered in Haryana during policy period for first 15,000
vehicles
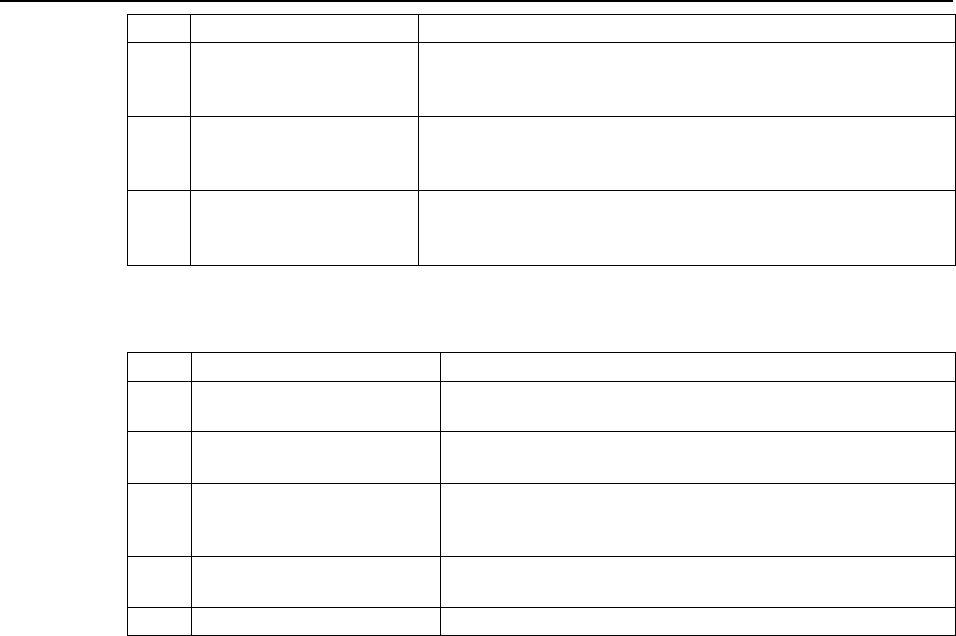
HARYANA GOVT. GAZ. (EXTRA.), JULY 8, 2022 (ASAR. 17, 1944 SAKA) 2271
S.No.
Vehicle Category
Rate of Tax exemption
3
Electric 4-wheeler /
Hydrogen fuel-based
Vehicle (FCEV)
75% exemption on Motor Vehicle Tax for vehicles purchased
and registered in Haryana during policy period for first 10,000
vehicles
4
Hybrid electric 4-wheeler
25% exemption on Motor Vehicle Tax for vehicles purchased
and registered in Haryana during policy period for first 2,500
vehicles
5
Electric buses
75% exemption on Motor Vehicle Tax for vehicles purchased
and registered in Haryana during policy period for first 1,000
vehicles
c. Vehicle Registration Fee
All Electric vehicles, Hybrid Electric vehicles or Hydrogen Electric Vehicles purchased and registered
in Haryana during policy period shall be charged the following discounted registration fee:
S.No.
Vehicle Category
Registration Fee
1
Electric 2-wheeler
INR 200 for all category two wheelers for first 30,000
vehicles
2
Electric 3-wheeler
INR 200 for all category three wheelers for first 15,000
vehicles
3
Electric 4-wheeler /
Hydrogen fuel-based Vehicle
(FCEV)
INR 500 for all category four wheelers for first 10,000
vehicles
4
Hybrid electric 4-wheeler
INR 500 for all category hybrid four wheelers for first 2,500
vehicles
5
Electric buses
INR 500 for all category buses for first 1,000 vehicles
7. Development of EV Charging Infrastructure
Government of Haryana shall ensure availability of adequate charging infrastructure in the State and undertake
the following initiatives:
i. Department of Town and Country Planning (TCP) shall mandatorily include the provisions for
charging stations / charging infrastructure for facilitating charging of electric vehicles in places such as
Group Residential buildings, commercial buildings, institutional buildings, Malls, Metro Station etc.,
and to amend The Haryana Building Code, 2017 accordingly.
ii. Department of Town and Country Planning (TCP) shall also support and motivate existing Group
Residential buildings, commercial buildings, institutional buildings, Malls, Metro Station etc. to have
adequate space reserved for developing charging infrastructure.
iii. Department of Town and Country Planning (TCP) shall also provide provision of setting up charging
infrastructure to promote EV usage and adoption in Green Belts.
iv. Charging infrastructure shall be developed in all existing and new public buildings, public parking
places, all bus depots / sub-depots of State Transport Undertakings
v. Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs) shall be encouraged to set-up charging infrastructure in the State
within their premises and at public areas.
vi. Privately owned public Charging Stations: The State Government shall encourage private players to set
up Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations and infrastructure in the state.
vii. All new and existing petrol pumps shall be encouraged to have charging stations and battery banks
depending upon demand and viability.
viii. Fast charging stations and battery swapping infrastructure shall be provided on highways and other
prominent roads within every 30 km.
ix. State Government will encourage oil companies (like IOCL, HPCL, IGL, EESL etc.) to invest in
providing a charging network, specially the fast-charging stations at inter-city routes like state and
national highways and in cities.
x. The companies installing Public Charging Station shall also be encouraged to set up battery swapping
stations with due intimation to the Distribution Licensee. The rebate on electricity tariff applicable for
Public Charging Stations shall also be applicable to Battery Swapping Stations.

2272 HARYANA GOVT. GAZ. (EXTRA.), JULY 8, 2022 (ASAR. 17, 1944 SAKA)
xi. Electricity Distribution companies shall be encouraged to propose capital Investment Plan for
upgrading its network for accommodating charging infrastructure to facilitate smooth and efficient
charging at respective charging stations. The capital investment plan shall be prepared after rigorous
discussions with investor/stakeholders/private players who are keen to set up charging station in the
license area of the Electricity Distribution company.
xii. Solar Power based Charging Stations will be promoted within the State. State Government will provide
applicable incentives for open access charges to the E-Vehicle Charging Stations with rooftop/ground
mounted solar power generation facility.
8. Incentives for Privately owned Public Charging Stations/Privately owned Battery Swapping Station
The following incentives will be for the areas other than FAME II (or FAME III or similar approved cities, if
applicable in future within the policy period):
i. One time subsidy of 20% of Fixed Capital Investment (FCI) up to INR 10 lakh for first 100 Battery
Swapping Stations set up with FCI of more than INR 50 lakh
ii. One time subsidy of 20% of the Fixed Capital Investment (FCI) maximum upto INR 5 lakh for first
200 privately owned public charging stations setup with FCI of more than INR 25 lakh
iii. One time subsidy of 20% of Fixed Capital Investment (FCI) up to INR 50,000 for first 2,000 privately
owned public charging stations to be established in Group Residential buildings, commercial buildings,
institutional buildings, Malls, Metro Station etc. with more than 1,000 inhabitants or that cater to more
than 1,000 people per day. Such residential buildings, office buildings, malls, metro stations, or others,
shall have at least 10 charging units in the designated area. The charging units shall be maintained
appropriately to cater to public demand.
9. Human Capacity Building
Training for various skill developments to the stake holders will be arranged and Industrial Training Institutes
will conduct courses for the repair of electric vehicles. Information Education Communication (IEC) plan will
also be prepared by HAREDA for wide scale public awareness.
In order to provide sufficient skilled employees to the manufacturers of Electric Vehicles in the State, Govt.
organizations / PSU/ private companies shall be encouraged to set up Centres of Excellence (CoE). Five such
CoEs shall be incentivized with a 50% grant of project cost up to INR 5 crore. CoE shall utilize 50% of the
grant in setting up of the CoE and the remaining 50% of the grant shall be used for running operations of the
CoE. The grant shall be released in 5 equal annual installments.
State Government shall also encourage skill development and training programmes for youth as per National
Skill Development Corporation Guidelines released by Government of India from time to time. Incentives
from Government of India can be availed by training institutes and EV manufacturing units providing job
linked trainings.
10. Research and Development
Research and development in the field of e-mobility in co-ordination with State/National or International level
Organizations will be promoted by the State Government. The following incentives shall be provided for
Research & Development:
i. Educational or Research Institutes setting up R&D centers shall be provided subsidy @50% of project
cost up to INR 1 crore for developing new electric charging technology for first 5 units and up to INR 5
crore for developing new electric vehicle technology for first 5 units as per selection of best proposals
by the state government in the policy period.
ii. First 10 Research Institutes / research centers conducting dedicated research on non-fossil-fuel based
mobility solution will be provided with INR 5 crore incentive for developing new technology as per
selection of best proposals by the state government in the policy period.
iii. Additional one-time subsidy of INR 25 lakh will be extended to first 20 college / ITI/ Polytechnic for
setting up of infrastructure related to R&D under EV segment.
11. Demand Creation
The Government Departments/Corporations shall provide leadership in the use of Electric Vehicles to create
the initial demand and to build confidence amongst buyers for buying and using Electric Vehicles. NRE
Department/HAREDA will be the coordinating agency for facilitating the deployment of e-vehicles by
adopting viable business models (lease based/ outright purchase/ any other feasible model) by different
Government Departments/Organizations. The following steps shall be taken by concerned departments:
i. The year of notification of this policy, shall be announced as the ―Year of the Electric Vehicle‖ in
Haryana.

HARYANA GOVT. GAZ. (EXTRA.), JULY 8, 2022 (ASAR. 17, 1944 SAKA) 2273
ii. Due consideration will be given to Electric Vehicles while hire / purchase of new vehicles by the
Government Departments of corresponding class/category as available in the market.
iii. Multiple Government offices and public areas will be chosen for installing public charging equipment
that can be used publicly.
iv. The cities of Gurugram & Faridabad will be declared as model Electric Mobility (EM) cities with
phase-wise goals to adopt Electric Vehicles (EVs), charging infrastructure to achieve 100% e-mobility.
v. Model Electric Mobility cities shall convert 100% of all commercial passenger carrying vehicles to
electric vehicles. These vehicles can belong to any government organization, State Transport
Undertakings, educational institutes, hospitals or corporations and other institutions. Panchkula,
Karnal, Gurugram & Faridabad will be the pilot cities for all new initiatives. Efforts will be taken to
phase out all fossil fuel based commercial passenger carrying vehicles in Gurugram and Faridabad by
2030.
vi. Efforts shall be made to convert 100% of bus fleet owned by Haryana State Transport Undertakings
into electric buses or Fuel Cell Vehicles or other non- fossil-fuel-based technologies by 2030. In this
regard, department shall convert 10% of existing bus fleet within next 2 years of launch of EV policy in
First Phase. Department shall convert 50% of bus fleet in Second Phase by 2026 and eventually, 100%
conversion of bus fleet shall be achieved in Third Phase by 2030.
vii. Efforts shall be made to convert all forms of Government vehicles, including vehicles under
Government Corporations, Boards and Government Ambulances etc., to electric vehicles in two phases
i.e., 50% by 2026 and in rest of the State by 2030.
12. Awareness
Awareness will be created among public to enhance the use of Electric Vehicle (EV). Test rides in
collaboration with various vehicle manufacturers, will be promoted to take the new technology to the common
man. Various state Departments will provide volunteers for the campaigns on demand basis. The state shall
also support the Bureau of Energy Efficiency in the ―Go Electric‖ awareness campaign at the state level for
creating awareness via print media.
Capacity building among local officials will be essential to increase awareness and knowledge of requirements
for EV and the charging infrastructure in the state. Awareness and orientation workshops shall be undertaken
focusing on a target audience.
13. Period of Policy
The policy shall be valid for a period of 5 years from the date of notification of this policy in the official
gazette.
*****************
9739—C.S.—H.G.P. Pkl.
