
Destination:
One Million New Jobs
GLOBAL SME FINANCE FACILITY PROGRESS REPORT
2012-2015

“With SMEs being an important driver
of employment and development, it is
essential that SMEs are given the access
to finance and the technical assistance to
enable them to play this key role. DFID has
been a strong supporter of this innovative
blended finance initiative which leverages
IFC’s extensive experience in blended
finance, its broad network of financial
institution partners and its expertise
in providing the technical assistance
needed to maximise the impact of SME
finance. DFID is especially supportive
of the initiative’s eorts in fragile and
conflict aected states and welcome’s the
initiative’s successes in some of the more
fragile countries of the world.”
— Rachel Turner, DFID Director for International Finance
“SMEs are crucial for
inclusive growth, jobs
and innovation. We are
happy to partner with
IFC, DFID and others in
the Global SME Finance
Facility and look forward
to a strong increase in SME
loan portfolios with local
banks.”
— Peter Le Poole, Senior Policy
Advisor Financial Sector
Development, Ministry of Foreign
Aairs, Netherlands

ACRONYMS & DEFINITIONS
DFID Department for International Development
DFI Development Finance Institutions
DRC Democratic Republic of Congo
EIB European Investment Bank
ETI Ecobank Transnational International
FCAS Fragile and Conflict-Aected States
FIG Financial Institutions Group
GPFI Global Partnership for Financial Inclusion
HBL Habib Bank Limited
IDA International Development Association**
IFC International Finance Corporation
IFI International Financial Institutions
M&E Monitoring and Evaluation
MIS Management Information System
MSME Micro, small and medium enterprises
MTR Mid-Term Review
ODA Ocial Development Assistance
RMG Ready Made Garments
RSF Risk-Sharing Facility
SDG Sustainable Development Goals
SME Small and medium enterprise
VSE Very small enterprise
WEDF Women Entrepreneurship Development Fund
Table of Contents
i Acronyms & Definitions
1 Letter from Nena Stoiljkovic
2 Destination: One Million
New Jobs
4 Inside the SME Financing Gap
6 Where We Operate
8 The Facility Works Through an
Ecosystem Approach
10 The Facility In Action
18 Already Creating Jobs and
Improving Lives
21 Addendum: List of Projects
i
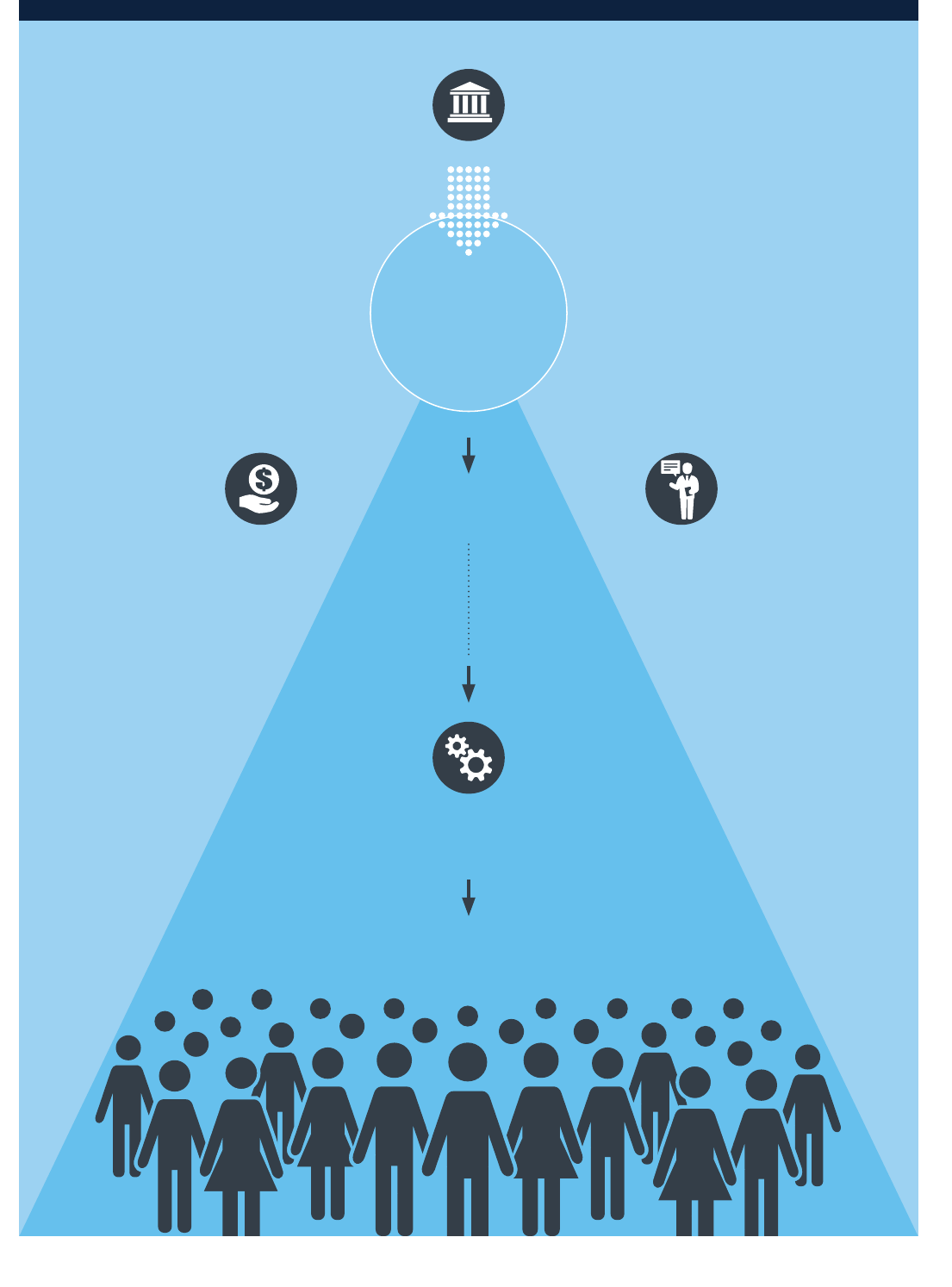
From:
• International Financial
Institutions / Development
Finance Institutions
• Donors
Investment Services
(for financial institutions)
• Loans
• Risk-Sharing Facilities
Advisory Services
• Capacity Building for
Financial Institutions
• Financial Infrastructure
Funding
Facility Activities
Lending is Increased to SMEs
(by financial institutions)
SMEs grow and create jobs
Global
SME Finance
Facility
ii

Dear Friends,
In 2009 the leaders of the G20 countries put supporting access to finance
for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) at the forefront of the global
development agenda as a means of driving economic growth and fostering
job creation. SMEs account for a significant share of employment and GDP
around the world, and they produce about two-thirds of all formal-sector jobs
in emerging markets. Yet these firms face pervasive challenges in accessing
finance, which is a critical lever for running and growing a successful business.
The Global SME Finance Facility was established in 2012 as multi-stakeholder
initiative focused on strengthening the ability of financial institutions to
better meet the financial needs of SMEs. For the last four years, the Facility
has partnered with the UK Department for International Development, the
European Investment Bank and the Netherlands Ministry of Foreign Aairs.
It has been able to leverage the power of these partnerships across some of
the most challenging markets to support nearly 100 SME Finance projects
through investment and advisory solutions that accelerate SMEs’ access to
finance in tough markets.
The Facility is particularly embracing its goal to support the creation of one
million jobs over ten years. We are proud that the Facility’s support has
already enabled its financial institution clients to facilitate US$ 6.4 billion in
over 67 thousand new SME loans, which are estimated to have helped SMEs
create over 414,000 jobs.
This key initiative, with support from its donors and partners, provides
unparalleled flexibility in terms of the range of investment instruments and
advisory services that it oers to its clients. It also plays a critical role in IFC’s
ability to leverage development assistance funds to mitigate risks and catalyze
private sector investments through blended finance instruments.
With the strong support of our partners, the Global SME Finance Facility will
continue implementing successful models for expanding SME finance, and we
fully expect to continue to report impressive results in the years to come.
Nena Stoiljkovic
Vice President, Global Client Services
1

Destination:
One Million New Jobs
T
he Global SME Finance Facility is a blended finance partnership focused on helping to
close the financing gap faced by SMEs in emerging markets. By playing a catalytic role
in increasing access to finance for SMEs, it aims to contribute to the creation of a
million jobs in the SME sector. The Facility focuses on supporting the most underserved
SME segments, such as SMEs in fragile countries, very small enterprises, and women-owned SMEs.
A global partnership to close the SME Financing Gap.
Established in response to a G-20 call for more innovative
approaches to financing SMEs, the Facility provides
funding, risk mitigation and advisory assistance to financial
institutions to help them expand lending to SMEs in
challenging markets and segments. In addition, the Facility
provides advice to governments to improve the financial
infrastructure, enabling financing to flow more eciently
to SMEs.
First four years of progress. The Facility has
demonstrated in its first four years the power of its
multi-pronged approach and its partnership model. Since
its creation in 2012, the Facility has supported 56 financial
institution clients who have lent over $6 billion through
more than 67 thousand new loans to SMEs. We estimate
that to date the Facility contributed to 414,000 new jobs
created through such lending.
Joining forces to accomplish more than any single
resource can. Managed by IFC, the Facility blends
commercial financing from IFC and the European
Investment Bank with donor funding from the UK
Department for International Development (DFID) and
the Netherlands.DFID provided the initial funding for the
Facility with US$ 120 million for investment and advisory
services. Subsequently, the Netherlands committed US$
27 million for investment and advisory services in IDA
countries, and the European Investment Bank committed
US$ 100 million for risk-sharing facilities.
Blended finance refers
to the strategic use of
donor funds to attract
private capital towards
investments that have a
high development impact.
2

ADDRESSING THE ENTIRE FINANCE
ECOSYSTEM.
Funding and/or guarantees are provided to commercial
banks and microfinance institutions to help expand their
lending to SMEs that would otherwise be considered
too risky.
As Banks work to understand the risks and manage the
costs of moving into new segments, the Facility also
provides IFC advisory services to help establish the new
products, processes and risk management systems that
will make their eorts sustainable.
Where credit information and the policy environment
are not conducive to expanding SME lending, the Facility
steps in to provide advice from the World Bank to improve
financial infrastructure that will ease the conditions for
banks to lend to SMEs.
With the support of its partners, the Facility will continue
providing investment and advisory services to institutions
committed to expanding SME lending, and it looks forward
to achieving its ultimate goal of facilitating disbursement
of US$ 8 billion in SME loans and creating one million new
jobs by 2019.
Global SME Finance Facility
2012 – 2015 Highlights
Ninety-
Nine
Investment and
Advisory Projects
56
WORKING WITH
financial
institutions
27
low-income
countries
ACTIVE IN
CONTRIBUTING TO
414,000
new jobs created
Building
financial
infrastructure in13 countries
RESULTING IN
$6.4 billion
incremental growth
in new SME loans
AND
67,539
new loans to SMEs
3

Recent studies estimate that over 90 percent of net job
creation in emerging markets is attributed to SMEs with
fewer than 250 employees. Small firms with under 100
employees contribute more than three-quarters of these
net new jobs, while young SMEs create new jobs at a
faster rate than older ones**. Moreover, research shows
that SMEs play a bigger role in low income and fragile
countries than more auent countries.
Because of this, expansion of the SME sector is critical to
boosting employment and reducing poverty in low income
countries. Yet SME owners in these markets face
significant challenges in building their businesses, from the
high cost of doing business and the pervasiveness of the
informal economy, to a lack of supporting infrastructure
and skilled capacity. However, at the top the list of
challenges for SMEs in most emerging markets is a severe
lack of access to finance, which can greatly limit their
ability to invest in growing their businesses and hiring
additional employees.
The dierence between the amount of financing SMEs
need and the amount they are able to obtain from formal
financial institutions is known as the Financing Gap. As
of 2011, the SME Financing Gap in emerging markets was
estimated at US$ 900 billion to US$ 1.1 trillion. Closing
the SME finance gap will accelerate the formation of new
SMEs and help existing ones thrive.
Women-owned SMEs. Approximately 31–38 percent
(8–10 million) of formal SMEs in developing economies are
owned fully or partly by women. These firms have access
to high-quality financial services to even a lesser degree
than SMEs owned by men, and they cite access to finance
as a major constraint more often than male business
owners. Women-owned SMEs are less likely to obtain
funding because they tend to be smaller and less formal,
and they often face socio-cultural norms and sometimes
legal constraints that makes it more dicult for women to
own and pledge assets as collateral to access finance.
The Facility is committed to working with its clients to
devote increased attention to this market segment and
its unmet demand for financial services. However, many
Facility clients are institutions that are just starting to
focus on SME banking. They need to put in place basic
SME products, risk management policies, marketing
and market research capabilities, and assign and train
specialized SME-focused sta before they can focus
on reaching specific segments, such as women-owned
enterprises. Currently, about 1/3 of the Facility projects
have a dedicated component focusing on supporting
women-owned SMEs.
As of December 2015, the Facility programs have enabled
financial institutions to ramp up lending to women-owned
SMEs with 7,270 loans, worth over US$370 million. We
expect these results to significantly increase in the coming
years as the Facility clients develop sustainable and
profitable SME business lines needed to reach women-led
businesses.
Very Small enterprises (VSEs). VSEs comprise firms too
large to be reached through micro lending approaches, yet
too small for most banks to find attractive. Very small
enterprises represent 54–68 percent
***
of formal SMEs.
These firms do not have strong, tangible collateral to oer
as backing for loans, and their lack of credit records and
financial history makes it dicult for financial institutions
to analyze and assess their credit risk. Additionally, VSEs
typically require smaller loans, which can be costly to service.
* Small and Medium Sized Enterprises (SMEs). To qualify as an SME a firm must meet at least two of the following three characteristics:
10 to 300 employees, $100,000 to < $15 Million in assests, $100,000 to < $15 Million in annual sales, SME loans typically are between $10,000 and $1 million.
** SMEs, Age, and Jobs, Policy Research Working Paper, World Bank Group’s Development Economics Global Indicators Group 7493, November 2015, p. 18"
*** IFC Enterprise Finance Gap Database (2011)
Inside the SME
*
Financing Gap
4
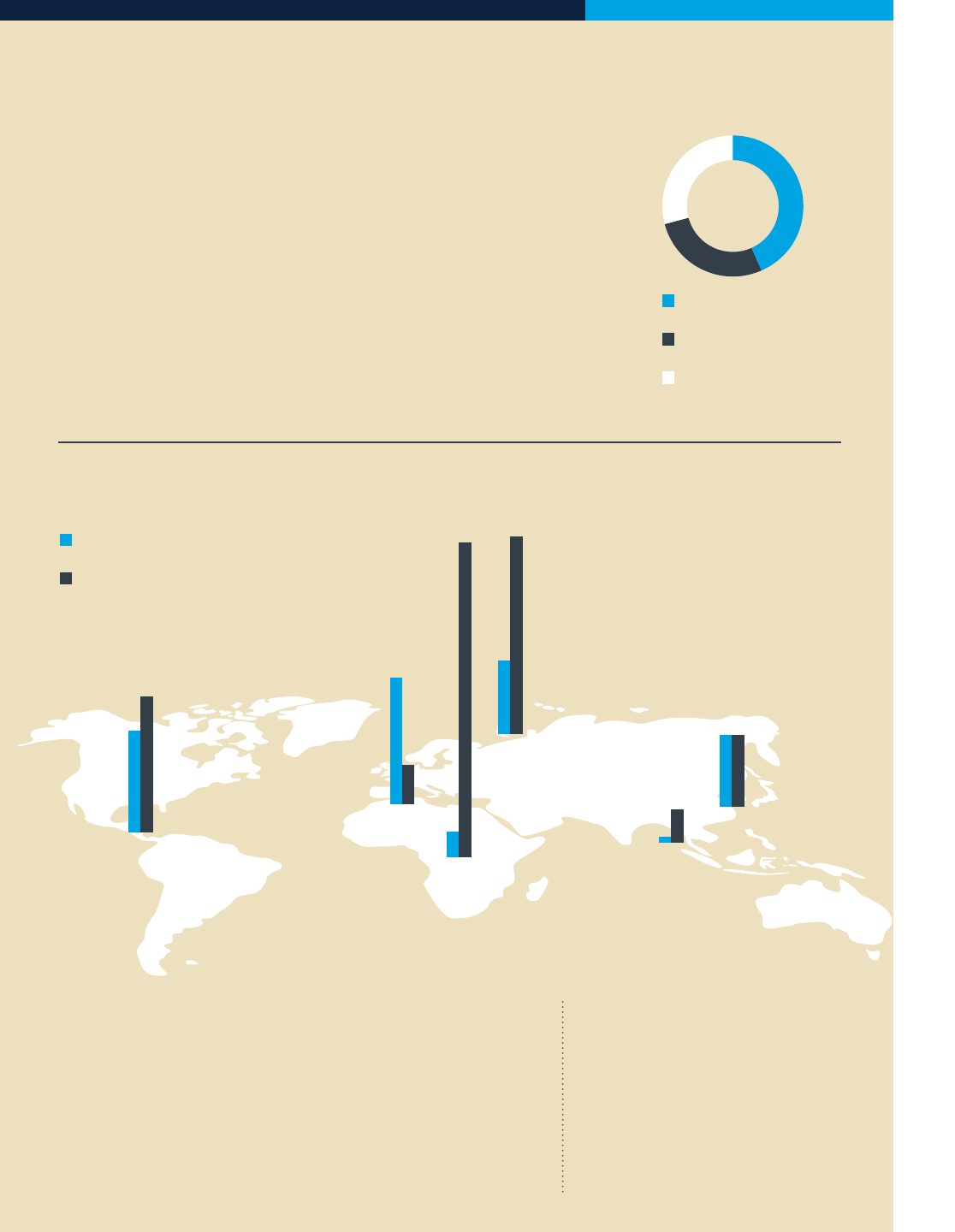
A One Trillion Financing Gap*
Medium Enterprises
29 – 36 percent
Small Enterprises
19 – 23 percent
Very Small Enterprises
19 – 24 percent
Finance
Gap
Amount of Total Credit Gap
In USD$
Percent of Unserved Formal SMEs
Varies Per Region
$80.09B
73.64%
Sub-
Saharan
Africa
$170.06B
47.67%
Central
Asia and
Eastern
Europe
Latin
America
$235.29B
32.92%
South
Asia
$14.88B
8.10%
East
Asia
$167.52B
17.49%
Middle
East and
North
Africa
$294.15B
9.57%
The financing gap data refers to formal SMEs
only. In regions with a large number of micro and
informal businesses, the total financing gap is
much larger.
Although the definition may vary by region and the
size of the market, VSEs are typically defined as
companies with between 5 and 25 employees and
annual turnover below US$ 0.12 million.
*IFC Enterprise Finance Gap Database (2011),
https://www.smefinanceforum.org/data-sites/ifc-
enterprise-finance-gap
And Disproportionately Aects Women
57-71 percent of women-owned SMEs in developing economies are
either unserved or under-served, totaling 5.3-6.6 million SMEs
US$ 260-320 billion in unmet financing needs of women-owned
businesses, representing a large opportunity for financial institutions
Total Gap
US$ 900 Billon
– US$ 1.1 Trillion
= 26 – 32 percent of
current outstanding
SME credit
Aects 55 – 68 percent of formal SMEs developing
countries representing 13 – 20 million firms
5

These factors contribute to the perception among
financial institutions that SMEs are riskier clients, and that
they increase the transaction costs of the commercial
banks and microfinance institutions that serve them.
Furthermore, the financial institutions in these countries
typically are just beginning to focus on SME banking. Basic
SME products, appropriate SME risk management policies,
tailored marketing and market research capabilities, and
trained specialized SME-focused sta are not yet in place.
As a result of these challenges, SMEs in IDA and FCAS
countries in particular have the most limited options for
accessing banking products that meet their financing
needs. In IDA and IDA blend countries alone, about 4.7
million SMEs are estimated to be financially unserved or
under-served, and financial institutions in these markets
need substantial support in building sustainable SME
banking models.
* The World Bank Group’s Fragile, Conflict and Violence Group annually releases the Harmonized List of Fragile Situations.
http://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/fragilityconflictviolence/brief/harmonized-list-of-fragile-situations
** The World Bank’s International Development Association (IDA) is one of the largest sources of assistance for the world’s 77poorest countries, 39 of which are in Africa, and is the
single largest source of donor funds for basic social services in these countries. Eligibility for IDA classification depends a country’s relative poverty, defined as GNI per capita below an
established threshold and updated annually ($1,215 in fiscal year 2016). Blend countries: IDA-eligible but also creditworthy for some IBRD borrowing. http://ida.worldbank.org/
15
FCAS Countries
reached
Targeting sectors vital to
rebuilding markets and
assisting recovery
CURRENT PROJECTS:
80%
are in IDA
countries
35%
are in FCAS
countries
20%
are in IDA-blend
countries
Where We Operate
Zeroing in on Fragile and Conflict Situations and
Poverty Economies: Acknowledging the need for
increasing SMEs’ access to finance in the most dicult
markets, the Facility has prioritized its activities in
the poorest countries as defined by the World Bank’s
International Development Association (IDA), and in
countries with Fragile and Conflict Situations (FCAS).*
The Facility’s ecosystem approach also allows the IFC to
have a larger footprint in IDA and FCAS countries. Global
SME Finance Facility has contributed over half of all IFC’s
Financial Institutions Group’s MSME Finance investments
in FCAS globally, and over 90 percent of the investments in
Africa FCAS.
Financial institutions in FCAS and IDA countries
face the greatest SME finance challenges. Financial
institutions in these markets operate in volatile and
unpredictable business environments, troubled by
heightened political instability, a dicult investment
climate, and a weak financial infrastructure that makes
eective assessment of SME credit risk dicult. In
addition, SMEs in these countries have limited financial
history and formal business records, possess few fixed
assets for collateral, and require smaller loans.
6

Solomon
Islands
Micronesia, FS
Marshall Islands
Kiribati
Tuvalu
Samoa
Tonga
Vanuatu
7
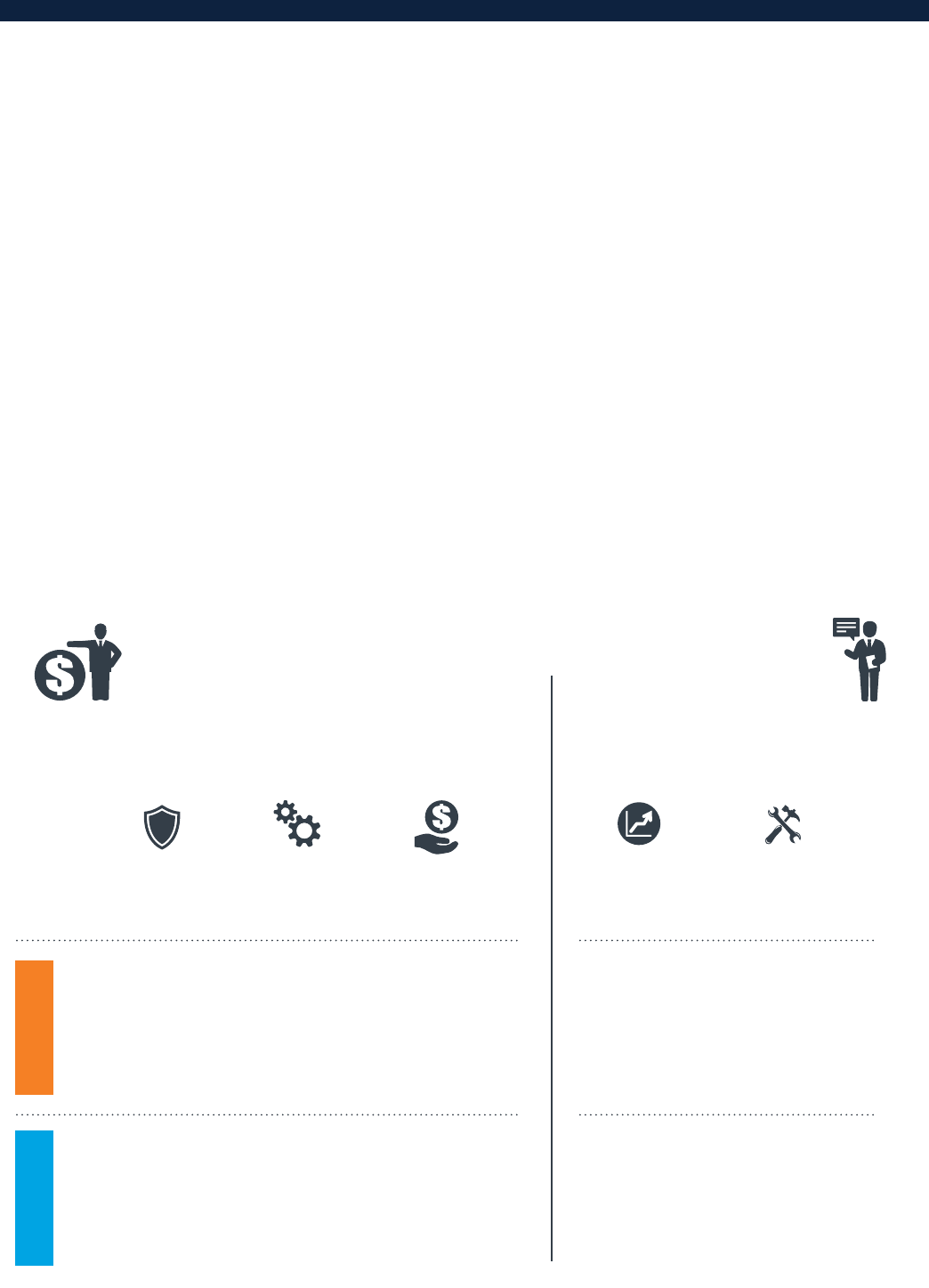
The Facility Works
Through an “Ecosystem” Approach
C
omplex challenges addressed at multiple levels. Given the range of challenges
facing SMEs, addressing the SME finance gap in a sustainable and scalable manner
requires a comprehensive approach. This includes integrated, multi-tiered solutions
that span the ecosystem of financing.
The Facility provides Investment and Advisory solutions,
crafted to the needs of each country and partner
institution. These projects are implemented through IFC’s
global network, comprised of 106 IFC country oces,
215 field and 73 HQ-based FIG Investment sta, 83 field
and 17 HQ-based FIG Advisory sta, and 765 Financial
Institutions clients.
INVESTMENT SERVICES
Blended funds from IFC, donors and other investors.
Performance incentives available for all investments.
ADVISORY SERVICES
Risk Sharing
Guarantees cover
a portion of losses
on loans to SMEs
Lowers risks
to financial
institutions of
moving into SME
markets
Senior or
Subordinated
Loans
Credit lines
designated for
on-lending to
underserved
SME segments,
including Women-
owned SMEs
Encourages
increased lending
to SMEs
Performance-
Based
Rebates
Flexible
rebates linked to
meeting specific
performance
targets related
to growing SME
portfolios
Incentives to
financial
institutions for
investments in
ramping up lending
to under-served
segments
Advisory Services
for Financial
Institutions
Capacity building
tailored to the
needs of banks
and microfinance
institutions
Strengthens
FIs institutional
capacity to better
serve SMEs
Financial
Infrastructure
Projects
Technical advisory
services for
establishing credit
bureaus, and
secured collateral
registries
Facilitates SME
lending by
strengthening
countries' financial
infrastructure
MECHANISMPURPOSE
8

Global SME Finance Facility
Activity 2012-2015
BLENDED FINANCE
INVESTMENT PROJECTS
TOTAL PROJECT SIZE
US$ 899 million
US$ 62 million in donor funding
ADVISORY PROJECTS
TOTAL PROJECT SIZE
US$ 97 million
US$ 41 million in donor funding
n 9 projects
completed
n 66 in
implementation
n 24 in pre-
implementation
IFC Blended Finance Facilities
Global SME
Finance Facility
The Women
Entrepreneurs
Opportunity
Facility (WEOF)
The Global
Agriculture
and Food
Security
Program (GAFSP)
MENA SME
Finance Facility
Climate related
Facilities
Blended Finance across IFC
TOTAL PROJECT SIZE
$996 million
leveraging US$ 103 million
in donor funding
99
34 investment projects
65 advisory projects
TOTAL
PROJECTS
18
13
56
Financial and financial in countries
Institutions infrastructure
projects
Since 1996, IFC has approved nearly US$ 407 million in
concessional funds for investment and advisory projects
in the climate, agriculture and SME sectors, leveraging
more than US$ 4 billion. By blending donor funds from its
partners alongside IFC’s own capital, IFC has been able
to undertake high-risk, high-impact projects that have
strong potential to improve lives and reduce poverty,
and catalyze investments in areas where market barriers
would otherwise stand in the way.
In 2012 IFC approved a blended finance policy, including
a rigorous governance structure led by a blended finance
committee.
The blended finance solutions, such as those provided by
the Global SME Finance Facility, are indicative of IFC’s role
in “turning billions into trillions” - the World Bank’s call for
action to mobilize, redirect and unlock trillions of dollars of
private capital needed to achieve the 2030 United Nation’s
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).Estimates for total
annual investment in developing countries that is needed
to achieve the 2030 SDGs range from $3.3 trillion to $4.5
trillion. Current Ocial Development Assistance (ODA)
falls far short of these demands, leaving an annual gap of
US$ 2.3 trillion.
9

Project Example: Access to financing
accelerates in Nigeria — particularly for
women-owned SMEs
The Facility is supporting Access Bank
Nigeria in expanding its lending to smaller
SMEs, with a special focus on women and
women-owned SMEs. We provided Access Bank
Nigeria with a loan, an RSF and advisory services to
support scaling up its SME lending and its Banking
on Women model. IFC helped the bank develop a
value proposition tailored to women needs, with a
special focus on helping the Bank incorporate full
banking services for women, including personal,
micro, SME and corporate banking solutions. The
project is expected to demonstrate to other financial
institutions in Nigeria the viability of lending to
women owned SMEs, and is expected to significantly
increase the finance options available to these firms.
The financing package, along with the performance-
based incentive and advisory services, already has
encouraged the bank to double its annual growth rate
target for the women-owned SME lending portfolio.
LOANS
Funding to financial institutions, including dedicated credit
lines for reaching specific SME segments such as women-
owned SMEs. Status: 18 loan projects.
Project Example: Loans grow Very Small
Enterprises in the DRC
The Facility is supporting Advans DRC, a microfinance
bank, in upscaling its lending to Very Small Enterprises
(VSEs). VSEs are too large to be serviced through
RISKSHARING FACILITIES RSF
Risk mitigation instruments that encourage financial
institutions to move into a new market and pursue SME
segments perceived to be higher risk.
Status: 16 RSF projects.
Project Example: Risk-sharing facilities
increase SME lending in West and Central
Africa
The Facility is supporting Ecobank Transnational
International Ltd (ETI) to increase its SME lending
in 8 FCAS countries in Africa. These countries face
persistent political instability, weak financial
infrastructure and a poor investment climate creating
a particularly dicult business and SME-financing
environment. With the support of the RSF that covers
a portfolio of up to US$ 110 million in loans to SMEs, ETI
is expanding its SME lending across eight subsidiaries
in West and Central Africa.
This RSF, along with a performance incentive, is
motivating ETI aliates in Burundi, Chad, Côte
d’Ivoire, the Democratic Republic of Congo, the
Republic of Congo, Guinea, Mali and Togo to take on
greater risk and increase their outreach to otherwise
unserved SME segments. ETI aliates are expected
to provide SME loans to over 5,000 SME borrowers.
Once the eectiveness of this outreach has been
demonstrated, ETI expects to scale up SME lending
across its entire network, including in other fragile
and conflict-aicted states.
The Facility in Action
Investment Services
10

traditional microfinance approaches and yet are too
small for banks to find attractive. They face more
challenges in accessing credit than micro enterprises
in the local market.
Historically focused on micro lending, Advans has
benefited from the Facility’s support to provide larger
loans to VSEs. The facility provided Advans with a loan
and a performance incentive linked to pre-agreed
stretch targets. The blended finance approach has
incentivized Advans to increase its lending to VSEs by
mitigating some of the higher risks of lending to them.
With the support of the loan, Advans plans to more
than triple its volume of outstanding MSME loans.
Mr. Matebo is a distributor for a leading beverage
company in DRC, Bracongo. He sells to shops
and restaurants as well as retail. With Facility
funding, Advans was able to provide Charles
Matelo Mutebo with a loan to finance the
construction of a new storage depot and grow his
drinks distributorship enterprise.
A new enclosed storage depot will provide Mr.
Matebo with needed security for his product. The
Facility enabled Advans to lend Mr. Matebo the
US$ 40,000 needed to build the depot, as well
as additional storage rental units. Even while
construction proceeds, Mr. Matebo is renting out
income-producing extra storage units, and he
is regularly repaying his loan. Looking forward,
he is preparing to increase his inventory and is
considering the next steps to grow his business.
11

PERFORMANCE INCENTIVES FOR
INVESTMENTS
Performance incentives are embedded in loans and RSFs,
and are linked to pre-defined performance targets.
Incentives are tailored to the structure of each investment,
and they reward financial institutions for setting and
meeting more ambitious SME lending targets, encouraging
them to rapidly reach and serve most SMEs. Status: All
loans and RSF projects include performance incentives.
Project Example: Performance incentives
spur life-saving loans in Bangladesh
The Ready-Made Garments (RMG) sector is the major
driver of Bangladesh’s growth, making Bangladesh
the second largest RMG producer in the world after
China. While the RMG sector in Bangladesh provides
employment for millions of people, most of whom are
women from poor backgrounds, the country has a
poor record of working conditions and worker safety,
as well as deficient factory infrastructure. The Facility
is supporting local banks to provide loans to small
garment factories, for the specific purpose of funding
capital improvements essential to worker safety.
The Facility support for four Bangladeshi banks —
City Bank, Eastern Bank, Prime Bank and United
Commercial Bank — is enabling small garment
factories to invest in structural, electrical, and fire
safety standard improvements. The Facility support
includes a performance incentive embedded into a
loan from IFC that specifically encourages banks to
give loans to smaller garment factories, which face
the most diculties in accessing finance. The program
estimates that this eort may help almost 500,000
workers, including about 400,000 women, benefit
from a safer work environment.
THE FACILITY IN ACTION: INVESTMENT SERVICES CONTINUED
Project Example: Incentives increase lending
to women entrepreneurs
in India
With support from the Facility, IFC provided
India’s Yes Bank with a loan featuring
an embedded performance incentive
to motivate the bank to scale up its lending to
SME borrowers in low income states (LIS) and in
underserved North East states (NES), including
women-owned SMEs in these disenfranchised regions.
The incentive, conditioned on Yes Bank meeting
stretch targets for reaching these markets, has
been successful in achieving a significant increase in
lending to women-owned SMEs. The bank refined its
strategy for reaching women-owned SMEs, and as a
result of this eort, the bank has decided to launch
a country-wide program to become a flagship lender
to women in India. By helping one of the largest and
most dynamic banks in India see the opportunity
within the women’s market, our support has spurred
Yes Bank to strive to become a market leader in the
gender space.
12

13

ADVISORY SERVICES FOR
FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Under the Facility, IFC leverages its regional SME Finance
Advisory Services Specialists to help financial institutions
improve their SME lending operations, including building
eective business models, developing appropriate products
and services, optimizing channels for delivery, increasing
eciency, and training sta to more ably identify, evaluate
and serve SME clients. Additional advisory services are
geared to helping financial institutions develop non-
financial services for SMEs, such as training, mentoring
and networking for business owners. Status: 47 advisory
service projects.
Project Example: Advisory services help
Kenya’s NIC Bank reach more SMEs
The Global SME Finance Facility is providing advisory
services to help Kenya’s NIC Bank strengthen its
capacity to sustainably serve SMEs. The program aims
to help the bank identify gaps in its existing SME
banking operations, and revise its SME strategies,
structures and processes. The project’s goal is to triple
the NIC’s volume of SME lending over three years. IFC
also has an investment in NIC Bank to help it expand
SME banking operations.
Project Example: Advisory services support
financing for women-owned SMEs in
Bangladesh
As a component of a wider SME-financing
Advisory Services for IDLC Finance Ltd.,
the Facility helped IDLC build a Women in
Business program and develop a range of products and
services specifically for women-owned SMEs. IDLC’s
Purnota products provide a comprehensive solution
for women-owned businesses to grow, including
loans, business facilitation services, training,
insurance, digital marketing, and other services to
women-owned businesses. This was the first time
any financial institution in Bangladesh launched a
comprehensive financial services program focused on
The Facility in Action
Advisory Services
“Our focus will be to
deepen our presence
and oerings in the retail
and SME segments, and
increase our footprint in
the region.”
— John Gachora, NIC Group Managing Director, Kenya
14

the women’s segment. With the help of this product,
IDLC expects to grow its portfolio to more than two
thousand women entrepreneurs over one year.
Project Example: In Pakistan, advisory
services transform SME lending capacity
The Facility has provided advisory services to Bank
Alfalah to help the bank redesign its SME business
model and improve its credit underwriting process.
With this support Bank Alfalah has created a
specialized SME business unit it introduced tailored
delivery models for SMEs, invested in its Management
Information System (MIS) to improve SME lending
operational eciency, and entirely revamped the SME
product line. Additionally, Bank Alfalah developed
a non-financial advisory services (NFS) for SMEs,
including the development of the SME Toolkit, and has
become the first bank in Pakistan to have a structured
NFS oering as part of its SME business model.
THE FACILITY IN ACTION: ADVISORY SERVCIES CONTINUED
“Our new non-financial
advisory services will add
significant value to SMEs
in managing their business
… and enable economic
progress.”
— Atif Bajwa, President and Chief Executive Ocer,
Bank Alfalah, Pakistan
15

STRENGTHENING STATES’
FINANCIAL INFRASTRUCTURES
The Facility also supports the building and/or
strengthening of secured collateral registries and
credit bureaus. Establishing proven credit histories and
expanding the types of assets entrepreneurs can use as
collateral have the potential to increase SME lending
dramatically. A robust financial infrastructure is expected
to especially benefit SMEs owned by women, who
generally have less access to land and property, currently
the preferred collateral for most financial institutions.
Status: 18 financial infrastructure projects in 13
countries.
Project Example: Advisory services improve
Liberia’s collateral registry
In Liberia, the Facility is supporting the development
of a collateral registry, including the appropriate
legal, regulatory and institutional framework
for secured transactions for movable collateral
lending. The collateral registry allows SMEs that
do not have access to traditional collateral, such as
land or real estate property, to register moveable
assets as collateral in order to access loans from the
participating financial institutions. These moveable
assets can be a car, a motorcycle, crops, agricultural
equipment, accounts receivable, etc. Despite being
launched in 2014 during the Ebola crisis, the movable
collateral registry is already making it possible for
farmers and entrepreneurs to borrow money against
such assets.
Project Example: Advisory services establish
a credit registry in Afghanistan
The Facility is supporting Afghanistan’s eorts to
establish credit information sharing systems to
provide lenders with information to make ecient
risk assessments of potential borrowers, and create a
secured lending framework that includes a collateral
registry for movable property to provide lenders with
the ability to eectively use borrowers’ property as
collateral. While the new Registry in Afghanistan is
still in a nascent stage, it is expected to significantly
improve access to finance for micro, small and
medium enterprises (MSMEs).
Global SME Finance Facility
works closely with the
World Bank’s Finance and
Markets Group, which leads
the implementation of the
financial infrastructure
projects.
16

THE PROMISE OF FINANCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE
The successful implementation of financial infrastructure project can have
a dramatic impact on increasing access to finance for SMEs. The IFC’s work in strengthening financial infrastructure
in China is a compelling example of the far-reaching impact a well-functioning secured collateral registry can have on
lowering the costs of credit and increasing access to finance to SMEs.
With IFC’s support, which took place prior to the Facility, China established a solid secured transactions system that
has resulted in a sustainable flow of additional credit to the SME sector. China created a security interest registry
for account receivables in October 2007. Three and half years later, the registry's data reported a cumulative US$
3.58 trillion accounts receivable financing, including USD$ 1.09 trillion in SME lending to over 68 thousand SME
borrowers. Sixty-three percent of SMEs that obtained new loans using accounts receivable had female ownership,
while 20 percent are majority-owned by women.
An example of a successful
Financial Infrastructure project
that makes a dierence.
17

Already Creating Jobs and
Improving Lives
I
nitial results, for the Facility are strong, and demonstrate that by leveraging the capital from
our partners along with IFC’s banking relationships globally, we can address the Financing
Gap more eectively than any single international financial institution, development finance
institution, or donor could alone.
Number and volume of loans: The Global SME Finance
Facility can report substantial progress towards achieving
our 2019 goal of facilitating the disbursement of US$ 8
billion in SME loans to 200,000 small and medium
enterprises, as well as creating one million jobs. The
Facility Investment and Advisory support has helped
its clients to provide US$ 6.4 billion in over 67 thousand
new SME loans. These results are expected to increase
significantly as projects reach a more advanced stage
of implementation, and all the supported financial
institutions, credit bureaus and collateral registries
start reporting results.
Supporting Job Creation: Since measuring job creation is
a key goal of the Facility, the Monitoring and Evaluation
(M&E) team has focused on developing an econometric
model to assess the Facility impact on the growth of SMEs,
and job creation in the SME sector. This data-driven
research model has yielded the conclusion that SMEs
receiving a loan from financial institutions supported by
the Facility added approximately 414,000 new jobs by the
end of 2015. Additionally, the findings of the jobs
extrapolation model indicate that the SMEs accessing
loans from our clients are likely to create more jobs than
other SMEs in the same markets. With additional data
collected every year, we will continue to refine this model.
Impact
FACILITATED INCREMENTAL GROWTH IN SME LENDING*
Number of loans
Target: 100,000
Actual:
67,539
Jobs
Target: 1,000,000
Actual:
414,000
Volume of loans
Target: 8 B
Actual:
6.4
billion
* Results are based on data reported by the Facility clients as of December 2015
18

Leveraging donor funds for investment projects: The
Facility aimed to leverage each donor dollar with eight
dollars in commercial financing through investments in 15
financial institutions. As of March 2016, the Facility
leverages the donors’ funds at a rate of one to 14.5 and
provides investment services to 32 banks and microfinance
institutions.
Mid-Term Review. In 2015, the Facility underwent a
formal Mid-Term Review (MTR). The evaluators concluded
that the Facility:
• Eectively deployed its funding to countries with less
developed financial markets at a rate that is higher
than other comparable portfolios within development
finance institutions.
• Eectively contributed to increases in lending to SMEs
by its partner financial institutions. The Facility will
likely surpass its targets with regard to the number
of firms reached, as well as the value of SME lending
facilitated, including targets in fragile states.
• Is on track to meeting its ultimate goal of supporting
the creation of one million jobs by the year 2019.
The MTR also noted that reaching women has been more
challenging because of the dicult markets in which the
Facility operates. Financial institutions in these countries
lack a rigorous reporting capacity to disaggregate portfolio
data based on the gender of SME owner. Additionally, in
many of these markets fewer SMEs are owned by women.
Finally, financial institutions in many markets where
the Facility works have nascent SME lending businesses,
requiring the Facility to help financial institutions build
their SME lending fundamentals before focusing on
increasing their reach to specific market segments such as
women-owned SMEs.
19

20

Addendum
List of Projects
Projects in Africa
BURUNDI
Ecobank Burundi RSF
The project consists of an RSF and performance incentive
for eight Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI) aliates in
Burundi, Chad, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Togo and
the Republic of Congo. The RSF provides a risk mitigation
mechanism to support ETI in expanding its SME lending,
with a particular focus on reaching more small firms, which
are some of the most underserved firms in these markets.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
KCB Burundi SME Advisory
This project supports Kenya Commercial Bank (KCB)
Burundi in expanding its SME banking business. The
advisory services will focus on market research and
segmentation, developing a SME strategy, business model
and a customer value proposition, as well as developing
appropriate SME products, services and delivery channels.
The Advisory will also include, strengthening the bank’s
credit operations and SME credit risk management
practices, policies and tools, and sta training.
Pre-Implementation* Stage • PFI Advisory
Secured Transactions, Burundi
The project aims to increase access to credit for businesses
in Burundi by developing an appropriate legal, regulatory
and institutional framework for movable assets-based
lending. The project introduces an innovative approach to
the development of an electronic centralized collateral
registry by integrating it with the development of a credit
information registry. This approach increases eciency
and provides more comprehensive information coverage
for financial institutions and users.
Pre-Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
CHAD
Ecobank Tchad RSF
The project consists of an RSF and performance incentive
for eight Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI) aliates in
Burundi, Chad, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Togo and
the Republic of Congo. The RSF provides a risk mitigation
mechanism to support ETI in expanding its SME lending,
with a particular focus on reaching more small firms, which
are some of the most underserved firms in these markets.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
CONGO
Credit du Congo RSF
The project consists of a Risk Sharing Facility to Credit du
Congo for developing a targeted approach to providing
finance to SMEs in key value chains that can serve as
sub-contractors to Total Exploration and Production
Congo. The RSF will help Credit du Congo manage its risk
exposure to SMEs and increase its reach to this new
business segment.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
* on hold
21

Ecobank Congo RSF
The project consists of an RSF and a performance incentive
for eight Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI) aliates in
Burundi, Chad, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Togo and
the Republic of Congo. The RSF provides a risk mitigation
mechanism to support ETI in expanding its SME lending,
with a particular focus on reaching more small firms, which
are some of the most underserved firms in these markets.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
COTE D’IVOIRE
Advans Cote d’Ivoire Loan
The project consists of a senior loan in local currency to
fund the SME lending expansion of Advans Côte d’Ivoire, a
Greenfield microfinance bank. The project includes a
performance incentive to motivate the bank to scale its
SME lending capacity to reach more small enterprises,
while maintaining portfolio quality.
Implementation Stage • Loan
BICICI RSF
The project consists of a Risk Sharing Facility for a portfolio
of short- and medium-term loans to SMEs, which will be
originated and serviced by Banque Internationale pour le
Commerce et l’Industrie de la Côte d’Ivoire (BICICI). The
RSF will support BICICI eorts to downscale its lending to
large corporate enterprises by developing an SME business
line. The RSF includes a performance incentive to motivate
a quick ramp-up in lending to new SMEs.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
Ecobank Cote d’Ivoire RSF
The project consists of an RSF and performance incentive
for eight Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI) aliates in
Burundi, Chad, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Togo and
the Republic of Congo. The RSF provides a risk mitigation
mechanism to support ETI in expanding its SME lending,
with a particular focus on reaching more small firms, which
are some of the most underserved firms in these markets.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
SocGen Cote d’Ivoire RSF
The project consists of an RSF for Société Générale des
Banques Côte d’Ivoire (SGBCI) to enable the bank to enter
into the SME segment. With the support of the RSF and
the embedded performance incentive, the bank is expected
to increase its lending to SMEs in the education, health and
agrifinance sectors, as well as to women-owned SMEs.
These SME segments are perceived as higher risk, and as a
result they have limited access to finance.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
SIB Cote d’Ivoire RSF
The project includes a Risk-Sharing Facility to support
Société Ivoirienne de Banques (SIB) eorts to expand and
develop its SME banking. The project includes a
performance incentive to motivate SIB to significantly
increase its reach to smaller SMEs, agri businesses and
SMEs owned by women. The Global SME Finance Facility is
collaborating with the Global Agriculture and Food
Security Program(GAFSP) on this investment.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
Bank of Africa SME Advisory
The project will support Bank of Africa (BoA) in increasing
its outreach to SMEs. The Advisory will focus on developing
a SME strategy; improving BoA’s SME sector market
knowledge and segmentation; strengthening its
organizational structure, risk management framework and
sales channels; and training SME sta.
Pre-Implementation* Stage • PFI Advisory
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF CONGO
Advans DRC Loan
The project includes a senior loan to Advans Bank Congo
(Advans DRC) to support the bank in expanding its services
in the regions outside of Kinshasa that are severely
underserved. The project will also support Advans DRC in
upscaling its lending to Very Small Enterprises, which face
more challenges in accessing credit than micro enterprises
in the local market. The project includes a performance
PROJECTS CONTINUED
* on hold
22

incentive linked to stretch targets related to the growth
rate and the quality of Advans’ SME portfolio.
Implementation Stage • Loan
Ecobank DRC RSF
The project consists of an RSF and performance incentive
for eight Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI) aliates in
Burundi, Chad, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Togo and
the Republic of Congo. The RSF provides a risk mitigation
mechanism to support ETI in an expansion of its SME
lending, with a particular focus on reaching more small
firms, which are some of the most underserved firms in
these markets.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
Rawbank Loan
The project consists of a senior loan to Rawbank to expand
its lending activities to SMEs, including women-owned
SMEs. The project also includes a performance incentive
linked to stretch targets to motivate the bank to increase
its outreach to the SME segment, and specifically to women-
owned SMEs. The incentive will provide a strong motivation
for Rawbank to move beyond its current SME lending
capacity to reach more SMEs and women-owned SMEs.
Pre-Implementation* Stage • Loan
Raw Bank SME Advisory
The project focuses on improving Rawbank’s overall risk
management framework, and strengthening its capacity
to sustainably serve its SME clients. The Advisory includes
a review of the existing risk management framework, the
roll out of a revised risk management procedures and
sta training.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
GHANA
UT Bank Ghana SME Advisory
The project focused on strengthening UT Bank Ghana’s
capacity to serve MSME customers, including the women
in business segment. The Advisory included enhancing the
bank’s credit risk management framework, institutional
capacity building, and sta training.
Completed Stage • PFI Advisory
* on hold
23

GUINEA
BICIGUI RSF
The project consists of an RSF for a portfolio of short- and
medium-term loans to SMEs originated and serviced by
Banque Internationale pour le Commerce et l’Industrie de
la Guinée (BICIGUI), the Guinean aliate of BNP Paribas.
The RSF together with a performance incentive will
motivate BICIGUI to target smaller businesses, which are
less sophisticated, more dicult to reach, and have higher
perceived risk.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
Ecobank Guinea RSF
The project consists of an RSF and performance incentive
for eight Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI) aliates in
Burundi, Chad, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Togo and
the Republic of Congo. The RSF provides a risk mitigation
mechanism to support ETI in expanding its SME lending,
with a particular focus on reaching more small firms, which
are some of the most underserved firms in these markets.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
KENYA
Chase Bank Loan
The project consists of a senior loan, 50 percent of which is
earmarked for on-lending to women-owned SMEs. A
performance incentive serves to motivate the bank to
significantly grow its SME portfolio, and specifically expand
lending to women-owned SMEs. The incentive motivates
the bank to shift resources to focus on SMEs and women-
owned businesses beyond what it would have done
otherwise. The Global SME Finance Facility is collaborating
with the Women’s Entrepreneurship Opportunity Facility
(WEOF) on this investment.
Implementation Stage • Loan
Cooperative Bank Loan
The project consists of a senior loan to provide
Cooperative Bank Kenya (Coop Bank) with long-term
funding to support increased lending to SMEs, including
women-owned enterprises. A performance incentive is
provided to motivate the bank to focus on growing its SME
portfolio, and specifically to increase its reach to women-
owned SMEs. The Global SME Finance Facility is
collaborating with the Women’s Entrepreneurship
Opportunity Facility (WEOF) on this investment.
Implementation Stage • Loan
DTB Kenya RSF
The project consists of a Risk Sharing Facility to help the
Diamond Trust Bank of Kenya (DTBK) expand its SME
lending program to include financing for Very Small
Enterprises (VSEs). The RSF includes a performance
incentive to support the bank in growing its SME lending
portfolio and to increase its reach to women-owned
businesses.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
Medical Credit Fund Loan
The project consists of a subordinated loan to support the
Medical Credit Fund (MCF) in increasing access to finance
for healthcare SMEs, improving the quality of healthcare
services and business practices through technical
assistance, and catalyzing financing from the banking
sector for SMEs operating in the healthcare sector.
Pre-Implementation Stage • Loan
Gulf African Bank SME Advisory
The project focuses on building Gulf African Bank’s
capacity to serve the SME segment, including women-
owned SMEs. The Advisory included refining the SME
segmentation and Islamic Finance products and services;
reengineering the relationship manager role and
enhancing the SME coverage model. Advisory support also
focused on reviewing and redesigning the SME credit
management process and developing products for
women-owned SMEs.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
PROJECTS CONTINUED
24

Equity Bank SME Risk Management Advisory
The project aims to strengthen Equity Bank’s institutional
capacity to serve the SME market segment. The Advisory
focused on improving its credit and risk management
framework; improving risk analytics; enhancing MIS
capabilities; developing credit scoring tools to improve
eciency in loan processing; and delivering credit training
for the bank sta.
Completed • PFI Advisory
NIC Kenya SME Advisory
The project aims to strengthen NIC Bank capacity to
sustainably serve SMEs. The Advisory will include refining
NIC’s SME segmentation model to include both asset and
liability data; augmenting the current SME banking
products; redesigning the credit-scoring model and credit
management processes; and strengthening the bank’s
SME credit recovery processes.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
LIBERIA
Access Bank Liberia SME Advisory
The project supports Access Bank Liberia in developing a
SME business line. The technical assistance focuses on
strengthening its SME credit operations, risk management
and internal controls, as well as sta capacity building and
training in SME lending. The project enabled Access Bank
Liberia to remain operational and continue to serve it is
clients during the Ebola crisis.
Completed • PFI Advisory
Secured Transactions, Liberia
The project focuses on increasing access to credit to SMEs
by developing an appropriate legal, regulatory and
institutional framework for secured-transactions and
movable collateral lending. The Advisory includes drafting
regulations that support the implementation of the
secured transactions law and designing and developing the
collateral registry. The project is also developing an
awareness program on the benefits of the reform.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
25

MALAWI
Secured Transactions, Malawi
The project focuses on increasing access to credit for
businesses in Malawi by developing an appropriate legal,
regulatory and institutional framework for movable
assets-based lending. The project will include developing a
secured transactions legal and regulatory framework,
designing a web-based centralized collateral registry for
security interests in movable property, and building the
local capacity to maximize the benefits of the new Secured
Transactions system.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
MALI
Ecobank Mali RSF
The project consists of an RSF and performance incentive
for eight Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI) aliates in
Burundi, Chad, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Togo and
the Republic of Congo. The RSF provides a risk mitigation
mechanism to support ETI in expanding its SME lending,
with a particular focus on reaching more small firms, which
are some of the most underserved firms in these markets.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
MOZAMBIQUE
Millennium BIM Loan
The project consists of a loan to Millennium Banco
Internacional de Moçambique (BIM) to support the bank’s
lending activities to SMEs. The transaction includes a
performance-incentive to motivate the bank to meet its
stretch targets for reaching under-served SME segments,
including small enterprises and SMEs in rural areas.
Pre-Implementation* Stage • Loan
ABC Bank SME Advisory
The project focuses on developing and growing the SME
banking business of Bank ABC Mozambique. The project
focuses on enhancing the bank’s operating eciency, risk
management capacity building, and sta development, as
well as on strengthening SME loan process, developing a
credit scoring system, and developing appropriate
products and services for SMEs.
Completed • PFI Advisory
NIGERIA
Access Bank RSF
The project includes an RSF for Access Bank Nigeria for a
portfolio of mostly women-owned distributors of the
National Bottling Company. The RSF and the performance
incentive embedded in this transaction will encourage
Access Bank to expand its lending to a new and riskier
market segment of small distributors, while helping the
bank mitigate its risk, gain greater confidence, and acquire
more experience in serving this segment.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
Access Bank Loan
The project includes a loan to support Access Bank
Nigeria’s lending program to SMEs, with a specific focus on
reaching more women-owned SMEs. The transaction
includes a performance incentive to motivate the bank to
scale up its lending to women-owned SMEs and to build a
more sustainable business line.
Implementation Stage • Loan
Access Bank Women SME Advisory
The project supported Access Bank Nigeria in developing a
value proposition for women by incorporating full banking
services for women, such as personal, SME and corporate
banking solutions. The Advisory focused on developing
tailored products that suit the needs of women customers
— including women-owned SMEs. The project also
supported the bank in strengthening its SME processes
and procedures, and provided training for Bank sta.
Completed • PFI Advisory
PROJECTS CONTINUED
* Project on hold due to country conditions
26

Diamond Bank SME Advisory
The project supports Diamond Bank Nigeria eorts to
increase access to finance to SMEs, with a specific focus on
SMEs operating in the agricultural sector. The Advisory
helped Diamond Bank develop a strategy, a product oering,
and risk management tools for the agricultural sector, and
develop a financing model to demonstrate the viability of
lending to agri SMEs, including value chain financing.
Completed • PFI Advisory
Diamond Bank SCF Advisory
The project will support Diamond Bank Nigeria to
sustainably increase financing to SMEs operating within its
corporate- customer supply chain. The Advisory will identify
and leverage internal and external opportunities for supply
chain finance in various sectors. Activities will focus on
market sizing to identify potential anchor firms from current
corporate clients with large supplier/distributor
opportunities; developing a tailored product plan and sales
approach; and enhancing credit processes, risk management
criteria, and an early warning system framework.
Pre-Implementation* Stage • PFI Advisory
FCMB SME Advisory
The project focused on improving FCMB Nigeria’s
operating eciency to better serve SMEs; improving the
bank’s SME operations; and developing tailored products
and services for SMEs. Additionally, the Advisory included
enhancing FCMB’s IT and MIS platforms to ensure that it
captures the information needed to monitor SMEs, as well
as comprehensive SME training for bank sta.
Completed • PFI Advisory
FCMB SEF Advisory
The project will provide technical assistance support to
FCMB to expand its energy eciency and renewable
energy SME lending program. The Advisory will consist of a
market assessment to identify key opportunities, and a
review of FCMB’s current portfolio to identify key target
clients. Additionally the project will include training for
FCMB sta, support for marketing events, pipeline
development, and risk assessment.
Pre-Implementation* Stage • PFI Advisory
* on hold
27

Skye Bank SME Advisory
This project aims to support Skye Bank in scaling its
lending to SMEs. The Advisory includes market
segmentation and product development, improving the
delivery channels, streamlining credit management
processes and procedures, and training for the bank sta.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Credit Bureau, Nigeria
The project provides advice and technical support to the
Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) on the regulatory and
legislative regime governing credit reporting, data
protection and other relevant legislation. The Advisory is
also supporting CBN in developing an appropriate
supervision and oversight role, sta training, and designing
an awareness campaign about credit reporting.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Secured Transactions, Nigeria
The project focuses on improving the secured transactions
legal regime in Nigeria, and the development and launch of
the electronic centralized collateral registry for security
interests in movable property. The Advisory includes
supporting Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) in drafting and
implementing regulations related to secured transactions
and collateral regimes; assisting the CBN in the design and
establishment of a collateral registry; and developing a
communications strategy to accelerate the
implementation of the reforms.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
RWANDA
AB Rwanda SME Advisory
This project provides management and capacity building
services to AB Bank Rwanda, a Greenfield microfinance
bank in Rwanda. The advisory services focus on supporting
AB Bank Rwanda in scaling up its activities to serve very
small enterprises and SMEs (including developing SME
products), and setting up appropriate processes and
procedures to ensure a quality SME portfolio.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
SIERRA LEONE
Secured Transactions, Sierra Leone
The project focuses on increasing access to finance for
MSMEs by developing a secured transaction platform in
Sierra Leone. The project will include supporting the
development of secured transactions and a collateral
registry law, developing criteria on collateral eligibility and
credit classification, developing the electronic collateral
registry, a communication and awareness campaign, as
well as training for public and private stakeholders.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
TANZANIA
CRDB Bank Loan
The project consists of a debt and guarantee facility to
support CRDB’s strategic focus on SMEs, including an
increased focus on reaching WSMEs. The investment will
incentivize the bank to grow its focus on women-owned
SMEs at a faster rate. The project also includes advisory
services to more eectively support this segment.
Implementation Stage • Loan
DTB Tanzania Loan
The project consists of a subordinated loan to help
Diamond Trust Bank (DTB) Tanzania implement its SME
loan portfolio growth strategy, and to support its
expansion outside major cities to severely under-served
provinces. The loan together with a performance incentive
will also encourage DTB to ramp up its Banking on Women
pilot program, and to develop a deeper engagement with
women-owned SMEs.
Implementation Stage • Loan
PROJECTS CONTINUED
28

CRDB SME Advisory
The project supports CRDB in enhancing its SME banking
capacity by focusing on segmentation for targeted
products and services, and development, customization
and rollout of SME products and delivery channels. The
Advisory is also focusing on risk management, as well as
support for key SME segments such as agrifinance and
trade finance procedures.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
TOGO
Ecobank Togo RSF
The project consists of an RSF and performance incentive
for eight Ecobank Transnational Inc. (ETI) aliates in
Burundi, Chad, DRC, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Togo and
the Republic of Congo. The RSF provides a risk mitigation
mechanism to support ETI in expanding SME lending, with
a particular focus on reaching more small firms, which are
some of the most underserved firms in these markets.
Implementation Stage • Risk-Sharing Facility
UGANDA
DTB Uganda Loan
The project consists of a subordinated loan to help
Diamond Trust Bank (DTB) Uganda implement its SME
loan portfolio growth strategy, and support its expansion
outside major cities to severely under-served provinces.
The loan together with a performance incentive will also
encourage DTB to ramp up its Banking on Women pilot
program and develop a deeper engagement with women-
owned SMEs.
Implementation Stage • Loan
ZAMBIA
Secured Transactions, Zambia
The project focuses on developing a secured transactions
legal and regulatory framework in Zambia. The Advisory
will include developing a legal framework to support
implementation of a modern system of financing secured
by movable assets and designing a web-based centralized
collateral registry for security interests in movable property.
The project will also focus on building local capacity to
maximize the benefits of the new Secured Transactions
system, including a public awareness campaign,
stakeholder training, and training to financial institutions.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Projects in South Asia
BANGLADESH
Ready Made Garments (RMG) Bangladesh Loan
Bangladesh RMG program is a comprehensive sectoral
program for strengthening the fire and safety
infrastructure in the RMG sector in Bangladesh. The
project includes loans and performance incentives to
support four local banks (City Bank, Eastern Bank, Prime
Bank, and UCB) in providing financing for small RMG
factories, specifically for investing in improving structural,
electrical, and fire safety standards in accordance with
international safety standards.
Implementation Stage • Loan
29

BRAC Bank SEF Advisory
The project focuses on supporting BRAC Bank eorts to
grow its SME banking portfolio and introducing
Sustainable Energy Finance (SEF). This is to be achieved by
strengthening BRAC’s systems, processes, policies and
products. The project will develop an SME credit scoring
model, and subsequently will focus on credit policy,
process re-engineering, collections and performance
management. The Advisory will also support the bank in
developing and launching an SEF product, and train the
sta to develop internal capacity for SEF operations.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
City Bank SME Advisory
The project is supporting City Bank's eorts to grow its
SME portfolio, with a focus on automation of the loan
origination process, upgrading the MIS platform, and
implementing a data warehouse. Additionally the Advisory is
focusing on risk management, automation of the collections
process, implementation of a customer management
program, and improving sta capacity through training.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Eastern Bank SME Advisory
The project focuses on improving the capacity of Eastern
Bank Limited (EBL) to expand its services to underserved
SMEs. The Advisory focuses on refining the bank’s
understanding of the SME segment, defining specific
target customer segments, aligning products and
marketing strategies with target segments, and creating a
sales eectiveness program. The Project will also include
support for designing non-financial services for SMEs.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
IDLC SME Advisory
The project delivers technical assistance to IDLC Finance
Limited to develop its SME finance service oering. The
Advisory focuses on enhancing IDLC’s SME banking
capacity, as well as developing a credit-scoring model, and
standardized and automated credit process workflows.
The project is also supporting IDLC in developing a
“Women in Business” program and providing non-financial
services to SMEs.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Financial Infrastructure, Bangladesh
This project supports increasing the level of SME finance in
Bangladesh through strengthening the secured lending and
movable collateral legal/regulatory framework, and the
establishment of the secured lending registry. The Advisory
will also include supporting the establishment of a collateral
registry, as well as awareness and capacity building activities.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
INDIA*
Fullerton Loan
The project consists of a loan to Fullerton India Credit
Company Ltd., a third of which is for on-lending to SMEs
in Low-Income States (LIS). The project utilizes a
performance incentive to motivate the company to shift
resources and expand its lending to underserved small
enterprises in LIS. Lending to this market is largely
untested by Fullerton, and serving this segment is
considered to be higher risk
Implementation Stage • Loan
PROJECTS CONTINUED
* projects approved as of May 2015
30

YES Bank Loan
The project involves a financing package to Yes Bank to
support its SME portfolio growth in India’s Low Income
States (LIS) as well as North Eastern States (NES). The
project has a specific focus on supporting Yes Bank eorts
to increase its reach to women-owned SMEs. The loan will
incentivize Yes Bank to develop a commercially viable SME
lending business in LIS. The incentive is also expected to
motivate the bank to significantly increase its lending to
women-owned SMEs.
Implementation Stage • Loan
India MSME Finance Umbrella Advisory
This umbrella project focuses on supporting financial
institutions’ eorts to increase their outreach to the SME
sector by helping them improve their business model and
management practices. The projects will include tailored
technical assistance to address the specific performance
constraints at each institution. This will include a
combination of the following interventions: business
model and strategy, product and channel innovation,
customer management, risk management, non-financial
services, and SME training and capacity building.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
India VSE Advisory Umbrella
This umbrella will provide a comprehensive suite of
advisory support to MFIs and Fintech firms to achieve their
chosen route of institutional transformation (e.g.,
transformation into a Small Finance Bank or a Payment
Bank). These advisory projects will help clients expand
financial services to their clients in low-income segments
or financially excluded areas. The main areas of technical
advisory are related to MSME product development (with
a special focus on women borrowers), operating model
design, development of alternative delivery channels, and
facilitation of study visits and knowledge exchange sessions.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Maanaveeya SME Advisory
The project assists Maanaveeya in building and growing a
profitable agricultural SME portfolio. The Advisory includes
improving and strengthening its organizational capabilities
to understand agri-value chains; enhancing the capacity of
Maanaveeya’s partner institutions to adequately support
agri-value chains; increasing Maanaveeya’s value-chain
lending program; and expanding the agri-value chain
customer base.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
SIDBI Bank SME Advisory
The project supports SIDBI in increasing access to finance
opportunities for MSMEs. The project focuses on three
segments within the SME sector: early-stage enterprises,
enterprises operating in the services sector, and enterprises
operating in the manufacturing sector. The advisory
program will support SIDBI in developing new products,
strengthening its risk management and credit processes,
designing a formal credit assessment scorecard for early
stage enterprises, and expanding its market outreach.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Utkarsh Upscaling Advisory
The project supports Utkarsh, a non-banking finance
company operating primarily in India’s low-income states,
in its eort to transform into a bank. The Advisory includes
the development of a detailed strategy and roll-out plan
for the transformation, as well as strengthening Utkarsh
enterprise business loans to expand its product to very
small enterprises (VSEs). The project will also focus on
developing a women-owned small business program and
receiving the Employer of Choice for Women Certification.
Subproject under the India VSE Advisory Umbrella.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
31

Collateral Registries, India
The project focuses on supporting the Central Registry of
Securitization Asset Reconstruction and Security Interest
(CERSAI) in expanding to include movable collateral. The
Advisory includes supporting the development of a
business plan and strategy for CERSAI to include dierent
types of collateral, engaging across a range of stakeholders,
and supporting the review and amendment of the legal
and regulatory framework.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Credit Bureau, India
This project focuses on integrating alternative data
sources into the credit reporting system, and encouraging
greater reporting and usage specifically for the SME sector.
The sectoral interventions include market assessment and
sector-level research, review of the existing legal and
regulatory framework, capacity building for financial
institutions, and awareness raising about the benefits of
credit reports and the importance of credit bureaus.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
NEPAL
Secured Transactions, Nepal
The project aims to facilitate greater access to finance for
underserved segments in Nepal, by strengthening the legal
and institutional frameworks for secured transactions and
credit reporting. The project includes strengthening the
legal and regulatory framework for secured transactions,
and supporting the implementation of the Credit
Information Bureau.
Pre-Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Projects in Middle East and
Northern Africa (MENA)
AFGHANISTAN
Afghanistan Secured Transactions Advisory
This project aims to increase access to credit to the private
sector in Afghanistan by developing a movable collateral
registry. The Advisory focuses on supporting relevant
legislative reforms and creating a functioning movable
asset registry. It will also include awareness raising and
capacity building activities to increase relevant stakeholders’
familiarity with the new Secured Transactions system.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Afghanistan Leasing Advisory
This project will focus on training key stakeholders on the
new leasing laws and regulations in Afghanistan. The
Advisory will include intensive awareness-raising and
industrywide training on leasing for financial institutions,
judges and other stakeholders. The project will specifically
focus on training financial institutions to support launching
leasing programs and developing leasing products. The
Facility will support any interested financial institutions,
through additional dedicated advisory engagements, in
developing and launching leasing programs.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Afghanistan MFI Upscaling Advisory Umbrella
The project aims to diversify the range of financial
products available to SMEs in Afghanistan, with a
particular focus on supporting the Very Small Enterprise
(VSE) segment, and developing Islamic finance products,
movable asset lending, agrifinance and value chain finance
programs. The Advisory will also focus on strengthening
risk management and governance frameworks to help
serve new SME segments, and on introducing alternative
delivery channels, such as branchless banking or mobile
payments, to maximize outreach to SMEs.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
PROJECTS CONTINUED
32

PAKISTAN
Bank Alfalah SME Advisory
The project helped strengthen Bank Alfalah’s SME
operational capacity for SME banking to facilitate
expanded outreach to the SME sector. The project focused
on understanding the SME segment, as well as developing
a strategy and business model for SME lending.
Additionally, the project provided support to Bank Alfalah
for improving its SME credit underwriting, streamlining the
organizational structure, and developing a non-financial
services oering for SMEs.
Completed Stage • PFI Advisory
HBL Agrifinance Advisory
The project is supporting Habib Bank Limited (HBL) eorts
to strengthen its capacity to develop appropriate products
and processes for eectively serving the rural banking
market. The project focuses on mapping the opportunities
for serving agribusinesses, and designing a suitable bundle
of products and services for this segment. The Advisory
includes the development of an agrifinance strategy,
market segmentation, and product development.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
HBL Women SME Advisory
This Advisory focused on strengthening HBL’s capabilities
for serving the women’s market. Activities included
conducting comprehensive research into the Pakistani
women’s market (including women-owned SMEs),
designing a new customer value proposition for women
SMEs, and positioning the bank to become an employer of
choice for women. The project also involved an internal
alignment of HBL towards gender equality.
Completed • PFI Advisory
UBL SME Advisory
This project helps United Bank Limited (UBL) develop and
implement an eective SME business model. The advisory
program is focused on designing an SME strategy and
business model, data mining and MIS, including an in-
depth analysis of the SME customers in UBL’s portfolio.
The Advisory also includes strategies for customer
segmentation, product and service management, sales
channels and marketing. Additionally, the program has a
strong focus on developing a value-chain financing
program through UBL’s corporate clients.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Pakistan SME Banking Advisory Umbrella
This umbrella will provide in-depth capacity building
aimed at growing the SME customer base of up to five
Pakistani banks. Each bank will receive a tailored advisory
package, which may include market sizing and
segmentation, developing a business plan and strategy,
developing and piloting products, improving sales/delivery
channels, developing and strengthening risk management
processes and procedures, non-performing loan (NPL)
management, and IT and MIS.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Pakistan SEF Advisory Umbrella
The project will focus on improving the market for
sustainable energy investments among MSMEs, corporate
clients and the residential sector. The Advisory will include
building awareness and supporting banks in the development
and marketing of sustainable energy lending products.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
33

Projects in East Asia
MYANMAR
Oriental Bank (MOB) SME Advisory
The project focuses on building the capacity of Myanmar
Oriental Bank (MOB) to improve its products and services
for SMEs. Specifically, this Advisory focuses on institution
building and risk management, including streamlining
operations related to credit risk, finance and treasury,
trade and international operations, human resources, and
information technology. The Advisory is also focusing on
developing MOB’s SME banking capacity, including the
development of new products for SMEs.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Yoma Bank SME Advisory
The project focuses on upgrading Yoma Bank’s operations,
expanding its financial services oerings, and building a
competitive market position. The project focuses on
developing an SME strategic plan, risk management, and
strengthening corporate policies, practices and internal
controls. The Advisory also helps the bank to better
understand the SME segment and to develop appropriate
SME products and services.
Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Myanmar Banking Sector Advisory Umbrella
This umbrella project aims to improve access to financial
services for Myanmar’s underserved SMEs by supporting
the sustainable development of the country’s nascent
banking sector. The project includes tailored advisory
support to at least two financial institutions that will focus
on trade finance, SME banking, risk management, and
corporate governance.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
34

Credit Bureau, Myanmar
This project aims to improve access to credit for individuals
and businesses in Myanmar by helping the country develop
a credit reporting system. The project focused on
developing regulations on credit reporting, strengthening
the Central Bank’s supervision capacity to regulate and
oversee the credit bureaus, and supporting public
education about credit reporting and financial consumers.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Secured Transactions, Myanmar
The project focuses on establishing the required legal and
institutional foundations for movable asset lending. The
project will focus on legal and regulatory reform, including
the development of a secured transactions registry and
movable asset lending capacity.
Pre-Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Projects in Latin America
and Caribbean
HAITI
Credit Bureau, Haiti
The project supports the development of a comprehensive
credit information-sharing platform to facilitate access to
credit for MSMEs and women entrepreneurs in Haiti. The
Advisory includes developing a code of conduct to serve as
interim guidance for the credit bureau while a legal and
regulatory framework is being developed. The Advisory will
also focus on capacity building and on raising awareness of
the role and value of credit reporting and access to finance.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Secured Transactions, Haiti
The project focuses on working with the government of
Haiti to develop and implement an electronic collateral
registry. The Advisory will include supporting the
development of the secured transactions legal and
regulatory framework, and the implementation of a
modern system of financing secured by movable assets.
Additionally, the Advisory will support the design of a
web-based centralized collateral registry for movable
property.
Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
Africa Regional Projects
Africa Agrifinance Advisory Umbrella
This umbrella focuses on supporting several financial
institutions’ eorts to develop a broad range of financial
services for the agriculture sector, including credit, savings
and transactional products. The project will provide
tailored capacity building to financial institutions to
improve their lending to the agriculture sector, and to
expand their products and services to SMEs operating in
the agriculture sector.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Africa Leasing Advisory Umbrella
This umbrella project will facilitate increased access to
finance to SMEs in fragile states in Africa by developing a
sustainable leasing infrastructure, and by working with
financial institutions to develop and grow leasing portfolios.
Advisory support to develop leasing projects is expected to
be provided to financial institutions in up to 10 countries.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
35

Africa Non-Bank VSE Upscaling Advisory
Umbrella
This umbrella will oer Advisory Services to non-bank
financial institutions that seek to provide financing
solutions to Very Small Enterprises (VSEs). The projects
under this umbrella will include tailored advisory services
based on the needs of each institution. Specific support
to include VSE product design, risk management, credit
methodology and internal processes, market strategy
and communications, data analytics, business planning,
financial modeling, and HR and training to individual
financial institutions.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Africa SME Banking Advisory Umbrella
This umbrella will provide advisory services to commercial
banks to strengthen their institutional capacity for
increasing lending to SMEs. The projects supported by this
umbrella will focus on institutional strengthening in areas
of risk management and corporate governance, market
assessment and segmentation, product development, as
well as non-financial services and increasing access to
finance for women-owned SMEs.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
Africa Financial Infrastructure Umbrella
The goal of this umbrella is to increase access to finance
for SMEs by closing the information gap between lenders
and borrowers. The program focuses establishing new or
improving existing collateral registries, credit registries and
credit bureaus, and training the lending community about
the ecient use of the available financial infrastructure.
Pre-Implementation Stage • Financial Infrastructure
South Asia Regional Projects
South Asia SME Banking Umbrella
This umbrella project will work with up to 10 financial
institutions in South Asia, primarily in Nepal and
Bangladesh, to enhance their SME service oering. The
Advisory will provide tailored capacity building programs
for each participating institution, and may include
developing SME products, designing non-financial services,
strengthening the MIS system to ensure that the PFIs are
capable of tracking SMEs owned by men and women,
streamlining credit processes and policies, and designing
gender-specific SME banking strategies. The Advisory can
also focus on improving financial institutions’ risk
management frameworks, developing credit scoring
models, and sta training.
Pre-Implementation Stage • PFI Advisory
PROJECTS CONTINUED
36

PHOTO CREDITS
Front Cover: © Nyani Quarmyne
Inisde Front Cover: © iwan Bagus/ IFC
Page 11: © Nyani Quarmyne
Page 12: unknown
Page 13: © Iwan Bagus/IFC
Page 14: unknown
Page 15: unknown
Page 17: © Iwan Bagus/IFC
Page 19: unknown
Page 20: unknown
Page 23: © Nyani Quarmyne
Page 25: unknown
Page 27: © Nyani Quarmyne
COPYRIGHT AND DISCLAIMER NOTICE
© International Finance Corporation 2016. All rights reserved.
2121 Pennsylvania Avenue, N.W.
Washington, D.C. 20433
Internet: www.ifc.org
The material in this work is copyrighted. Copying and/or transmitting portions or all of this work without permission may
be a violation of applicable law. IFC encourages dissemination of its work and will normally grant permission to reproduce
portions of the work promptly, and when the reproduction is for educational and non-commercial purposes, without a
fee, subject to such attributions and notices as we may reasonably require.
IFC does not guarantee the accuracy, reliability or completeness of the content included in this work, or for the
conclusions or judgments described herein, and accepts no responsibility or liability for any omissions or errors (including,
without limitation, typographical errors and technical errors) in the content whatsoever or for reliance thereon. The
boundaries, colors, denominations, and other information shown on any map in this work do not imply any judgment
on the part of The World Bank concerning the legal status of any territory or the endorsement or acceptance of such
boundaries. The findings, interpretations, and conclusions expressed in this volume do not necessarily reflect the views of
the Executive Directors of The World Bank or the governments they represent.
The contents of this work are intended for general informational purposes only and are not intended to constitute legal,
securities, or investment advice, an opinion regarding the appropriateness of any investment, or a solicitation of any type.
IFC or its aliates may have an investment in, provide other advice or services to, or otherwise have a financial interest in,
certain of the companies and parties (including named herein).
All other queries on rights and licenses, including subsidiary rights, should be addressed to IFC’s Corporate Relations
Department, 2121 Pennsylvania Avenue, N.W., Washington, D.C. 20433.
International Finance Corporation is an international organization established by Articles of Agreement among its
member countries, and a member of the World Bank Group. All names, logos and trademarks are the property of IFC
and you may not use any of such materials for any purpose without the express written consent of IFC. Additionally,
“International Finance Corporation” and “IFC” are registered trademarks of IFC and are protected under international law.

Global SME Finance Facility
Wendy Teleki,
Head SME Finance, International
Finance Corporation
