
74 Volume 4, Number 3
Exploring the Business Potential of Chipotle
Mexican Grill's Expansion in China
By Bel Wang
case study
Introduction
Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. is an American restaurant chain with
a high reputation for quality good-tasting food. Currently Chipotle
has expanded to other countries such as the United Kingdom, Canada,
and France (Jones et al, 2009). Chipotle’s main products are burritos,
burrito bowls, tacos, and salads. The products are assembled based on
the customer’s preferences using a wide variety of meats, sauces, and
vegetables (University of Oregon Investment Group, 2012). Chipotle
oers naturally raised meat and supports sustainable agriculture. As
one of the rst chains to successfully develop fast casual dining ser-
vice, Chipotle focuses on its mission of oering “Food with Integrity”
(Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. 2012). Chipotle supports its mission by
continuing to oer consumers organic and fresh ingredients (Chipotle
Mexican Grill, Inc. 2012).
The success of Chipotle has grown at an amazing rate since Steven
Ells founded the rst Chipotle in 1993. By 2012, Chipotle Mexican Grill
became a household name, gaining popularity at a steady pace. This
year alone, Chipotle has generated approximately $280 million in net
income, and employs roughly 37,000 employees (Chipotle Mexican
Grill, Inc. 2012). Chipotle became a publically traded company in the
beginning of 2006. Soon after, its stock value rose 100% within one day.
Today, the price of Chipotle’s stock remains around $400.00, which is
tenfold compared to the price in 2006 (Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. 2012).
Huge Potential in China's Market
Most U.S. restaurant chains are seeking growth in international
markets whose middle class consumers are increasing, based on 2009
Data monitor report. China is proved to be an ideal choice for such as
one of the biggest developing countries. It has 1.3 billion dense popula-
tion, among which the middle working class in enlarging—fast, healthy,
convenient eating experience which Chipotle can provide is also what
Chinese middle class and white-collar workers are seeking for. China’s
market can provide further global expansion opportunities for Chipotle.
Chipotle has gained abundant capital and popular presence in
most states in the U.S. and while it has already expanded so much
within the American domestic market in recent years, there is smaller
development space for Chipotle to grow in this market. To sustain its
continued expansion and development, Chipotle has focused its at-
tention on the global scale and has successfully opened restaurants
in several European countries and Canada. However, Chipotle does
not currently have a plan to develop its business in China’s market yet.
Considering many other U.S. fast service restaurant chains have gained
sizeable prots in China, Chipotle could also further explore its oversea
growth ability in China’s market.
Business Plan
Objectives:
• To establish two to ve company-owned Chipotle Mexican Grill
restaurants in Beijing.
• To advertise Chipotle’s brand and improve customer satisfac-
tion and loyalty in China.
• To expand into at least ten outlets in three years and chose a
model for further expansion: Self-owned or franchising.
Mission
The mission of this plan is to help Chipotle Mexican Grill become
the rst and the most popular Mexican fast and causal restaurant
chain in China, targeting at the younger generation, white-collar work-
ers and the middle class. In the beginning stage, Chipotle shall focus
on enlarging potential customers and establishing a close relationship
with local government. In the growth stage, opening more outlets
and exploring diverse sales channels are crucial. Overall, maintaining a
high reputation and distinguished public relation are the primary mis-
sions of Chipotle China.
Keys to Success
• Location.
To ensure the popularity of CMG’s fast and casual dining style in
China’s market, its target customer should be younger generation,
from students to white-collar middle class workers. Therefore locations
near school and oce building would be spots of interest to get prox-
imity to target customers.
• Sustainable food supply chain and high-quality ingredients.
A huge kitchen backup and several logistics centers are needed
for Chipotle to ensure food freshness and the abundant supply of
ingredients. Locally sourced ingredients can be a wise choice for both
cutting purchasing expenditures and maintaining close local relation-
ship. Chipotle shall also monitor its purchasing process to ensure
obtaining high-quality ingredients.
Bel Wang is aliated with the University of Delaware.

75
Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Cases
• Reasonable pricing and meal strategy.
The target customers of Chipotle China are youth oce workers
who has limited lunch time (0.5-1hr) in regular business days but who
want a fast and healthy lunch at an aordable and appropriate price.
As a result, it is suggested to oer multiple set meals which are quick
to service, varied enough to be chosen from and can signicantly in-
crease customers’ repeat visit rate.
• Comprehensive advertising and promotion strategy.
Chipotle shall eectively advertise and promote Mexican cuisine
to Chinese customers to let them warm up to its dinning style. Instruc-
tions on how to order a meal in store could familiarize them with the
self-selecting fast-casual dining style. It is necessary for Chipotle to
launch eective in-store customer trainings as well as to oer discount
and coupon strategies to stimulate customers’ motivation.
• Measure global and local environment.
Business environments, policies, purchasing power, government
regulation, and customers’ taste are vastly dierent between the U.S.
and China. This dynamic and uncertain environment could be ex-
plored eciently for Chipotle’s advantage if proper methodology are
adopted. Co-alignment model outlines the exact necessary strategy
Figure 1
Olsen, Strategic Management, P 3-7
to make the most eective use of core resources and capabilities that
are durable for CMG to survive and thrive in the long term in Chinese
market. As showed below:
When making strategic choice, CMG can refer co-alignment prin-
ciple to achieve their objectives. According to Olsen et al., the concept
of strategy choice suggests that management is constantly engaged
in making choices about how to compete. It is therefore important to
adopt appropriate environment-measuring strategy—maintain CMG’s
core Mexican ingredients, meanwhile deliver localized meal combos
that both keep the company concept and adapt to Chinese taste; nur-
ture a good public relationship with the government and residents is
also necessary for its market advantage.
Market Analysis and Strategies
1. SWOT analysis of Chipotle China
Strengths:
• High position as a famous and well regarded U.S. chain
brand with highly regarded brand image;
• Mature restaurant chain operation and brand manage-
ment methods;
• The menu variety provides wide choices for customers
with dierent tastes;
• The spicy taste of Chipotle Mexican Grill ts in most Chi-
nese tastes.
• Fast, healthy, low-cost eating experiences ts in the life-
style of modern Chinese, specically:
• Convenient food packaging increases the number of
deliveries;
• Eective order line can serve more customers in
high trac time;
• Aordable price can attract students, blue-and-
white collar workers, and middle class.
Weaknesses:
• Chipotle and China’s market are not familiar with each other;
Figure 2
Blue and Red Ocean Strategy
Blue Ocean Strategy Red Ocean Strategy
- Create uncontested market space - Compete in existing market space
- Make the competition irrelevant - Beat in competition
- Create and capture new demand - Exploit existing demand
- Break the value-cost trade o - Make the value-cost trade o
- Align the whole system of a rm’s activities in pursuit of
dierentiation and low cost
- Align the whole system of a rm’s activities with its strategic choice
of dierentiation or low cost
Source From: Blue Ocean vs. Red Ocean (W. Chan, 2005)

76 Volume 4, Number 3
• Chipotle needs to build brand awareness and local rela-
tionships;
• Further expansion in China can be time-consuming.
Opportunities:
• China’s continued development and ever-expanding
middle class provide a large demand for healthy, reason-
able-priced quick-service food;
• Many potential locations for Chipotle’s outlets in China;
• Increasing purchasing power and dense population in
China’s market lays the foundation for high prots;
• Developed agriculture in China provides abundant high-
quality suppliers with cheaper prices;
• China can act as a platform to support further Asian ex-
pansion, such Japan and South Korea.
Threats:
• A number of competitors, such as foreign and Chinese
fast-food restaurant chains;
• Food safety and public boycott;
• As the rst Mexican fast casual restaurant in China, Chi-
potle can refer to no previous business models or cases,
yielding high unpredictability.
2. Blue Ocean in China’s market
Admittedly Beijing and Shanghai have witnessed Tex-Mex and
Mexican restaurants sprouting in the market including MAYA
and Pistolera. Whilst there has no current Mexican quick-service
fast food chains prevalent. Once Chipotle enters China’s market,
it thus will be the rst U.S. chain restaurant oering Mexican fast-
causal food in China’s market. As a “blue ocean” for such dinning
concept, China oers more opportunities for Chipotle’s growth.
The “Blue Ocean and Red Ocean concept” can be referred below:
3. Distribution Strategy
High quality, responsibly produced but reasonably priced in-
gredients are vital to Chipotle’s revenue and philosophy. Thus
Chipotle China shall pursue direct distribution to customers,
avoiding using a separate distributor channel. Local sourcing is
recommended for the supply chain management because not
only does it foster local economic growth, which in return helps
Chipotle build stable relationships with locals and the govern-
ment, but also deduces transportation costs. Chipotle shall
therefore adopt reputable local suppliers who oer farm-fresh
meat and produce and consider to use supplier rating system
to rate the cost, speed, and quality of the ingredients delivered
by dierent suppliers, and select highest rated ones for long-
term business relationship.
4. Advertising strategies
Eective promotion strategies can help Chipotle China create
and reinforcing customers’ brand awareness, which including
location choice, outbound and inbound advertising. Aside
from above-discussed location selection, outbound methods
such as billboards, posts, and newsletters surrounding its store
can also greatly attract public attention. Meanwhile it is highly
recommended to create Chipotle China website, to build its
social media page, such as Webo, Renren and QQ social media
platform in the case of China, in order to facilitate ordering on-
line and establish presence among netizens.
Performance Metrics for Chipotle China
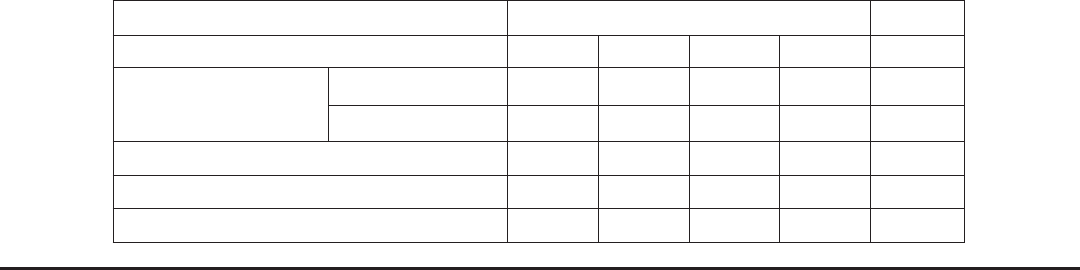
1. Personnel
It is suggested that Chipotle develop ve restaurants and one
Backup Kitchen Center in Beijing in the rst year, with the goal
to expand to dierent regions in the following years. Figure 3
Figure 3
Position Number
Annual Income
(Before tax and include welfare and bonus)
Regional Manager 1 $ 120,000
Store Manager 5 $ 15,000
Salesclerks 50 $ 7,000
Regional Manager Assistant 2 $ 15,000
Kitchen Manager 1 $ 25,000
Cooks 10 $ 7,000
Kitchen Manager Assistant 1 $ 10,000
Market Monitoring Director 1 $ 80,000
Local Product Developer 2 $ 30,000
Total 73 $820,000
77
Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Cases
below is a projected personnel plan of the rst year based on
the general data records of other U.S. restaurant chains and on
the knowledge of Chinese foodservice industry:
2. Financial
Figure 4 and 5 below function as a start-up plan focusing on
the rst year of Chipotle China’s expansion. It gives a nancial
projection to ve stores in Beijing in the rst operational year,
based on the research behind this paper. It serves as a situation
analysis for Chipotle China income estimation.
As Figure 4 and 5 shows, Chipotle will approximately gain
$3,494,000 in the rst operational year. Meanwhile as Chipo-
tle opening ve outlets in Beijing, each restaurant could earn
$2,120,000 annually if based on $5.5 average consumption and
250 customer daily turnovers. The total revenue of the ve out-
lets in Beijing estimated be over 10 million in the rst year. Cost
items ranges from raw food ingredients cost, operational cost,
to marketing expenses. Marketing fees shall be mainly applied
to public relation maintenance and brand advertising. Accord-
ing to Chinese business law, foreign businesses need to turn
over around 8% of the total revenue as business income taxes
annually (Deloitte, 2013). It is showed that Chipotle China will
gain $3,494,000 in net income in the rst year after calculating
each expenditure detail. Therefore exploring the China market
is estimated to be a protable path for Chipotle Mexican Grill.
3. Long term
The long-term plan is to establish at least 50 Chipotle’s res-
taurants in China within ve years. In the rst ve-years of the
expansion plan, all Chipotle restaurants in China shall be com-
pany-owned and a franchising plan may be considered in the
second ve-year plan. Concerning Chipotle’s quick-service din-
ning style caters mostly to high-paced big-city working class
whose majority centered in Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou,
most of the 50 outlets should be located in such cities in the
Figure 4
Estimated Restaurant Unit Data
20XX Quarters Ended Total
Mar, 31 Jun, 30 Sep, 30 Dec, 31
The Number of Outlet Beginning of the Year 0 0 0 0
Openings 5 5 5 5
Average Restaurant Sales (in dollars) 530,000 530,000 530,000 530,000 2,120,000
Average Consumption (in dollars) 5.5 5.5 5.5 5.5
Customer Turnover Per Unit (Daily) 250 250 250 250
rst ve-year expansion. Chipotle China shall properly adjust
food prices based on the local economic situation too and its
growth in China needs adequate shareholder investment and
the approval of Chipotle’s managers.
Conclusion
The case study discussed whether the market in China is an ap-
propriate place for CMG’s globalization. With the analysis conducted
above, bringing Mexican quick-service restaurant chain Chipotle into
china is akin to a new product entering into a new market on one
hand, facing high risks and opportunities in the unknown business
environment. On the other hand, its healthy ingredients, well-tailored
Mexican spicy taste and time-sensitive serving manner are in line with
the meal needs of Chinese rising middle class in big, developing cities.
Therefore the paper demonstrated the feasibility of operating CMG in
China through analytics on the company, the environment, marketing
strategies and estimated nancial performances.
The business plan discussed above provided readers with in-
formation about the advantages and comprehensive strategies for
Chipotle’s China expansion. The nancial plan estimated the internal
costs, marketing spending, revenue, and prot per unit. These num-
bers can provide investors a rough nancial budget in execution. The
paper henceforth believes it can yield satisfactory revenue return for
CMG to open chain restaurants in China after the discussion initiated
above. If it performs positively, the prots gained can be deployed to
Chipotle China’s further internal optimization such as innovate new
meals, opening more outlets and strengthen internal management.
Exploring the market of China can also extract Chipotle out of purely
competing in the “Red Ocean” of U.S. fast casual dining market and
bring it into regeneration stage. As such, it is not unsafe to predict Chi-
potle can be a household name in its new “Blue Ocean” of China just
like KFC and McDonald’s when they rst entered.
In the long run after Chipotle enters Chinese market, an inte-
grated supply chain and many logistics centers could subsequently be

78 Volume 4, Number 3
created and these resources can simplify CMG’s further expansion in
other Asian countries, such as India, Japan, South Korea. It concludes
that it is worthwhile for Chipotle Mexican Grill to attempt to explore
the potential market in China.
Due to the limitation of time, length and resources, the case study
is not a complete strategy and knowledge database for Chipotle’s
practical comprehensive expansion plan in China. The ve sections,
from executive summary, huge potential in China’s market to perfor-
mance metrics of this paper, are combined to present the rst stage
scope and analytics of restaurant oversea growth strategies. It helps
Chipotle managers and ambitious investors form a vision of entering
into the market in China and functions as a reference for more compli-
cated practices to be followed.
References
Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. SWOT Analysis (2012), Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. 1-8.
Company prole: Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. (2012), Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. 1-8
Chen M & Flannery R (2013). China KFC Supplier Runner Post” 1st-Qrt low, busi-
ness hurt by H7N9, safety concern. From: Forbes.com
Deloitte International Tax Source, (2013). Taxation and Investment in China
2013. Retrieved from http://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/
global/Documents/Tax/dttl-tax-chinaguide-2013.pdf
Fung M, Lain H, Remais J, Xu L & Sun S (2013). Food supply and Food Safety
Issues in China. Lancet, 381 (9882), 2044-2053.
Kim, W. Chan., and Renée Mauborgne (2005).Blue Ocean Strategy: How to
Figure 5
Income Statement projections
20XX Quarters Ended (dollars in thousands) Total
Mar, 31 Jun, 30 Sep, 30 Dec, 31
Revenue 2,650 2,650 2,650 2,650 10,600
Food, beverage and packaging cost 622.5 622.5 622.5 622.5 2,490
Labor cost 205 205 205 205 820
Occupancy cost 170 170 170 170 680
Other operating cost 266.5 16.5 16.5 16.5 316
General and administrative expenses 150 150 150 150 600
Depreciation and amortization 70 70 70 70 280
Pre-opening cost 100 100 100 100 400
Marketing cost 180 180 180 180 720
Total operating cost 1,764 1,514 1,514 1,514 6,306
Income from operation 886 1,136 1,136 1,136 4,294
Interest and other income (expenses) 100 (150) 200 50 200
Income before taxes 986 986 1,336 1,186 4,494
Provision for income taxes 250 250 250 250 1,000
Net income 736 736 1,086 936 3,494
Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition Irrelevant.
Boston, MA: Harvard Business School.
Miller, P (2004). “Quick service hits China,” China Business Review, 31(4), 18-28.
Olsen, Michael D., Eliza Ching-Yick. Tse, and Joseph J. West (1998).Strategic
Management in the Hospitality Industry. New York: J. Wiley.
Orr, H (2013). CMG-Chipotle Mexican Grill Inc. --- Company Analysis and ASR
Rank Report. Alpha Street Research Reports. 1-9.
Qi M (2012). The analysis of Chinese food safety issues: Legislations and govern-
ment supervision, Chinese Law & Government. 45 (1), 3-9
Sacks, D (2012). Chipotle: For exploring all the rules of fast food. Fast Company.
163, 124-126.
